Abstract
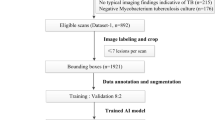
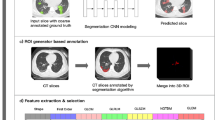
This study aimed to develop and evaluate a CT-based deep learning radiomics model for differentiating between Crohn’s disease (CD) and intestinal tuberculosis (ITB). A total of 330 patients with pathologically confirmed as CD or ITB from the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University were divided into the validation dataset one (CD: 167; ITB: 57) and validation dataset two (CD: 78; ITB: 28). Based on the validation dataset one, the synthetic minority oversampling technique (SMOTE) was adopted to create balanced dataset as training data for feature selection and model construction. The handcrafted and deep learning (DL) radiomics features were extracted from the arterial and venous phases images, respectively. The interobserver consistency analysis, Spearman’s correlation, univariate analysis, and the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression were used to select features. Based on extracted multi-phase radiomics features, six logistic regression models were finally constructed. The diagnostic performances of different models were compared using ROC analysis and Delong test. The arterial-venous combined deep learning radiomics model for differentiating between CD and ITB showed a high prediction quality with AUCs of 0.885, 0.877, and 0.800 in SMOTE dataset, validation dataset one, and validation dataset two, respectively. Moreover, the deep learning radiomics model outperformed the handcrafted radiomics model in same phase images. In validation dataset one, the Delong test results indicated that there was a significant difference in the AUC of the arterial models (p = 0.037), while not in venous and arterial-venous combined models (p = 0.398 and p = 0.265) as comparing deep learning radiomics models and handcrafted radiomics models. In our study, the arterial-venous combined model based on deep learning radiomics analysis exhibited good performance in differentiating between CD and ITB.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- CD:
-
Crohn’s disease
- ITB:
-
Intestinal tuberculosis
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- CTE:
-
Computed tomography enterography
- SMOTE:
-
Synthetic minority oversampling technique
- ATT:
-
Anti-tuberculosis therapy
- ECCO:
-
European Crohn’s and Colitis Organization
- MPR:
-
Multiplanar reconstruction
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- ICCs:
-
Intraclass/interclass correlation coefficients
- LASSO:
-
Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator
- ROIs:
-
Regions of interest
- ResNet:
-
Residual convolutional neural networks
- LR:
-
Logistic regression
- UC:
-
Ulcerative colitis
References
Gajendran M, Loganathan P, Catinella AP, Hashash JG: A comprehensive review and update on Crohn's disease. Dis Mon 64:20-57, 2018.
Feuerstein JD, Cheifetz AS: Crohn Disease: Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Management. Mayo Clin Proc 92:1088-1103, 2017.
Rogler G, Singh A, Kavanaugh A, Rubin DT: Extraintestinal Manifestations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Current Concepts, Treatment, and Implications for Disease Management. Gastroenterology 161:1118-1132, 2021.
Ravimohan S, Kornfeld H, Weissman D, Bisson GP: Tuberculosis and lung damage: from epidemiology to pathophysiology. Eur Respir Rev 27, 2018.
Kalra N, Agrawal P, Mittal V, Kochhar R, Gupta V, Nada R, Singh R, Khandelwal N: Spectrum of imaging findings on MDCT enterography in patients with small bowel tuberculosis. Clin Radiol 69:315-322, 2014.
Oñate-Ocaña LF, Pérez-Díaz L: Intestinal Tuberculosis. N Engl J Med 386:e30, 2022.
Kedia S, Das P, Madhusudhan KS, Dattagupta S, Sharma R, Sahni P, Makharia G, Ahuja V: Differentiating Crohn's disease from intestinal tuberculosis. World J Gastroenterol 25:418-432, 2019.
Limsrivilai J, Lee CK, Prueksapanich P, Harinwan K, Sudcharoen A, Cheewasereechon N, Aniwan S, Sripongpan P, Wetwittayakhlang P, Pongpaibul A, Sanpavat A, Pausawasdi N, Charatcharoenwitthaya P, Higgins PDR, Ng SC: Validation of models using basic parameters to differentiate intestinal tuberculosis from Crohn's disease: A multicenter study from Asia. PLoS One 15:e0242879, 2020.
Weinberg SE, Mughal AM: A Case of Intestinal Tuberculosis Mimicking Crohn's Disease: A Clinical and Diagnostic Dilemma. Eur J Case Rep Intern Med 8:002699, 2021.
Seo H, Lee S, So H, Kim D, Kim SO, Soh JS, Bae JH, Lee SH, Hwang SW, Park SH, Yang DH, Kim KJ, Byeon JS, Myung SJ, Yang SK, Ye BD: Temporal trends in the misdiagnosis rates between Crohn's disease and intestinal tuberculosis. World J Gastroenterol 23:6306-6314, 2017.
Pulimood AB, Amarapurkar DN, Ghoshal U, Phillip M, Pai CG, Reddy DN, Nagi B, Ramakrishna BS: Differentiation of Crohn's disease from intestinal tuberculosis in India in 2010. World J Gastroenterol 17:433-443, 2011.
Jiang M, Zeng Z, Chen K, Dang Y, Li L, Ma C, Cheng R, Hu K, Li X, Zhang H: Enterogenous Microbiotic Markers in the Differential Diagnosis of Crohn's Disease and Intestinal Tuberculosis. Front Immunol 13:820891, 2022.
Epstein D, Watermeyer G, Kirsch R: Review article: the diagnosis and management of Crohn's disease in populations with high-risk rates for tuberculosis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 25:1373-1388, 2007.
Banerjee R, Pal P, Girish BG, Reddy DN: Risk factors for diagnostic delay in Crohn's disease and their impact on long-term complications: how do they differ in a tuberculosis endemic region? Aliment Pharmacol Ther 47:1367-1374, 2018.
Kim YG, Kim KJ, Min YK: Comparison of small bowel findings using capsule endoscopy between Crohn's disease and intestinal tuberculosis in Korea. Yeungnam Univ J Med 37:98-105, 2020.
Wei JP, Wu XY, Gao SY, Chen QY, Liu T, Liu G: Misdiagnosis and Mistherapy of Crohn's Disease as Intestinal Tuberculosis: Case Report and Literature Review. Medicine (Baltimore) 95:e2436, 2016.
Spada C, Hassan C, Riccioni ME, Costamagna G: False positive at colon capsule endoscopy or false negative at conventional colonoscopy? Endoscopy 42:427–428; author reply 428, 2010.
Kim SY, Kim HS, Park HJ: Adverse events related to colonoscopy: Global trends and future challenges. World J Gastroenterol 25:190-204, 2019.
Gomollón F, Dignass A, Annese V, Tilg H, Van Assche G, Lindsay JO, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Cullen GJ, Daperno M, Kucharzik T, Rieder F, Almer S, Armuzzi A, Harbord M, Langhorst J, Sans M, Chowers Y, Fiorino G, Juillerat P, Mantzaris GJ, Rizzello F, Vavricka S, Gionchetti P: 3rd European Evidence-based Consensus on the Diagnosis and Management of Crohn's Disease 2016: Part 1: Diagnosis and Medical Management. J Crohns Colitis 11:3-25, 2017.
Ilangovan R, Burling D, George A, Gupta A, Marshall M, Taylor SA: CT enterography: review of technique and practical tips. Br J Radiol 85:876-886, 2012.
Yang H, Zhang H, Liu W, Han W, Guo T, Lai Y, Tan B, Wang C, Chen M, Gao X, Ran Z, Liu Z, Wu K, Cao Q, Qian J: Computed tomography enterography increases the ability of endoscopy to differentiate Crohn's disease from intestinal Behçet's disease. Front Med (Lausanne) 9:900458, 2022.
Fidler JL, Goenka AH, Fleming CJ, Andrews JC: Small Bowel Imaging: Computed Tomography Enterography, Magnetic Resonance Enterography, Angiography, and Nuclear Medicine. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am 27:133-152, 2017.
Kedia S, Sharma R, Sreenivas V, Madhusudhan KS, Sharma V, Bopanna S, Pratap Mouli V, Dhingra R, Yadav DP, Makharia G, Ahuja V: Accuracy of computed tomographic features in differentiating intestinal tuberculosis from Crohn's disease: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Intest Res 15:149-159, 2017.
Goyal P, Shah J, Gupta S, Gupta P, Sharma V: Imaging in discriminating intestinal tuberculosis and Crohn's disease: past, present and the future. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 13:995-1007, 2019.
Bezzi C, Mapelli P, Presotto L, Neri I, Scifo P, Savi A, Bettinardi V, Partelli S, Gianolli L, Falconi M, Picchio M: Radiomics in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: methodological issues and clinical significance. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 48:4002-4015, 2021.
Bortolotto C, Lancia A, Stelitano C, Montesano M, Merizzoli E, Agustoni F, Stella G, Preda L, Filippi AR: Radiomics features as predictive and prognostic biomarkers in NSCLC. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 21:257-266, 2021.
Wu J, Mayer AT, Li R: Integrated imaging and molecular analysis to decipher tumor microenvironment in the era of immunotherapy. Semin Cancer Biol 84:310-328, 2022.
Avanzo M, Wei L, Stancanello J, Vallières M, Rao A, Morin O, Mattonen SA, El Naqa I: Machine and deep learning methods for radiomics. Med Phys 47:e185-e202, 2020.
Avberšek LK, Repovš G: Deep learning in neuroimaging data analysis: Applications, challenges, and solutions. Front Neuroimaging 1:981642, 2022.
Currie G, Hawk KE, Rohren E, Vial A, Klein R: Machine Learning and Deep Learning in Medical Imaging: Intelligent Imaging. J Med Imaging Radiat Sci 50:477-487, 2019.
Chen Q, Pan T, Wang YN, Schoepf UJ, Bidwell SL, Qiao H, Feng Y, Xu C, Xu H, Xie G, Gao X, Tao XW, Lu M, Xu PP, Zhong J, Wei Y, Yin X, Zhang J, Zhang LJ: A Coronary CT Angiography Radiomics Model to Identify Vulnerable Plaque and Predict Cardiovascular Events. Radiology 307:e221693, 2023.
Zheng Y, Zhou D, Liu H, Wen M: CT-based radiomics analysis of different machine learning models for differentiating benign and malignant parotid tumors. Eur Radiol 32:6953-6964, 2022.
Zhang AQ, Zhao HP, Li F, Liang P, Gao JB, Cheng M: Computed tomography-based deep-learning prediction of lymph node metastasis risk in locally advanced gastric cancer. Front Oncol 12:969707, 2022.
Peng H, Dong D, Fang MJ, Li L, Tang LL, Chen L, Li WF, Mao YP, Fan W, Liu LZ, Tian L, Lin AH, Sun Y, Tian J, Ma J: Prognostic Value of Deep Learning PET/CT-Based Radiomics: Potential Role for Future Individual Induction Chemotherapy in Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 25:4271-4279, 2019.
Ligero M, Jordi-Ollero O, Bernatowicz K, Garcia-Ruiz A, Delgado-Muñoz E, Leiva D, Mast R, Suarez C, Sala-Llonch R, Calvo N, Escobar M, Navarro-Martin A, Villacampa G, Dienstmann R, Perez-Lopez R: Minimizing acquisition-related radiomics variability by image resampling and batch effect correction to allow for large-scale data analysis. Eur Radiol 31:1460-1470, 2021.
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J: Deep residual learning for image recognition. Proc. Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition: City.
Chawla NV, Bowyer KW, Hall LO, Kegelmeyer WP: SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. Journal of artificial intelligence research 16:321-357, 2002.
Ren S, Zhao R, Zhang J, Guo K, Gu X, Duan S, Wang Z, Chen R: Diagnostic accuracy of unenhanced CT texture analysis to differentiate mass-forming pancreatitis from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Abdominal Radiology 45:1524-1533, 2020.
Carretero C: Small bowel Crohn's disease: optimal modality for diagnosis and monitoring. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 38:292-298, 2022.
Minordi LM, Scaldaferri F, Marra RS, Pecere S, Larosa L, Poscia A, Gasbarrini A, Vecchioli A, Bonomo L: Enterography CT without and with water enema in patients with Crohn's disease: Results from a comparative observational study in comparison with endoscopy. Eur J Radiol 85:404-413, 2016.
Zhao XS, Wang ZT, Wu ZY, Yin QH, Zhong J, Miao F, Yan FH: Differentiation of Crohn's disease from intestinal tuberculosis by clinical and CT enterographic models. Inflamm Bowel Dis 20:916-925, 2014.
Huang M, Tu L, Li J, Yue X, Wu L, Yang M, Chen Y, Han P, Li X, Zhu L: Differentiation of Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and intestinal tuberculosis by dual-layer spectral detector CT enterography. Clin Radiol, 2023.
Ma JY, Tong JL, Ran ZH: Intestinal tuberculosis and Crohn's disease: challenging differential diagnosis. J Dig Dis 17:155-161, 2016.
Guglielmo FF, Anupindi SA, Fletcher JG, Al-Hawary MM, Dillman JR, Grand DJ, Bruining DH, Chatterji M, Darge K, Fidler JL, Gandhi NS, Gee MS, Grajo JR, Huang C, Jaffe TA, Park SH, Rimola J, Soto JA, Taouli B, Taylor SA, Baker ME: Small Bowel Crohn Disease at CT and MR Enterography: Imaging Atlas and Glossary of Terms. Radiographics 40:354-375, 2020.
Ray D, Thukral BB, Gupta R, Chintamani, Prasad R: Small bowel tuberculosis by multidetector CT enteroclysis. Jpn J Radiol 31:471-479, 2013.
Dutta AK, Sahu MK, Gangadharan SK, Chacko A: Distinguishing Crohn's disease from intestinal tuberculosis--a prospective study. Trop Gastroenterol 32:204-209, 2011.
Li Y, Zhang LF, Liu XQ, Wang L, Wang X, Wang J, Qian JM: The role of in vitro interferonγ-release assay in differentiating intestinal tuberculosis from Crohn's disease in China. J Crohns Colitis 6:317-323, 2012.
Lee YJ, Yang SK, Byeon JS, Myung SJ, Chang HS, Hong SS, Kim KJ, Lee GH, Jung HY, Hong WS, Kim JH, Min YI, Chang SJ, Yu CS: Analysis of colonoscopic findings in the differential diagnosis between intestinal tuberculosis and Crohn's disease. Endoscopy 38:592-597, 2006.
Du KP, Huang WP, Liu SY, Chen YJ, Li LM, Liu XN, Han YJ, Zhou Y, Liu CC, Gao JB: Application of computed tomography-based radiomics in differential diagnosis of adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma at the esophagogastric junction. World J Gastroenterol 28:4363-4375, 2022.
Starmans MPA, Timbergen MJM, Vos M, Renckens M, Grünhagen DJ, van Leenders G, Dwarkasing RS, Willemssen F, Niessen WJ, Verhoef C, Sleijfer S, Visser JJ, Klein S: Differential Diagnosis and Molecular Stratification of Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors on CT Images Using a Radiomics Approach. J Digit Imaging 35:127-136, 2022.
Bibault JE, Giraud P, Housset M, Durdux C, Taieb J, Berger A, Coriat R, Chaussade S, Dousset B, Nordlinger B, Burgun A: Deep Learning and Radiomics predict complete response after neo-adjuvant chemoradiation for locally advanced rectal cancer. Sci Rep 8:12611, 2018.
Kiehl L, Kuntz S, Höhn J, Jutzi T, Krieghoff-Henning E, Kather JN, Holland-Letz T, Kopp-Schneider A, Chang-Claude J, Brobeil A, von Kalle C, Fröhling S, Alwers E, Brenner H, Hoffmeister M, Brinker TJ: Deep learning can predict lymph node status directly from histology in colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer 157:464-473, 2021.
Ge YX, Li J, Zhang JQ, Duan SF, Liu YK, Hu SD: Radiomics analysis of multicenter CT images for discriminating mucinous adenocarcinoma from nomucinous adenocarcinoma in rectal cancer and comparison with conventional CT values. J Xray Sci Technol 28:285-297, 2020.
Li H, Mo Y, Huang C, Ren Q, Xia X, Nan X, Shuai X, Meng X: An MSCT-based radiomics nomogram combined with clinical factors can identify Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Ann Transl Med 9:572, 2021.
Meng J, Luo Z, Chen Z, Zhou J, Chen Z, Lu B, Zhang M, Wang Y, Yuan C, Shen X, Huang Q, Zhang Z, Ye Z, Cao Q, Zhou Z, Xu Y, Mao R, Chen M, Sun C, Li Z, Feng ST, Meng X, Huang B, Li X: Intestinal fibrosis classification in patients with Crohn's disease using CT enterography-based deep learning: comparisons with radiomics and radiologists. Eur Radiol 32:8692-8705, 2022.
Acknowledgements
We thank the investigators at all participating study sites.
Funding
This work was supported by the Key Project of Science and Technology Research of Henan Province (Grant number 222102210112) and the National Natural and Science Fund of China (Grant numbers 61802350 and 81971615).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Hanyue Zhang and Wenpeng Huang. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Ming Cheng and Hanyue Zhang, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This retrospective study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University.
Consent to Participate
The requirement for informed consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of the study.
Consent to Publication
Not applicable.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, M., Zhang, H., Huang, W. et al. Deep Learning Radiomics Analysis of CT Imaging for Differentiating Between Crohn’s Disease and Intestinal Tuberculosis. J Digit Imaging. Inform. med. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-024-01059-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-024-01059-0