Abstract
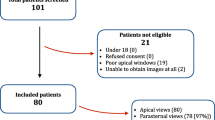
We aimed to investigate whether an offsite expert could effectively evaluate visually estimated ejection fraction (EF) while watching and guiding the echocardiographic procedure of an onsite novice practitioner using a social network video call. Sixty patients presenting to the intensive care unit and requiring echocardiography between October and November 2016 were included. Sixty novice sonographers without any previous experience of echocardiography participated. Prior to the procedure, the onsite cardiologist completed the echocardiography and determined the EF using the modified Simpson’s method (reference value). Then, the novice practitioner performed the echocardiography again with the offsite expert’s guidance via a social network video call. The EF was visually estimated by the offsite expert while watching the ultrasound video on the smartphone display. Spearman’s rank correlation and Bland-Altman plot analysis were conducted to assess the agreement between the two methods. There was excellent agreement between the two methods, with a correlation coefficient of 0.94 (p < 0.001). The Bland-Altman plot showed that the average bias was −3.05, and the limit of agreement (−10.3 to 4.2) was narrow. The offsite expert was able to perform an accurate visual estimation of ejection fraction remotely via a social network video call by mentoring the onsite novice sonographer.
ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02960685.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arntfield RT, Millington SJ. Point of care cardiac ultrasound applications in the emergency department and intensive care unit—a review. Curr Cardiol Rev 2012;8(2):98–108.
Lebeau R, Sas G, El Rayes M, Serban A, Moustafa S, Essadiqi B, DiLorenzo M, Souliere V, Beaulieu Y, Sauve C, Amyot R, Serri K. Left ventricular ejection fraction assessment by non-cardiologists from transverse views using a simplified wall motion score index Echo Res Pract 2015;2(1):1–8.
Vermeiren GL, Malbrain ML, Walpot JM. Cardiac Ultrasonography in the critical care setting: a practical approach to asses cardiac function and preload for the “non-cardiologist”. Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther 2015;47 Spec No:s89–104.
Unlüer EE, Karagöz A, Akoğlu H, Bayata S. Visual estimation of bedside echocardiographic ejection fraction by emergency physicians. West J Emerg Med 2014;15(2):221–6.
Sievers B, Kirchberg S, Franken U, Puthenveettil BJ, Bakan A, Trappe HJ. Visual estimation versus quantitative assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction: a comparison by cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging. Am Heart J 2005;150(4):737–42.
Ünlüer EE, Karagöz A, Bayata S, Akoğlu H. An alternative approach to the bedside assessment of left ventricular systolic function in the emergency department: displacement of the aortic root. Acad Emerg Med 2013;20(4):367–73.
Moore CL, Rose GA, Tayal VS, Sullivan DM, Arrowood JA, Kline JA. Determination of left ventricular function by emergency physician echocardiography of hypotensive patients. Acad Emerg Med 2002;9(3):186–93.
Ogedegbe C, Morchel H, Hazelwood V, Chaplin WF, Feldman J. Development and evaluation of a novel, real time mobile telesonography system in management of patients with abdominal trauma: study protocol. BMC Emerg Med 2012;12:19.
McBeth P, Crawford I, Tiruta C, et al. Help is in your pocket: the potential accuracy of smartphone- and laptop-based remotely guided resuscitative telesonography. Telemed J E Health 2013;19:924–30.
Biegler N, McBeth PB, Tiruta C, et al. The feasibility of nurse practitioner-performed, telementored lung telesonography with remote physician guidance—‘a remote virtual mentor’. Crit Ultrasound J 2013;5:5.
Levine AR, Buchner JA, Verceles AC, Zubrow MT, Mallemat HA, Papali A, McCurdy MT. Ultrasound images transmitted via FaceTime are non-inferior to images on the ultrasound machine. J Crit Care. 2016;33:51–5.
Agboma F, Liotta A. Quality of experience management in mobile content delivery system. Telecommun Syst 2012;49(1):85–98.
Huynh-Thu Q, Ghanbari M. Temporal aspect of perceived quality in mobile video broadcasting. IEEE Tran Broadcast 54(3), 2008
Kim C, Cha H, Kang BS, Choi HJ, Lim TH, Oh J. A feasibility study of smartphone-based telesonography for evaluating cardiac dynamic function and diagnosing acute appendicitis with control of the image quality of the transmitted videos. J Digit Imaging 2016;29(3):347–56
Kim C, Kang BS, Choi HJ, Lim TH, Oh J, Chee Y. Clinical application of real-time tele-ultrasonography in diagnosing pediatric acute appendicitis in the ED. Am J Emerg Med 2015;33:1354–9.
The state of the internet, 1st quarter 2016 Akamai’s report. Available at https://www.akamai.com/es/es/multimedia/documents/state-of-the-internet/akamai-state-of-the-internet-report-q1-2016.pdf. Accessed 26 November 2016.
FaceTime vs Skype: the video- and voice-calling services compared. Available at http://www.pcadvisor.co.uk/feature/software/facetime-vs-skype-3634425/. Accessed 6 October 2016.
Skype vs Facetime: looking for the best video calling experience on iOS. Available at http://www.guidingtech.com/17889/skype-vs-facetime-best-video-calling-ios/. Accessed 6 October 2016.
Statista; Number of monthly active Kakaotalk users from 1st quarter 2013 to 3rd quarter 2016. Available at http://www.statista.com/statistics/278846/kakaotalk-monthly-active-users-mau/. Accessed 6 October 2016.
Norweck JT, Seibert JA, Andriole KP, et al. ACR-AAPM-SIIM technical standard for electronic practice of medical imaging. J Digit Imaging 2013;26(1):38–52.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Hanyang university guri hospital.
Funding Source
No external funding was secured for this study.
Financial Disclosure
The authors have no financial relationships relevant to this article to disclose.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, C., Hur, J., Kang, B.S. et al. Can an Offsite Expert Remotely Evaluate the Visual Estimation of Ejection Fraction via a Social Network Video Call?. J Digit Imaging 30, 718–725 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-017-9974-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-017-9974-5