Abstract
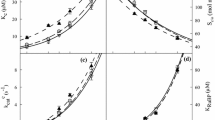
The kinetic properties of Rubisco, a key enzyme for photosynthesis, have been examined in numerous plant species. However, this information on some plant groups, such as ferns, is scarce. This study examined Rubisco carboxylase activity and leaf Rubisco levels in seven ferns, including four Equisetum plants (E. arvense, E. hyemale, E. praealtum, and E. variegatum), considered living fossils. The turnover rates of Rubisco carboxylation (kcatc) in E. praealtum and E. hyemale were comparable to those in the C4 plants maize (Zea mays) and sorghum (Sorghum bicolor), whose kcatc values are high. Rubisco CO2 affinity, estimated from the percentage of Rubisco carboxylase activity under CO2 unsaturated conditions in kcatc in these Equisetum plants, was low and also comparable to that in maize and sorghum. In contrast, kcatc and CO2 affinities of Rubisco in other ferns, including E. arvense and E. variegatum were comparable with those in C3 plants. The N allocation to Rubisco in the ferns examined was comparable to that in the C3 plants. These results indicate that E. praealtum and E. hyemale have abundant Rubisco with high kcatc and low CO2 affinity, whereas the carboxylase activity and abundance of Rubisco in other ferns were similar to those in C3 plants. Herein, the Rubisco properties of E. praealtum and E. hyemale were discussed regarding their evolution and physiological implications.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson LE (1971) Chloroplast and cytoplasmic enzymes. II. Pea leaf triose phosphate isomerases. Biochim Biophys Acta 235:237–244
Atkinson N, Leitão N, Orr DJ, Meyer MT, Carmo-Silva E, Griffiths H, Smith AM, McCormick AJ (2017) Rubisco small subunits from the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas complement Rubisco-deficient mutants of Arabidopsis. New Phytol 214:655–667
Bird IF, Cornelius MJ, Keys AJ (1982) Affinity of RuBP carboxylases for carbon dioxide and inhibition of the enzymes by oxygen. J Exp Bot 33:1004–1013
Bouvier JW, Emms DM, Rhodes T, Bolton JS, Brasnett A, Eddershaw A, Nielsen JR, Unitt A, Whitney SM, Kelly S (2021) Rubisco adaptation is more limited by phylogenetic constraint than by catalytic trade-off. Mol Biol Evol 38:2880–2896
Christenhusz MJM, Chase MJ, Fay MF, Hidalgo O, Leitch IJ, Pellicer J, Viruel J (2021) Biogeography and genome size evolution of the oldest extant vascular plant genus, Equisetum (Equisetaceae). Ann Bot 127:681–695
Dahl TW, Harding MAR, Brugger J, Feulner G, Norrman K, Lomax BN, Junium CK (2022) Low atmospheric CO2 levels before the rise of forested ecosystems. Nat Commun 13:7616
Dean C, Pichersky E, Dunsmuir P (1989) Structure, evolution and regulation of rbcS genes in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 40:415–439
Doi M, Kitagawa Y, Shimazaki K (2015) Stomatal blue light response is present in early vascular plants. Plant Physiol 169:1205–1213
Domozych DS, Bagdan K (2022) The cell biology of charophytes: exploring the past and models for the future. Plant Physiol 190:1588–1608
Elgorriaga A, Escapa IH, Rothwell GW, Tomescu AMF, Cúneo R (2018) Origin of Equisetum: evolution of horsetails (Equisetales) within the major euphyllophyte clade Sphenopsida. Am J Bot 105:1286–1303
Epstein E (1994) The anomaly of silicon in plant biology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:11–17
Evans JR (1986) The relationship between CO2-limited photosynthetic rate and ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate-carboxylase content in two nuclear-cytoplasm substitution lines of wheat, and the coordination of ribulose-bisphosphate-carboxylation and electron-transport capacities. Planta 167:351–358
Evans JR (1989) Photosynthesis and nitrogen relationships in leaves of C3 plants. Oecologia 78:9–19
Farquhar GD, von Caemmerer S, Berry JA (1980) A biochemical model of photosynthetic CO2 assimilation in leaves of C3 species. Planta 149:78–90
Feller U, Anders I, Mae T (2008) Rubiscolytics: fate of Rubisco after its enzymatic function in a cell is terminated. J Exp Bot 59:1615–1624
Flamholz AV, Prywes N, Moran U, Davidi D, Bar-On YM, Oltrogge LM, Alves R, Savage D, Milo R (2019) Revisiting trade-offs between Rubisco kinetic parameters. Biochemistry 58:3365–3376
Flügel F, Timm S, Arrivault S, Florian A, Stitt M, Fernie AR, Bauwe H (2017) The photorespiratory metabolite 2-phosphoglycolate regulates photosynthesis and starch accumulation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 29:2537–2551
Foster GL, Royer DL, Lunt DJ (2017) Future climate forcing potentially without precedent in the last 420 million years. Nat Commun 8:14845
Gago J, Coopman RE, Cabrera HM, Hermida C, Molins A, Conesa MÀ, Galmés J, Ribas-Carbó, Flexas J (2013) Photosynthesis limitations in three fern species. Physiol Plant 149:599–611
Galmés J, Kapralov MV, Andralojc PJ, Conesa MÀ, Keys AF, Parry MAJ, Flexas J (2014) Expanding knowledge of the Rubisco kinetics variability in plant species: environmental and evolutionary trends. Plant Cell Environ 37:1989–2001
Genkov T, Spreitzer RJ (2009) Highly conserved small subunit residues influence rubisco large subunit catalysis. J Biol Chem 284:30105–30112
Getzoff TP, Zhu G, Bohnert HJ, Jensen RG (1998) Chimeric Arabidopsis thaliana ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase containing a pea small subunit protein is compromised in carbamylation. Plant Physiol 116:695–702
Ghimire B, Riley WJ, Koven CD, Kattge J, Rogers A, Reich PB, Wright IJ (2017) A global trait-based approach to estimate leaf nitrogen functional allocation from observations. Ecol Appl 27:1421–1434
Gitzendanner MA, Soltis PS, Wong GKS, Ruhfel BR, Soltis DE (2018) Plastid phylogenomic analysis of green plants: a billion years of evolutionary history. Am J Bot 105:291–301
Goudet MMM, Orr DJ, Melkonian M, Müller KH, Meyer MT, Carmo-Silva E, Griffiths H (2020) Rubisco and carbon-concentrating mechanism co-evolution across chlorophyte and streptophyte green algae. New Phytol 227:810–823
Hall NP, Tolbert NE (1978) A rapid procedure for the isolation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from spinach leaves. FEBS Lett 96:167–169
Haworth M, Elliott-Kingston C, McElwain JC (2011) Stomatal control as a driver of plant evolution. J Exp Bot 62:2419–2423
Hermida-Carrera C, Kapralov MV, Galmés J (2016) Rubisco catalytic properties and temperature response in crops. Plant Physiol 171:2549–2561
Hirotsu N, Makino A, Yokota S, Mae T (2005) The photosynthetic properties of rice leaves treated with low temperature and high irradiance. Plant Cell Physiol 46:1377–1383
Hothorn T, Bretz F, Westfall P (2008) Simultaneous inference in general parametric models. Biom J 50:346–363
Hudson GS, Evans JR, von Cammerer S, Arvidsson YBC, Andrews TJ (1992) Reduction of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase content by antisense RNA reduces photosynthesis in transgenic Tobacco plants. Plant Physiol 98:294–302
Ihaka R, Gentleman R (1996) R. A language for data analysis and graphics. J Comput Graph Stat 5:299–314
Iñiguez C, Capó-Bauçà S, Niinemets Ü, Stoll H, Aguiló-Nicolau P, Galmés J (2020) Evolutionary trends in RuBisCO kinetics and their co-evolution with CO2 concentrating mechanisms. Plant J 101:897–918
Ishikawa C, Hatanaka T, Misoo S, Miyake C, Fukayama H (2011) Functional incorporation of sorghum small subunit increases the catalytic turnover rate of Rubisco in transgenic rice. Plant Physiol 156:1603–1611
Izumi M, Tsunoda H, Suzuki Y, Makino A, Ishida H (2012) RBCS1A and RBCS3B, two major members within the Arabidopsis RBCS multigene family, function to yield sufficient Rubisco content for leaf photosynthetic capacity. J Exp Bot 63:2159–2170
Johansen DA (1940) Plant microtechnique. McGraw-Hill Book, New York
Jordan DB, Ogren WL (1981) Species variation in the specificity of ribulose biphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Nature 291:513–515
Jordan DB, Ogren WL (1983) Species variation in kinetic properties of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Arch Biochem Biophys 227:425–433
Kapralov MV, Filatov DA (2007) Widespread positive selection in the photosynthetic rubisco enzyme. BMC Evol Biol 7:73
Kapralov MV, Kubien DS, Andersson I, Filatov DA (2011) Changes in Rubisco kinetics during the evolution of C4 photosynthesis in Flaveria (Asteraceae) are associated with positive selection on genes encoding the enzyme. Mol Biol Evol 28:1491–1503
Kaufman PB, Bigelow WC, Schmid R, Ghosheh NS (1971) Electron microprobe analysis OF silica in epidermal cells of Equisetum. Am J Bot 38:309–316
Larcher W (2001) Ökophysiologie der Pflanzen 6. Auflage. Eugen Ulmer, Stuttgart
Lenton TM, Daines SJ, Mills BJW (2016) COPSE reloaded: an improved model of biogeochemical cycling over phanerozoic time. Earth-Sci Rev 178:1–28
Li J, Weraduwage SM, Preiser AL, Tietz S, Weise SE, Strand DD, Froehlich JE, Kramer DM, Hu J, Sharkey TD (2019) A cytosolic bypass and G6P shunt in plants lacking peroxisomal hydroxypyruvate reductase. Plant Physiol 180:783–792
Lilley RM, Walker DA (1974) An improved spectrophotometric assay for ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta 358:226–229
Mae T, Makino A, Ohira K (1983) Changes in the amounts of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase synthesized and degraded during the life span of rice leaf (Oryza sativa L). Plant Cell Physiol 24:1079–1086
Makino A, Osmond B (1991) Solubilization of ribulose-l,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from the membrane fraction of pea leaves. Photosynth Res 29:79–85
Makino A, Mae T, Ohira K (1984) Relation between nitrogen and ribulose-l,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in rice leaves from emergence through senescence. Plant Cell Physiol 25:429–437
Makino A, Mae T, Ohira K (1985) Enzymic properties of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase purified from rice leaves. Plant Physiol 79:57–61
Makino A, Mae T, Ohira K (1988) Differences between wheat and rice in the enzyme properties of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase and their relationship to photosynthetic gas exchange. Planta 174:30–38
Makino A, Sakashita H, Hidema J, Mae T, Ojima K, Osmond B (1992) Distinctive responses of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase and carbonic anhydrase in wheat leaves to nitrogen nutrition and their possible relationships to CO2 transfer resistance. Plant Physiol 100:1737–1743
Makino A, Shimada T, Takumi S, Kaneko K, Matsuoka M, Shimamoto K, Nakano H, Miyao-Tokutomi M, Mae T, Yamamoto N (1997) Does decrease in ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase by antisense RbcS lead to a higher N-use efficiency of photosynthesis under conditions of saturating CO2 and light in rice plants? Plant Physiol 114:483–491
Makino A, Sakuma H, Sudo E, Mae T (2003) Differences between maize and rice in N-use efficiency for photosynthesis and protein allocation. Plant Cell Physiol 44:952–956
Manhart JR (1994) Phylogenetic analysis of green plant rbcL sequences. Mol Phylogen Evol 3:114–127
Mao Y, Catherall E, Díaz-Ramos A, Greiff GRL, Azinas S, Gunn L, McCormick AJ (2023) The small subunit of Rubisco and its potential as an engineering target. J Exp Bot 74:543–561
Martin-Avila E, Lim YL, Birch R, Dirk LMA, Buck S, Rhodes T, Sharwood RE, Kapralov MV, Whitney SM (2020) Modifying plant photosynthesis and growth via simultaneous chloroplast transformation of Rubisco large and small subunits. Plant Cell 32:2898–2916
Matsumura H, Shiomi K, Yamamoto A, Taketani Y, Kobayashi N, Yoshizawa T, Tanaka SI, Yoshikawa H, Endo M, Fukayama H (2020) Hybrid rubisco with complete replacement of rice Rubisco small subunits by sorghum counterparts confers C4 plant-like high catalytic activity. Mol Plant 13:1570–1581
Nakano H, Muramatsu S, Makino A, Mae T (2000) Relationship between the suppression of photosynthesis and starch accumulation in the pod-removed bean. Aust J Plant Physiol 27:167–173
Ogawa S, Suzuki Y, Yoshizawa R, Kanno K, Makino A (2012) Effect of individual suppression of RBCS multigene family on Rubisco contents in rice leaves. Plant Cell Environ 35:546–553
Ogren WL (1984) Photorespiration: pathways, regulation, and modification. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 35:415–442
Onoda Y, Wright IJ, Evans JR, Hikosaka K, Kitajima K, Niinemets Ü, Poorter H, Tosens T, Westoby M (2017) Physiological and structural tradeoffs underlying the leaf economics spectrum. New Phytol 214:1447–1463
Orr DJ, Alcântara A, Kapralov MV, Andralojc PJ, Carmo-Silva E, Parry MAJ (2016) Surveying rubisco diversity and temperature response to improve crop photosynthetic efficiency. Plant Physiol 172:707–717
Quick WP, Fichtner K, Schulze ED, Wendler R, Leegood RC, Mooney H, Rodermel SR, Bogorad L, Stitt M (1992) Decreased ribulose- 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase in transgenic Tobacco transformed with antisense rbcS. IV. Impact on photosynthesis in conditions of altered nitrogen supply. Planta 188:522–531
Reid CD, Tissue DT, Fiscus EL, Strain BR (1997) Comparison of spectrophotometric and radioisotopic methods for the assay of Rubisco in ozone-treated plants. Physiol Plant 101:398–404
Rothfels CJ, Li FW, Sigel EM, Huiet L, Larsson A, Burge DO, Ruhsam M et al (2015) The evolutionary history of ferns inferred from 25 low-copy nuclear genes. Am J Bot 102:1089–1107
Savir Y, Noor E, Milo R, Tlusty T (2010) Cross-species analysis traces adaptation of Rubisco toward optimality in a low-dimensional landscape. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:3475–3480
Seemann JR, Badger MR, Berry JA (1984) Variations in the specific activity of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase between species utilizing differing photosynthetic pathways. Plant Physiol 74:791–794
Sharkey TD (1985) Photosynthesis in intact leaves of C3 plants: physics, physiology and rate limitations. Bot Rev 51:53–105
Sharkey TD, Savitch LV, Butz ND (1991) Photometric method for routine determination of kcat and carbamylation of rubisco. Photosynth Res 28:41–48
Spreitzer RJ (2003) Role of the small subunit in ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Arch Biochem Biophys 414:141–149
Suzuki Y, Ohkubo M, Hatakeyama H, Ohashi K, Yoshizawa R, Kojima S, Hayakawa T, Yamaya T, Mae T, Makino A (2007) Increased rubisco content in transgenic rice transformed with the ‘sense’ rbcS gene. Plant Cell Physiol 48:626–637
Suzuki Y, Kihara-Doi T, Kawazu T, Miyake C, Makino A (2010) Differences in Rubisco content and its synthesis in leaves at different positions in Eucalyptus globulus seedlings. Plant Cell Environ 33:1314–1323
Suzuki Y, Ohsaki K, Takahashi Y, Wada S, Miyake C, Makino A (2023) Behavior of photosystems II and I is modulated depending on N partitioning to Rubisco in mature leaves acclimated to low N levels and senescent leaves in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 64:55–63
Takahashi Y, Wada S, Noguchi K, Miyake C, Makino A, Suzuki Y (2021) Photochemistry of photosystems II and I in rice plants grown under different N levels at normal and high temperature. Plant Cell Physiol 62:1121–1130
Tcherkez GGB, Farquhar GD, Andrews TJ (2006) Despite slow catalysis and confused substrate specificity, all ribulose bisphosphate carboxylases may be nearly perfectly optimized. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:7246–7251
Testo W, Sundue M (2016) A 4000-species dataset provides new insight into the evolution of ferns. Mol Phylogen Evol 105:200–211
Whitney SM, Houtz RL, Alonso H (2011) Advancing our understanding and capacity to engineer nature’s CO2-sequestering enzyme, Rubisco. Plant Physiol 155:27–35
Yeoh HH, Badger MR, Watson L (1981) Variations in kinetic properties of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylases among plants. Plant Physiol 67:1151–1155
Yoon DK, Ishiyama K, Suganami M, Tazoe Y, Watanabe M, Imaruoka S, Ogura M, Ishida H, Suzuki Y, Obara M, Mae T, Makino A (2020) Transgenic rice overproducing Rubisco exhibits increased yields with improved nitrogen-use efficiency in an experimental paddy field. Nat Food 1:134–139
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (21K190590 and 21H02084 to YS and 19H030060 to S-IM) and Research Grant #201705 of Forestry and Forest Products Research Institute (Japan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YS conceived and designed the experiments. S-IM and AM supported the experimental design. KI, SS, SK, NS, TH, and YS performed the experiments. All the authors analyzed and discussed the data. KI and YS wrote the manuscript. All authors reviewed and edited the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, K., Sugawara, S., Kageyama, S. et al. Equisetum praealtum and E. hyemale have abundant Rubisco with a high catalytic turnover rate and low CO2 affinity. J Plant Res 137, 255–264 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-023-01514-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-023-01514-z