Abstract
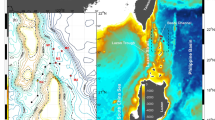
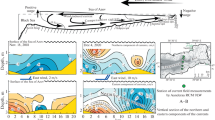
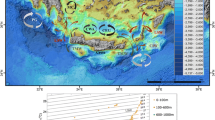
Current meter and hydrographic properties at the entrance of the Araçá Bay (AB), an intertidal flat adjacent to the São Sebastião channel, were collected between July 2013 and February 2014. These data sets show two different hydrographic periods, marked by a sharp change in the temperature and salinity values, clearly caused by the arrival of the South Atlantic Central Water (SACW). The first period is characterized by small variabilities on both properties with the dominance of coastal water, with relatively low salinity values. The second period shows a strong increase in the average salinity values and a much larger variability of temperature. This change in the hydrographic characteristics seems to be caused by anomalous winds, capable of displacing the SACW toward the coast. On the other hand, current meter data shows that the dynamics is mainly driven by the large-scale wind and is not impacted by the arrival of the SACW. Also, the currents are dominated by the barotropic mode, independently of the stratification differences that are observed between the beginning and end of the observational period.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amaral ACZ, Migotto AE, Turra A, Schaeffer-Novelli Y (2010) Araçá: biodiversity, impacts and threats. Biota Neotrop 10(1):219–264
Campos EJ, Velhote D, da Silveira IC (2000) Shelf break upwelling driven by Brazil Current cyclonic meanders. Geophys Res Lett 27(6):751–754
Castro BM (1990) Wind driven currents in the channel of São Sebastião: winter, 1979. In: Braz J Oceanogr 38(2):111–132
Castro BM (1996) Correntes e massas de água da Plataforma Continental Norte de São Paulo. Dissertation (Tese de Livre Docência), Instituto Oceanográfico da Universidade de São Paulo
Castro BM (2014) Summer/winter stratification variability in the central part of the South Brazil Bight. Cont Shelf Res 89:15–23
Castro BM, Lee TN (1995) Wind-forced sea level variability on the southeast Brazilian shelf. J Geophys Res 100(8):16045–16056
Castro BM, Miranda LB, Miyao SY (1987) Condições hidrográficas na plataforma continental ao largo de Ubatuba. Bol Inst Oceanogr, S Paulo 35(2):135–151
Castro BM et al (2008) Processos físicos: hidrografia, circulação e transporte, Oceanografia de um Ecossistema Subtropical: Plataforma de São Sebastião, SP, São Paulo: Editora da Universidade de São Paulo: 59-121
Cerda C, Castro BM (2013) Hydrographic climatology of South Brazil Bight shelf waters between Sao Sebastiao (24° S) and Cabo Sao Tome (22° S). Cont Shelf Res 89:5–14
Clarke AJ, Brink KH (1985) The response of stratified, frictional flow of shelf and slope waters to fluctuating large-scale, low-frequency wind forcing. J Phys Oceanogr 15(4):439–453
Coelho AL (1997) Massas de água e circulação no Canal de São Sebastião (SP). Massas de água e circulação no Canal de São Sebastião (SP). Dissertation (Masters), Instituto Oceanográfico da Universidade de São Paulo
Csanady GT (1977) Intermittent ‘full’upwelling in Lake Ontario. J Geophys Res 82(3):397–419
Csanady GT (1978) The arrested topographic wave. J Phys Oceanogr 8(1):47–62
Castro BM, de Miranda LB (1998) Physical oceanography of the western Atlantic continental shelf located between 4 N and 34 S. The Sea 11(1):209–251
Dionne J (1988) Characteristic features of modern tidal flats in cold regions. Tide-Influenced Sedimentary Environments and Facies, Springer, pp 301–332
Dottori M, Castro B (2009) The response of the Sao Paulo Continental Shelf, Brazil, to synoptic winds. In: Ocean Dyn 59(4):603–614
Dyer K, Christie M, Wright E (2000) The classification of intertidal mudflats. In: Cont Shelf Res 20(10):1039–1060
Emilsson I (1961) The shelf and coastal waters of Southern Brazil. Bol Inst Oceanogr 7(2):101–112
Emilsson I (1962) As correntes martimas no Canal de São Sebastião. Ciência e Cultura 14(4):269–270
Gill AE, Schumann EH (1974) The generation of long shelf waves by the wind. J Phys Oceanogr 4(1):83–90
Kanamitsu M, Ebisuzaki W, Woollen J, Yang SK, Hnilo JJ, Fiorino M, Potter GL (2002) NCEP-DOE AMIP-II reanalysis (R-2). Bull Am Meteorol Soc 83(11):1631–1643
Kvinge T (1967) On the special current and water level variations in the Channel of São Sebastião. Bol Inst Oceanogr 16(1):23–38
McClimans TA (1986) Laboratory modeling of dynamic processes in fjords and shelf waters. The Role of Freshwater Outflow in Coastal Marine Ecosystems. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 67–84
Silva LDS, Miranda LBD, Castro Filho BMD (2005) Numerical study of circulation and thermohaline structure in the São Sebastião Channel. Rev Bras Geof 23(4):407–425
Stech JL, Lorenzzetti JA (1992) The response of the South Brazilian Bight to the passage of wintertime cold fronts. J Geophys Res 97(6):9507–9520
Villamarin BC (2014) Alterações morfológicas da Baia do Araçá: implicações em sua dinâmica, Graduation monography
Welch PD (1967) The use of fast Fourier transform for the estimation of power spectra: a method based on time averaging over short, modified periodograms. IEEE Trans Audio Electroacoust 15(2):70–73
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by FAPESP (Fundação de Apoio a Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo) through the project “Biodiversity and Functioning of a Subtropical Coastal Ecosystem: a contribution to integrated management” (FAPESP no 2011/50317-5). Eduardo Siegle and Belmiro Mendes Castro are sponsored by CNPq research fellowships. We also thank the two anonymous reviewers for their comments that substantially improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Arnoldo Valle-Levinson
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Physics of Estuaries and Coastal Seas 2014 in Porto de Galinhas, PE, Brazil, 19-23 October 2014
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dottori, M., Siegle, E. & Castro, B.M. Hydrodynamics and water properties at the entrance of Araçá Bay, Brazil. Ocean Dynamics 65, 1731–1741 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-015-0900-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-015-0900-4