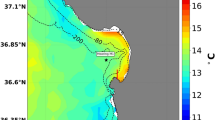
Abstract
In the framework of climate change, the increase in ocean heat wave frequency is expected to impact marine life. Large-scale positive temperature anomalies already occurred in the northwestern Mediterranean Sea in 1999, 2003 and 2006. These anomalies were associated with mass mortality events of macrobenthic species in coastal areas (0–40 m in depth). The anomalies were particularly severe in 1999 and 2003 when thousands of kilometres of coasts and about 30 species were affected. The aim of this study was to develop a methodology to assess the current risk of mass mortality associated with temperature increase along NW Mediterranean continental coasts. A 3D regional ocean model was used to obtain the temperature conditions for the period 2001–2010, for which the model outputs were validated by comparing them with in situ observations in affected areas. The model was globally satisfactory, although extremes were underestimated and required correction. Combined with information on the thermo-tolerance of a key species (the red gorgonian P. clavata) as well as its spatial distribution, the modelled temperature conditions were then used to assess the risk of mass mortality associated with thermal stress for the first time. Most of the known areas of observed mass mortality were found using the model, although the degree of risk in certain areas was underestimated. Using climatic IPCC scenarios, the methodology could be applied to explore the impacts of expected climate change in the NW Mediterranean. This is a key issue for the development of sound management and conservation plans to protect Mediterranean marine biodiversity in the face of climate change.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andre G, Garreau P, Garnier V, Fraunié P (2005) Modelled variability of the sea surface circulation in the north-western Mediterranean Sea and in the Gulf of Lions. Ocean Dyn 55:294–308
Andre G, Garreau P, Fraunié P (2009) Mesoscale slope current variability in the Gulf of Lions. Interpretation of in situ measurements using a three-dimensional model. Cont Shelf Res 29:407–423
Bally M, Garrabou J (2007) Thermodependent bacterial pathogens and mass mortalities in temperate benthic communities: a new case of emerging disease linked to climate change. Glob Change Biol 13:2078–2088
Baums I (2008) A restoration genetics guide for coral reef conservation. Mol Ecol 17:2796–2811
Bensoussan N, Romano JC, Harmelin JG, Pascual J, Garrabou J (2009) Warming trends, regional fingerprints and future trajectories of NW Mediterranean coastal waters. Proceedings of the first Mediterranean symposium on coralligenous and other calcareous bioconcretions, Tabarka, 15–16 January 2009, Tunisia, pp 167–168
Bensoussan N, Romano JC, Harmelin JG, Garrabou J (2010) High resolution characterization of northwest Mediterranean coastal waters thermal regimes: to better understand responses of benthic communities to climate change. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 87:431–441
Calvo E, Simó R, Coma R, Ribes M, Pascual J, Sabatés A, Gili JM, Pelejero C (2011) Effects of climate change on Mediterranean marine ecosystems: the case of the Catalan Sea. Clim Res 50:1–29
Cebrian E, Uriz MJ, Garrabou J, Ballesteros E (2011) Sponge mass mortalities in a warming Mediterranean Sea: are cyanobacteria-harboring species worse off? PLoS ONE 6(6):e20211. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020211
Cerrano C, Bavestrello G, Bianchi CN et al (2000) A catastrophic mass-mortality episode of gorgonians and other organisms in the Ligurian Sea (north-western Mediterranean), summer 1999. Ecol Lett 3:284–293
Coll M, Piroddi C, Steenbeek J, Kaschner K, Ben Rais Lasram F et al (2010) The biodiversity of the Mediterranean Sea: estimates, patterns, and threats. PLoS ONE 5:e11842
Coma R, Ribes M, Gili JM, Zabala M (2000) Seasonality in coastal benthic ecosystems. Trends Ecol Evol 15(11):448–453
Coma R, Ribes M, Serrano E, Jiménez E, Salat J, Pascual J (2009) Global warming-enhanced stratification and mass mortality events in the Mediterranean. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:6176–6181
Crisci C (2011) Détermination des risques pour la conservation des populations d’espèces longévives de Méditerranée nord-occidentale dans le contexte du changement climatique. Dissertation, Université de la Méditerranée
Crisci C, Bensoussan N, Romano JC, Garrabou J (2011) Temperature anomalies and mortality events in marine communities: insights on factors behind differential mortality impacts in the NW Mediterranean. PLoS ONE 6(9):e23814. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0023814
Déqué M (2007) Frequency of precipitation and temperature extremes over France in an anthropogenic scenario: model results and statistical correction according to observed values. Global Planet Change 57:16–26
Doney SC, Ruckelshaus M, Duffy JE, Barry JP et al (2012) Climate change impacts on marine ecosystems. Annu Rev Mar Sci 4:11–37
Dufois F, Garreau P, Le Hir P, Forget P (2008) Wave and current-induced bottom shear stress distribution in the Gulf of Lions. Cont Shelf Res 28:1920–1934
Garrabou J, Coma R, Bensoussan N, Bally M et al (2009) Mass mortality in northwestern Mediterranean rocky benthic communities: effects of the 2003 heat wave. Global Change Biol 15:1090–1103
Giorgi F, Lionello P (2008) Climate change projections for the Mediterranean region. Global Planet Change 63:90–104
Grell GA, Dudhia J, Stauffer DR (1994) A Description of the Fifth-Generation Penn State/NCAR Mesoscale Model (MM5). NCAR Tech. Note NCAR/TN 398STR
Harley CDG, Randall Hughes A, Hultgren KM, Miner BG, Sorte CJB et al (2006) The impacts of climate change in coastal marine systems. Ecol Lett 9:228–241
Harvell CD, Kim K, Burkholder JM, Colwell RR, Epstein PR et al (1999) Emerging marine diseases. Climate links and anthropogenic factors. Science 285:1505–1510
IPCC 2007 (2007) Climate Change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the IPCC, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. http://www.ipcc.ch/publications_and_data/publications_ipcc_fourth_assessment_report_wg1_report_the_physical_science_basis.htm
Kipson S (2013) Community and population ecology analysis of gorgonian dominated communities in the Adriatic sea. Dissertation, University of Zagreb
Lazure P, Dumas F (2008) An external-internal mode coupling for a 3D hydrodynamical model for applications at regional scale (MARS). Adv Water Resour 31:233–250
Levitus S, Antonov J, Boyer TP, Stephens C (2000) Warming of the world ocean. Science 287:2225–2229
Linares C, Coma R, Garrabou J, Diaz D, Zabala M (2008) Size distribution, density and disturbance in two Mediterranean gorgonians: Paramuricea clavata and Eunicella singularis. J Appl Ecol 45:688–699
Millot C (1979) Wind induced upwellings in the Gulf of Lions. Oceanol Acta 2:262–274
Millot C (1990) The Gulf of Lions’ hydrodynamics. Cont Shelf Res 10(9–11):885–894
Nicolle A, Garreau P, Liorzou B (2009) Modelling for anchovy recruitment studies in the Gulf of Lions (Western Mediterranean Sea). Ocean Dyn 59:953–968
Pairaud I, Gatti J, Bensoussan N, Verney R, Garreau P (2011) Hydrology and circulation in a coastal area off Marseille: validation of a nested 3D model with observations. J Mar Syst 88:20–33
Pérez T, Garrabou J, Sartoretto S, Harmelin JG, Francour P, Vacelet J (2000) Mortalités massives d’invertébrés marins: un évènement sans précédent en Méditerranée nord-occidentale. C R Acad Sc Paris Biol 323:853–865
Perry AL, Low PJ, Ellis JR, Reynolds JD (2005) Climate change and distribution shifts in marine fishes. Science 308:1912–1915
Previati M, Scinto A, Cerrano C, Osinga R (2010) Oxygen consumption in Mediterranean octocorals under different temperatures. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 390:39–48
Rubio A, Taillandier V, Garreau P (2009) Reconstruction of the Mediterranean northern current variability and associated cross-shelf transport in the Gulf of Lions from satellite-tracked drifters and model outputs. J Mar Syst 78:63–78
Russell B, Connell S (2012) Origins and consequences of global and local stressors: incorporating climatic and non-climatic phenomena that buffer or accelerate ecological change. Mar Biol 159:2633–2639
Schaeffer A, Garreau P, Molcard A, Fraunie P, Seity Y (2011) Influence of high-resolution wind forcing on hydrodynamic modeling of the Gulf of Lions. Ocean Dyn 61(11):1823–1844
Somot S, Sevault F, Déqué M (2006) Transient climate change scenario simulation of the Mediterranean Sea for the twenty-first century using a high resolution ocean circulation model. Clim Dyn 27:851–879
Somot S, Sevault F, Déqué M, Crépon M (2008) 21st century climate change scenario for the Mediterranean using a coupled atmosphere–ocean regional climate model. Global Planet Change 63:112–126
Trenberth K (2012) Framing the way to relate climate extremes to climate change. Clim Chang 115:283–290
Wernberg T, Russell B, Thomsen M, Gurgel C, Bradshaw C, Poloczanska E, Connell S (2011) Seaweed communities in retreat from ocean warming. Curr Biol 21:1828–1832
Wernberg T, Smale DA, Tuya F, Thomsen MS, Langlois TJ, De Bettignies T, Bennett S, Rousseaux CS (2013) An extreme climatic event alters marine ecosystem structure in a global biodiversity hotspot. Nature Clim Change 3:78–82
Zabala M, Ballesteros E (1989) Surface-dependent strategies and energy flux in benthic marine communities or, why corals do not exist in the Mediterranean. Sci Mar 53(1):3–17
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the CLIMCARES project funded by the TOTAL foundation (http://climcares.medrecover.org). We thank the Pytheas Observation Service, the Reserve Naturelle Marine de Cerbere-Banyuls, the Reserve Naturelle de Scandola, the Parc Natural del Montgrí and the Illes Medes i Baxi Ter for providing the temperature records and information on the red gorgonian distribution. The mortality risk assessment could not be possible without the collaboration of MPA managers and scientists that kindly answer our questionnaire on the distribution of gorgonian: Silvia Cocito (ENEA), Carlo Cerrano (Polytechnic University of Marche), Giovanni Santangelo (Univesity of Pisa), Luisa Mangialajo (ECOMERS), Stéphane Sartoretto (IFREMER) and managers from Aire Marine Protégée des Posidonies du Cap d’Agde and Parc Marin de la Côte Bleue. Finally, we are thankful to Cristina Linares, Emma Cebrian, Núria Teixidó, Jean-Baptsite Ledoux, Silvija Kipson and members of the Marine Conservation Research Group MedRecover 2009-SGR-1174 (www.medrecover.org), for the use of demographic data of the red gorgonian populations. This study was also part of the ‘Mistrals Mermex WP2-ICOCE’ and international ‘IMBER’, ‘SOLAS’ and ‘LOICZ’ projects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Martin Verlaan
This article is part of the Topical Collection on the 16th biennial workshop of the Joint Numerical Sea Modelling Group (JONSMOD) in Brest, France 21-23 May 2012
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pairaud, I.L., Bensoussan, N., Garreau, P. et al. Impacts of climate change on coastal benthic ecosystems: assessing the current risk of mortality outbreaks associated with thermal stress in NW Mediterranean coastal areas. Ocean Dynamics 64, 103–115 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-013-0661-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-013-0661-x