Abstract
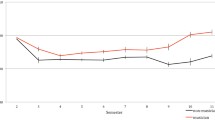
Although music training has been related to better school performance, the processes that may mediate this improvement are unknown. Given that study habits and techniques are one of the variables most closely related to academic achievement, the present study analyzed the differences in study habits and techniques between children with and without musical training, checking whether the age at which training began is a significant variable and whether study habits and techniques act as a mediator between musical training and academic achievement. A total of 132 children aged 9–12 years from the Autonomous Community of the Basque Country were studied using the Questionnaire of Habits and Study Techniques and school grades. Significant differences were found in the attitude toward study, exams and exercises; personal and environmental conditions for study; and general study habits and techniques in favor of children with musical training. In addition, children who started training before the age of seven showed better results in study habits and techniques. In turn, study habits and techniques significantly mediated the relationship between music training and academic achievement. Therefore, music training, especially before the age of seven, seems to have a beneficial effect on academic achievement, which could be explained, at least in part, by study habits and techniques.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Álvarez, M., & Fernández, R. (2015). Cuestionario de Hábitos y Técnicas de Estudio. TEA Ediciones.
Alves, A. F., Gomes, C. M. A., Martins, A., & da Almeida, L. S. (2017). Cognitive performance and academic achievement: How do family and school converge? European Journal of Education and Psychology, 10(2), 49–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejeps.2017.07.001
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Manual diagnóstico y estadístico de trastornos mentales (DSM-5) (5ª). Editorial Médica Panamericana.
Appelgren, A., Osika, W., Theorell, T., Madison, G., & Bojner Horwitz, E. (2019). Tuning in on motivation: Differences between non-musicians, amateurs, and professional musicians. Psychology of Music, 47(6), 864–873. https://doi.org/10.1177/0305735619861435
Ashbourne, D., & Andres, L. (2015). Athletics, music, languages, and leadership: How parents influence the extracurricular activities of their children. Canadian Journal of Education, 38(2), 1–34. https://doi.org/10.2307/canajeducrevucan.38.2.09
Association for Media Research. (2015). Nuevo sistema de clasificación socioeconómica en el EGM. Retrieved December 12, 2023, from https://www.aimc.es/
Authors. (2021). Intelligence quotient, short-term memory and study habits as academic achievement predictors of elementary school: A follow-up study. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 70(101020), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stueduc.2021.101020
Ayodele, C., & Adebiyi, D. (2013). Study habits as influence of academic performance of university undergraduates in Nigeria. Research Journal in Organizational Psychology and Educational Studies, 2(3), 72–75. Bayliss, D. M., Jarrold, C., Baddeley, A. D.
Bagci, H., & Can, U. K. (2016). Effects of study habits of music students on the success of musical instrument training. Journal of Education and Sociology, 7(1), 21–28. https://doi.org/10.7813/jes.2016/7-1/4
Basque Institute of Statistics [EUSTAT]. (2016). Información estadística clasificada. Administración de la Comunidad Autónoma del País Vasco. https://www.eustat.eus/indice.html
Bialystok, E., & DePape, A. M. (2009). Musical expertise, bilingualism, and executive functioning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 35(2), 565–574. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0012735
Bueno, D. (2019). Genetics and learning: How the genes influence educational attainment. Frontiers in Psychology, 10(1622), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01622
Capdevila Seder, A., & Bellmunt Villalonga, H. (2016). Importancia de los hábitos de estudio en el rendimiento académico del adolescente: Diferencias por género. Educatio Siglo XXI, 34(1), 157–172. https://doi.org/10.6018/j/253261
Cárdenas, M., & Arancibia, H. (2014). Potencia estadística y cálculo del tamaño del efecto en G*Power: Complementos a las pruebas de significación estadística y su aplicación en psicología [Statistical power and calculation of effect size in G * Power: Complements of statistical significance tests and their application in psychology]. Salud y Sociedad, 5(2), 210–224. https://doi.org/10.22199/S07187475.2014.0002.00006
Chabra, S., Bansal, T., & Misra, M. (2012). Does learning music affect study habits of learners? Scholarly Research Journal for Interdisciplinary Studies, 1(2), 276–283.
Chen, J., Scheller, M., Wu, C., Hu, B., Peng, R., Liu, C., Liu, S., Zhu, L., & Chen, J. (2022). The relationship between early musical training and executive functions: Validation of effects of the sensitive period. Psychology of Music, 50(1), 86–99. https://doi.org/10.1177/0305735620978690
Degé, F. (2021). Music lessons and cognitive abilities in children: How far transfer could be possible. Frontiers in Psychology, 11(557807), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.557807
Dos Santos-Luiz, C., Mónico, L. S. M., Almeida, L. S., & Coimbra, D. (2016). Exploring the long-term associations between adolescents’ music training and academic achievement. Musicae Scientiae, 20(4), 512–527. https://doi.org/10.1177/1029864915623613
Dumont, E., Syurina, E. V., Feron, F. J. M., & van Hooren, S. (2017). Music interventions and child development: A critical review and further directions. Frontiers in Psychology, 8(1694), 1–20. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01694
Guhn, M., Emerson, S. D., & Gouzouasis, P. (2020). A population-level analysis of associations between school music participation and academic achievement. Journal of Educational Psychology, 112(2), 308–328. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000376
Hayes, A. F. (2018). Introduction to mediation, moderation, and conditional process analysis: A regression-based approach. The Gilford Press.
Hille, A., & Schupp, J. (2015). How learning a musical instrument affects the development of skills. Economics of Education Review, 44, 56–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econedurev.2014.10.007This
IBM, C. (2017). IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 25.0. IBM Corp.
Ireland, K., Iyer, T. A., & Penhune, V. B. (2019). Contributions of age of start, cognitive abilities and practice to musical task performance in childhood. PLoS ONE, 14(4), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0216119
Koelsch, S. (2010). Towards a neural basis of music-evoked emotions. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 14(3), 131–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2010.01.002
Kraus, N., & Chandrasekaran, B. (2010). Music training for the development of auditory skills. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 11(8), 599–605. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2882
Leung, M. C., & Cheung, R. Y. M. (2020). Music engagement and well-being in Chinese adolescents: Emotional awareness, positive emotions, and negative emotions as mediating processes. Psychology of Music, 48(1), 105–119. https://doi.org/10.1177/0305735618786421
Linnavalli, T., Adriana, S. G., & Tervaniemi, M. (2021). Perspectives on the potential benefits of children’s group-based music education. Music and Science, 4, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1177/20592043211033578
McPherson, G. E., & O’Neill, S. A. (2010). Students’ motivation to study music as compared to other school subjects: A comparison of eight countries. Research Studies in Music Education, 32(2), 101–137. https://doi.org/10.1177/1321103X10384202
McPherson, G. E., Osborne, M. S., Evans, P., & Miksza, P. (2019). Applying self-regulated learning microanalysis to study musicians’ practice. Psychology of Music, 47(1), 18–32. https://doi.org/10.1177/0305735617731614
Miñano-Pérez, P., & Castejón-Costa, J. L. (2011). Variables cognitivas y motivacionales en el rendimiento académico en lengua y matemáticas: Un modelo estructural. Revista De Psicodidáctica, 16(2), 203–230.
Moreno, S., & Bidelman, G. M. (2014). Examining neural plasticity and cognitive benefit through the unique lens of musical training. Hearing Research, 308, 84–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.2013.09.012
Murillo, F. J., & Hernández-Castilla, R. (2020). Does parental involvement matter in children’s performance? A Latin American primary school study. Revista De Psicodidactica, 25(1), 13–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psicod.2019.10.002
Oladejo, M. A., & Oladejo, M. A. (2017). Correlation of extracurricular activities with students’ study habits in university of Lagos. Sokoto Educational Review, 17(1), 211–221. https://doi.org/10.35386/ser.v17i2.36
Peng, P., & Kievit, R. A. (2020). The development of academic achievement and cognitive abilities: A bidirectional perspective. Child Development Perspectives, 14(1), 15–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdep.12352
Rabia, M., Mubarak, N., Tallat, H., & Nasir, W. (2017). A study on study habits and academic performance of students. International Journal of Asian Social Science, 7(10), 891–897. https://doi.org/10.18488/journal.1.2017.710.891.897
Román-Caballero, R., Vadillo, M. A., Trainor, L. J., & Lupiáñez, J. (2022). Please don’t stop the music: A meta-analysis of the cognitive and academic benefits of instrumental musical training in childhood and adolescence. Educational Research Review, 35(100436), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2022.100436
Schellenberg, E. G. (2006). Long-term positive associations between music lessons and IQ. Journal of Educational Psychology, 98(2), 457–468. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.98.2.457
Schellenberg, E. G. (2011). Examining the association between music lessons and intelligence. British Journal of Psychology, 102, 283–302. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2044-8295.2010.02000.x
Schellenberg, E. G. (2020). Correlation = causation? Music training, psychology, and neuroscience. Psychology of Aesthetics, Creativity, and the Arts, 14(4), 475–480. https://doi.org/10.1037/aca0000263
Sichivitsa, V. O. (2007). The influences of parents, teachers, peers and other factors on students’ motivation in music. Research Studies in Music Education, 29(1), 55–68. https://doi.org/10.1177/1321103X07087568
Slater, J., & Kraus, N. (2016). The role of rhythm in perceiving speech in noise: A comparison of percussionists, vocalists and non-musicians. Cognitive Processing, 17, 79–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10339-015-0740-7
Spencer, M., Fuchs, L. S., Geary, D. C., & Fuchs, D. (2022). Connections between mathematics and reading development: Numerical cognition mediates relations between foundational competencies and later academic outcomes. Journal of Educational Psychology, 114(2), 273–288. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000670
Steinmayr, R., Meibner, A., Weidinger, A., & Wirthwein, L. (2015). Academic achievement. Oxford Bibliographies.
Stelzer, F., & Cervigni, M. (2011). Desempeño académico y funciones ejecutivas en infancia y adolescencia. Una revisión de la literatura. Revista de Investigación en Educación, 1(9), 148–156.
Swaminathan, S., & Schellenberg, E. G. (2018). Musical competence is predicted by music training, cognitive abilities, and personality. Scientific Reports, 6(43), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-27571-2
The Jamovi Project (2022). jamovi (Version 2.3.26) [Computer Software]. Retrieved from https://www.jamovi.org
Venet, R., & Carbo, I. (2017). Las técnicas de studio. Reflexiones e instrucciones metodológicas para su aprendizaje y uso pertinentes en el contexto universitario. Revista Maestro y Sociedad, 14(3), 502–516.
Wetter, O. E., Koerner, F., & Schwaninger, A. (2009). Does musical training improve school performance? Instructional Science, 37(4), 365–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11251-008-9052-y
Young, L. N., Cordes, S., & Winner, E. (2014). Arts involvement predicts academic achievement only when the child has a musical instrument. Educational Psychology, 34(7), 849–861. https://doi.org/10.1080/01443410.2013.785477
Zárate-Depraect, N. E., Soto-Decuir, M. G., Martínez-Aguirre, E. G., Castro-Castro, M. L., García-Jau, R. A., & López-Leyva, N. M. (2018). Hábitos de estudio y estrés en estudiantes del área de la salud. Revista de la Fundación Educación Médica, 21(3), 153. https://doi.org/10.33588/fem.213.948
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Katya Martin-Requejo
Current themes of research:
Neuroeducation. Psychology of education. Cognitive assessment. Music training.
Relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
Martin-Requejo, K., González-Andrade, A., Álvarez-Bardón, A., & Santiago-Ramajo, S. (2023). Involvement of executive functions, emotional intelligence, and study habits in mathematical problem-solving and calculation in elementary school. Revista de Psicodidáctica. Article in press.
Martín-Requejo, M. & Santiago-Ramajo, S. (2022). Últimos avances científicos de los efectos neuropsicológicos de la educación musical. ArtsEduca, 31, 275-286. https://doi.org/10.6035/artseduca.5976.
Martin-Requejo, K., & Santiago-Ramajo, S. (2021). Predicting academic skills in 9-year-olds: intelligence quotient, executive functions, and emotional intelligence. Electronic Journal of Research in Educational Psychology, 19(55), 533-582. https://doi.org/10.25115/ejrep.v19i55.4546.
Martin‐Requejo, K., & Santiago‐Ramajo, S. (2021). Reduced Emotional Intelligence in Children Aged 9–10 caused by the COVID‐19 Pandemic Lockdown. Mind, Brain, and Education, 15(4), 269-272. https://doi.org/10.1111/mbe.12297.
Alejandro González-Andrade
Current themes of research:
Clinical neuropsychology. Neuroeducation. Cognitive assessment. Executive function.
Relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
Martin-Requejo, K., González-Andrade, A., Álvarez-Bardón, A., & Santiago-Ramajo, S. (2023). Involvement of executive functions, emotional intelligence, and study habits in mathematical problem-solving and calculation in elementary school. Revista de Psicodidáctica. Article in press.
Quilez-Robres, A., González-Andrade, A., Ortega, Z., & Santiago-Ramajo, S. (2021). Intelligence quotient, short-term memory and study habits as academic achievement predictors of elementary school: A follow-up study. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 70, 101020.
Aitor Álvarez-Bardón
Current themes of research:
Neuroeducation. Cyberbullying. Health-related quality of life.
Relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
Martin-Requejo, K., González-Andrade, A., Álvarez-Bardón, A., & Santiago-Ramajo, S. (2023). Involvement of executive functions, emotional intelligence, and study habits in mathematical problem-solving and calculation in elementary school. Revista de Psicodidáctica. Article in press.
González-Cabrera, J., Machimbarrena, J. M., Ortega-Barón, J., & Álvarez-Bardón, A. (2020). Joint association of bullying and cyberbullying in health-related quality of life in a sample of adolescents. Quality of life research, 29, 941-952. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-019-02353-z.
Machimbarrena, J. M., Álvarez-Bardón, A., León-Mejía, A., Gutiérrez-Ortega, M., Casadiego-Cabrales, A., & González-Cabrera, J. (2019). Loneliness and personality profiles involved in bullying victimization and aggressive behavior. School mental health, 11, 807-818. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12310-019-09328-y.
González-Cabrera, J., León-Mejía, A., Beranuy, M., Gutiérrez-Ortega, M., Álvarez-Bardón, A., & Machimbarrena, J. M. (2018). Relationship between cyberbullying and health-related quality of life in a sample of children and adolescents. Quality of life research, 27, 2609-2618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-018-1901-9.
Sandra Santiago-Ramajo
Current themes of research:
Clinical neuropsychology. Neuroeducation. Addictions. Mild cognitive impairment.
Relevant publications in the field of Psychology of Education:
Martin-Requejo, K. González-Andrade, A., Álvarez-Bardón, A., & Santiago-Ramajo, S. (2023). Involvement of executive functions, emotional intelligence, and study habits in mathematical problem-solving and calculation in elementary school. Revista de Psicodidáctica. Article in press.
Sepúlveda-Durán, C.M., Martín-Lobo, P., & Santiago-Ramajo, S. (2023). Impact of musical training in specialized centres on learning strategies, auditory discrimination and working memory in adolescents. British Journal of Music Education, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0265051723000190.
Martín-Requejo, M. & Santiago-Ramajo, S. (2022). Últimos avances científicos de los efectos neuropsicológicos de la educación musical. ArtsEduca, 31, 275-286. https://doi.org/10.6035/artseduca.5976.
Martin-Requejo, K., & Santiago-Ramajo, S. (2021). Predicting academic skills in 9-year-olds: intelligence quotient, executive functions, and emotional intelligence. Electronic Journal of Research in Educational Psychology, 19(55), 533-582. https://doi.org/10.25115/ejrep.v19i55.4546.
Martin‐Requejo, K., & Santiago‐Ramajo, S. (2021). Reduced Emotional Intelligence in Children Aged 9–10 caused by the COVID‐19 Pandemic Lockdown. Mind, Brain, and Education, 15(4), 269-272. https://doi.org/10.1111/mbe.12297.
Quilez-Robres, A., González-Andrade, A., Ortega, Z., & Santiago-Ramajo, S. (2021). Intelligence quotient, short-term memory and study habits as academic achievement predictors of elementary school: A follow-up study. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 70, 101020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stueduc.2021.101020.
Cid-Sillero, S., Santiago-Ramojo, S., & Martín-Lobo, M. P. (2018). Relation between executive functions and empathy and their influence on academic performance in students of basic vocational training. Electronical Journal of Research in Educational Psychology, 16(2), 517-536.
Campeño‐Martínez, Y., Santiago‐Ramajo, S., Navarro‐Asencio, E., Vergara‐Moragues, E., & Santiuste Bermejo, V. (2017). Efficacy of an Intervention Program for Attention and Reflexivity in Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. Mind, Brain, and Education, 11(2), 64-74. https://doi.org/10.1111/mbe.12136.
Impact statement
The present study shows the role that music training can play in children’s academic development, especially if the training begins before the age of 7. Furthermore, it finds that part of the benefits of music training on academic achievement are mediated by improvements in study habits and techniques.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Martin-Requejo, K., González-Andrade, A., Álvarez-Bardón, A. et al. Mediation of study habits and techniques between music training and academic achievement in children. Eur J Psychol Educ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-023-00792-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10212-023-00792-4