Abstract
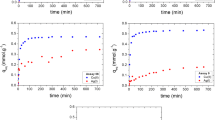
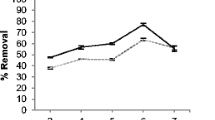
There is an increasing need for the investigation of recovery techniques for valuable elements, especially for the growing waste streams. This study focuses on the biosorption of commonly found valuable elements in e-waste: Ag+ and Nd3+ from aqueous solutions by using living and dried forms of Chlorella vulgaris. Optimization of the processes was conducted by changing the process parameters. In addition, biosorption from multi-metal solution (with Ag+, Nd3+, Au3+) was also investigated. Maximum removals were found as 174.6 ± 4.83 mg/g for Ag+, 239.7 ± 3.39 mg/g for Nd3+ by dried algae, and 161.6 ± 18.2 mg/g for Ag+, 296.8 ± 30.54 mg/g for Nd3+ by living algae. Both processes were very fast, representing 60 and 5–10 min during which a significant amount of the biosorption was completed for dried and living algae, respectively. FTIR and SEM–EDS showed that the algae were able to sorb the elements. Pseudo-second-order kinetics fit better to all processes. Freundlich model suited to the dried algae process, while the linear model fit to living algae process. The biosorption efficiency of Ag+ and Nd3+ decreased when there were co-ions present in the solution. Biosorption of Au3+ was affected depending on the experimental conditions in the case of multi-metal solutions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
JEITA (2018) Production Forecasts for the Global Electronics and Information Technology Industries, Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association. https://www.jeita.or.jp/english/topics/2018/1218.pdf. Accessed May 2019
Cayumil R, Khanna R, Rajarao R, Mukherjee PS, Sahajwalla V (2016) Concentration of precious metals during their recovery from electronic waste. Waste Manag 57:121–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2015.12.004
Oguchi M, Sakanakura H, Terzono A (2013) Toxic metals in WEE: characterization and substance flow analysis in waste treatment processes. Sci Total Environ 463–464:1124–1132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.07.078
Namias J (2013) The future of electronic waste recycling in the united states: obstacles and domestic solutions. Earth Engineering Center, Columbia University
Buchert M, Manhart A, Bleher D, Pingel D (2012) Recycling critical raw materials from waste electronic equipment. Freiburg: Öko-Institut ev. https://www.oeko.de/oekodoc/1375/2012-010-en.pdf. Accessed Oct 2015
UN University (2015) E-waste: not your normal trash Web-Page. http://ourworld.unu.edu/en/e-waste-not-your-normal-trash. Accessed October 2015
World Economic Forum (2019) A New Circular Vision for Electronics: Time for a Global Reboot. http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_A_New_Circular_Vision_for_Electronics.pdf. Accessed June 2019
Dodson JR, Hunt AJ, Parker HL, Yang Y, Clark JH (2012) Elemental sustainability: towards the total recovery of scarce metals. Chem Eng Process 51:69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cep.2011.09.008
Dobson RS, Burgess JE (2007) Biological treatment of precious metal from refinery wastewater: a review. Miner Eng 20:519–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2006.10.011
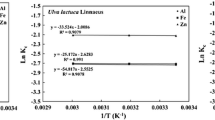
Kutahyali C, Sert S, Çetinkaya B, Inan S, Eral M (2010) Factors affecting lanthanum and cerium biosorption on Pinus brutia leaf powder. Sep Sci Technol 45:1456–1462. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496391003674266
Das N (2010) Recovery of precious metals through biosorption—a review. Hydrometallurgy 103:180–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2010.03.016
Yi Z, Yao J, Chen H, Wang F, Yuan Z, Liu X (2016) Uranium biosorption from aqueous solution onto Eichhornia crassipes. J Environ Radioact 154:43–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2016.01.012
Bagda E, Tuzen M, Sarı A (2017) Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic investigations for biosorption of uranium with green algae (Cladophora hutchinsiae). J Environ Radioact 175–176:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2017.04.004
Bulgariu D, Bulgariu L (2012) Equilibrium and kinetics studies of heavy metal ions biosorption on green algae waste biomass. Bioresour Technol 103:489–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.10.016
Das S, Dash HR (2017) Handbook of metal-microbe interactions and bioremediation, Taylor & Francis. ISBN 9781498762434
Gadd GM (2008) Biosorption: critical review of scientific rationale, environmental importance and significance for pollution treatment. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 84:13–28
Rezaei H (2016) Biosorption of chromium by using Spirulina sp. Arab J Chem 9:846–853
Gupta VK, Shrivastava AK, Jain N (2001) Biosorption of chromium(VI) from aqueous solutions by green algae spirogyra species. Water Res 35:4079–4085
Karthikeyan S, Balasubramanian R, Iyer CSP (2007) Evaluation of the marine algae Ulva fasciata and Sargassum sp. for the biosorption of Cu(II) from aqueous solutions. Bioresour Technol 98:452–455
Ji L, Xie S, Feng J, Li Y, Chen L (2012) Heavy metal uptake capacities by the common freshwater green alga Cladophora fracta. J Appl Phycol 24:979–983
Areco MM, Hanela S, Duran J, dos Santos AM (2012) Biosorption of Cu(II), Zn(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) by dead biomasses of green alga Ulva lactuca and the development of a sustainable matrix for adsorption implementation. J Hazard Mater 213–214:123–132
Maznah WO, Al-Fawwaz AT, Surif M (2012) Biosorption of copper and zinc by immobilised and free algal biomass, and the effects of metal biosorption on the growth and cellular structure of Chlorella sp. and Chlamydomonas sp. isolated from rivers in Penang, Malaysia. J Environ Sci 24:1386–1393
Dönmez GC, Aksu Z, Öztürk A, Kutsal T (1999) A comparative study on heavy metal biosorption characteristics of some algae. Process Biochem 34:885–892
Mata YN, Torres E, Blázquez ML, Ballester A, González F, Muñoz JA (2009) Gold(III) biosorption and bioreduction with the brown alga Fucus vesiculosus. J Hazard Mater 166:612–618
Vijayaraghavan K, Mahadevan A, Sathishkumar M, Pavagadhi S, Balasubramanian R (2011) Biosynthesis of Au(0) from Au(III) via biosorption and bioreduction using brown marine alga Turbinaria conoides. Chem Eng J 167:223–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2010.12.027
Deschatre M, Ghillebaert F, Guezennec J, Colin CS (2013) Sorption of copper(II) and silver(1) by four bacterial exopolysaccharides. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 171:1313–1327
Palmieri MC, Garcia O, Melnikov P (2000) Neodymium biosorption from acidic solutions in batch system. Process Biochem 36:441–444
Kucuker MA, Wieczorek N, Kuchta K, Copty NK (2017) Biosorption of neodymium on Chlorella vulgaris in aqueous solution obtained from hard disk drive magnets. PLoS ONE 12(4):e0175255
Vilar VJP, Botelho CMS, Boaventura RAR (2005) Influence of pH, ionic strength and temperature on lead biosorption by Gelidium and agar extraction algal waste. Process Biochem 40:3267–3275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2005.03.023
Zhang Y, Banks C (2005) Factors affecting the removal of selected heavy metals using a polymer immobilised sphagnum moss as a biosorbent. Environ Technol 26:733–744. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593332608618515
Goher ME, Abd El-Monem AM, Abdel-Satar AM, Ali MH, Hussian AM, Napiórkowska-Krzebietke A (2016) Biosorption of some toxic metals from aqueous solution using non-living algal cells of Chlorella vulgaris. J Elem 21:703–714. https://doi.org/10.5601/jelem.2015.20.4.1037
Aksu Z (2002) Determination of the equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of the batch biosorption of nickel (II) ions onto Chlorella vulgaris. Process Biochem 38:89–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(02)00051-1
Martins RJE, Pardo R, Boaventura RAR (2004) Cadmium(II) and zinc(II) adsorption by the aquatic moss Fontinalis antipyretica: effect of temperature, pH and water hardness. Water Res 38:693–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2003.10.013
Gupta VK, Rastogi A (2008) Biosorption of lead from aqueous solutions by green algae Spirogyra species: kinetics and equilibrium studies. J Hazard Mater 152:407–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00138-5
Chen Z, Ma W, Han M (2008) Biosorption of nickel and copper onto treated alga (Undaria pinnatifida): application of isotherm and kinetic models. J Hazard Mater 155:327–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007
Pahlavanzadeh H, Keshtkar AR, Safdari J, Abadi Z (2010) Biosorption of nickel(II) from aqueous solution by brown algae: equilibrium, dynamic and thermodynamic studies. J Hazard Mater 175:304–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.10.004
Bishnoi NR, Garima AP (2004) Biosorption of copper from aqueous solution using algal biomass. J Sci Ind Res India 63:813–816
Abdel-Aty AM, Ammar NS, Abdel Ghafar HH, Ali RK (2013) Biosorption of cadmium and lead from aqueous solution by fresh water alga Anabaena sphaerica biomass. J Adv Res 4:367–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2012.07.004
Ibrahim WM, Hassan AF, Azab YA (2016) Biosorption of toxic heavy metals from aqueous solution by Ulva lactuca activated carbon, Egypt. J Basic Appl Sci 3:241–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejbas.2016.07.005
Aksu Z, Dönmez G (2006) Binary biosorption of cadmium (II) and nickel(II) onto dried Chlorella vulgaris: Co-ion effect on mono-component isotherm parameters. Process Biochem 41:860–868. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2005.10.025
Sulaymon AH, Mohammed AA, Al-Musawi TJ (2013) Competitive biosorption of lead, cadmium, copper, and arsenic ions using algae. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:3011–3023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1208-2
Anastopoulos I, Kyzas GZ (2015) Progress in batch biosorption of heavy metals onto algae. J Mol Liq 209:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.05.023
Ding Y, Zhang S, Liu B, Zheng H, Chang C, Ekberg C (2019) Recovery of precious metals from electronic waste and spent catalysts: a review. Resour Conserv Recycl 141:284–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.10.041
Tunali M, Tunali MM, Yenigun O (2020) Characterization of different types of electronic waste: heavy metal, precious metal and rare earth element content by comparing different digestıon methods. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-020-01108-0
Chen W, Nie Z, Wang Z, Gong X, Sun B, Gao F, Liu Y (2018) Substance flow analysis of neodymium based on the generalized entropy in China. Resour Conserv Recycl 133:438–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.02.019
United Nations Sustainable Development Goals Web-site. https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/
Stein J (ed) (1980) Handbook of phycological methods. Culture methods and growth measurements. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 448
SOLIDS 2540 (2017) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (23rd ed). https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.2105/SMWW.2882.030
Mehta SK, Gaur JP (2001) Characterization and optimization of Ni and Cu sorption from aqueous solution by Chlorella vulgaris. Ecol Eng 18:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-8574(00)00174-9
El-Sheekh M, El Sabagh S, Abou El-Souod G, Elbeltagy A (2019) Biosorption of cadmium from aqueous solution by free and immobilized dry biomass of Chlorella vulgaris. Int J Environ Res 13:511–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-019-00190-z
Hosseinizand H, Sokhansanj S, Lim CJ (2018) Studying the drying mechanism of microalgae Chlorella vulgaris and the optimum drying temperature to preserve quality characteristics. Dry Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/07373937.2017.1369986
Volesky B (2003) Sorption and biosorption. BV Sorbex Inc., Montreal, p 316
Azizian S (2004) Kinetic models of sorption: a theoretical analysis. J Colloid Interface Sci 276:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.03.048
Bhattacharya AK, Venkobachar C (1984) Removal of cadmium (II) by low cost adsorption. J Env Eng (New York) 110:110–122. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(1984)110:1(110)
Langmuir I (1916) The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part. I: solids. J Am Chem Soc 38:2221–2295. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02254a006
Science Direct Freundlich Equation Web-Page. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/freundlich-equation
Sheng PX, Ting YP, Chen JP, Hong L (2004) Sorption of lead, copper, cadmium, zinc, and nickel by marine algal biomass: characterization of biosorptive capacity and investigation of mechanisms. J Colloid Interface Sci 275:131–141
Laurens LML, Wolfrum EJ (2011) Feasibility of spectroscopic characterization of algal lipids: chemometric correlation of NIR and FTIR spectra with exogenous lipids in algal biomass. Bioenergy Res 4:22–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-010-9098-y
Al-Homaidan AA, Al-Houri HJ, Al-Hazzani AA, Elgaaly G, Moubayed NMS (2014) Biosorption of copper ions from aqueous solutions by Spirulina platensis biomass. Arab J Chem 7:57–62
Ibrahim WM (2011) Biosorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by red macroalgae. J Hazard Mater 192:1827–1835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.07.019
Sari A, Mendil D, Tuzen M, Soylak M (2008) Biosorption of Cd(II) and Cr(III) from aqueous solution by moss (Hylocomium splendens) biomass: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem Eng J 144:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2007.12.020
Bishnoi NR, Garima AP (2004) Biosorption of copper from aqueous solution using algal biomass. J Sci Ind Res (India) 63:813–816
Alpat S, Alpat SK, Cadirci BH, Özbayrak Ö, Yasa I (2010) Effects of biosorption parameter: kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics for Ni(II) biosorption from aqueous solution by Circinella sp. Electron J Biotechnol 13:20. https://doi.org/10.2225/vol13-issue5-fulltext-20
Lau PS, Lee HY, Tsang CCK, Tam NFY, Wong YS (1999) Effect of metal interference, pH and temperature on Cu and Ni biosorption by Chlorella vulgaris and Chlorella miniata. Environ Technol 20:953–961. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593332008616890
El-Sikaily A, El Nemr A, Khaled A (2011) Copper sorption onto dried red alga Pterocladia capillacea and its activated carbon. Chem Eng J 168:707–714
Akbari M, Hallajisani A, Keshtkar AR, Shahbeig H, Ali Ghorbanian S (2015) Equilibrium and kinetic study and modeling of Cu(II) and Co(II) synergistic biosorption from Cu(II)-Co(II) single and binary mixtures on brown algae C. indica. J Environ Chem Eng 3:140–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2014.11.004
Kalak T, Dudczak-Hałabuda J, Tachibana Y, Cierpiszewski R (2020) Effective use of elderberry (Sambucus nigra) pomace in biosorption processes of Fe(III) ions. Chemosphere 246:125744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125744
Zaib M, Makshoof MM, Saeed A, Farooq U, Salman M, Makshoof MN (2016) Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic biosorption studies of Hg(II) on red algal biomass of Porphyridium cruentum. Green Chem Lett Rev 9:179–189. https://doi.org/10.1080/17518253.2016.1185166
Zou HX, Li N, Wang LH, Yu P, Yan XF (2014) Equilibrium and kinetic studies of Cd2+ biosorption by the brown algae Sargassum fusiforme. PLoS ONE 9(4):e95242. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0095242
Pirbazari AE, Saberikhah E, Badrouh M, Emami MS (2014) Alkali treated Foumanat tea waste as an efficient adsorbent for methylene blue adsorption from aqueous solution. Water Resour Ind 6:64–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wri.2014.07.003
Igwe JC, Abia AA (2007) Equilibrium sorption isotherm studies of Cd(II), Pb(II) and Zn(II) ions detoxification from waste water using unmodified and EDTA-modified maize husk. Electron J Biotechnol 10:536–548. https://doi.org/10.2225/vol10-issue4-fulltext-15
Dada AO, Olalekan AP, Olatunya A, Dada AO (2012) Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin-Radushkevich isotherms studies of equilibrium sorption of Zn2+ unto phosphoric acid modified rice husk. J Appl Chem 3:38–45. https://doi.org/10.9790/5736-0313845
Nishikawa E, Silva MGA, Vieira MGA (2018) Cadmium biosorption by alginate extraction waste and process overview in life cycle assessment context. J Clean Prod 178:166–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.025
Barquilha CER, Cossich ES, Tavares CRG, Silva EA (2017) Biosorption of nickel (II) and copper (II) ions in batch and fixed-bed columns by free and immobilized marine algae Sargassum sp. J Cleaner Prod 150:58–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.02.199
Ali RM, Hamad HA, Hussein MM, Malash GF (2016) Potential of using green adsorbent of heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions: adsorption kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic, mechanism and economic analysis. Ecol Eng 91:317–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.03.015
Ray L, Paul S, Bera D, Chattopadhyay P (2005) Bioaccumulation of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions by Bacillus cereus. J Haz Sub Res. https://doi.org/10.4148/1090-7025.1031
Donmez GC, Aksu Z, Öztürk A, Kutsal T (1999) A comparative study on heavy metal biosorption characteristics of some algae. Process Biochem 34:885–892
McKay G, Blair HS, Gardner JR (1982) Adsorption of dyes on chitin. I. Equilibrium studies. J Appl Polym Sci 27:3043–3057
Cheng J, Yin W, Chang Z, Lundholm N, Jiang Z (2017) Biosorption capacity and kinetics of cadmium(II) on live and dead Chlorella vulgaris. J Appl Phycol 29:211–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-016-0916-2
Abu Al-Rub FA, El-Naas MH, Benyahia F, Ashour I (2004) Biosorption of nickel on blank alginate beads, free and immobilized algal cells. Process Biochem 39:1767–1773. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2003.08.002
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Bogazici University Research Fund, Project No: 16Y00D7. The authors would like to thank Oleksiy Myronyuk from National Technical University of Ukraine “Igor Sikorsky Kyiv Polyechnic Institute,” Kyiv, Ukraine, for his support on FTIR interpretation and Filiz Ayılmaz from Boğaziçi University for her support on ICP-OES analysis. The authors also thank Uzoefuna Edwin Nnaemeka for his partial support in SEM Imaging.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tunali, M., Yenigun, O. Biosorption of Ag+ and Nd3+ from single- and multi-metal solutions (Ag+, Nd3+, and Au3+) by using living and dried microalgae. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 23, 764–777 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-020-01168-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-020-01168-2