Abstract
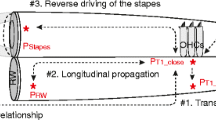
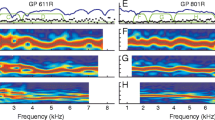
When driven at sound pressure levels greater than ~110 dB stimulus pressure level, the mammalian middle ear is known to produce subharmonic distortion. In this study, we simultaneously measured subharmonics in the ear canal pressure, intracochlear pressure, and basilar membrane or round window membrane velocity, in gerbil. Our primary objective was to quantify the relationship between the subharmonics measured in the ear canal and their intracochlear counterparts. We had two primary findings: (1) The subharmonics emerged suddenly, with a substantial amplitude in the ear canal and the cochlea; (2) at the stimulus level for which subharmonics emerged, the pressure in scala vestibuli/pressure in the ear canal amplitude relationship was similar for the subharmonic and fundamental components. These findings are important for experiments and clinical conditions in which high sound pressure level stimuli are used and could lead to confounding subharmonic stimulation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts JRM, Dirckx JJJ (2010) Nonlinearity in eardrum vibration as a function of frequency and sound pressure. Hear Res 263:26–32
Dallos PJ (1966a) On the generation of odd-fractional subharmonics. J Acoust Soc Am 40:1381–1391
Dallos PJ (1966b) Subharmonic squelch effect. J Acoust Soc Am 40:1264–1264
Dallos PJ, Linnell CO (1966a) Even-order subharmonics in the peripheral auditory system. J Acoust Soc Am 40:561–564
Dallos PJ, Linnell CO (1966b) Origin of subharmonics in the peripheral auditory system. J Acoust Soc Am 39:1252
Dallos PJ, Linnell CO (1966c) Subharmonic components in cochlear-microphonic potentials. J Acoust Soc Am 40:4–11
de La Rochefoucauld O, Olson ES (2010) A sum of simple and complex motions on the eardrum and manubrium in gerbil. Hear Res 263:9–15
de La Rochefoucauld O, Kachroo P, Olson ES (2010) Ossicular motion related to middle ear transmission delay in gerbil. Hear Res 270:158–172
Décory L, Franke RB, Dancer AL (1990) Measurement of the middle ear transfer function in cat, chinchilla and guinea pig. The mechanics and biophysics of hearing. Springer, Berlin, pp 270–277
Decraemer WF, Khanna SM, Funnell WRJ (1989) Interferometric measurement of the amplitude and phase of tympanic membrane vibrations in cat. Hear Res 38:1–17
Dong W, Olson ES (2006) Middle ear forward and reverse transmission in gerbil. J Neurophysiol 95:2951–2961
Dong W, Olson ES (2009) In vivo impedance of the gerbil cochlear partition at auditory frequencies. Biophys J 97:1233–1243
Eldredge DH (1951) Some responses of the ear to high frequency sound. Am Soc Exp Biol Fed Proc A 9:37
Fitch WT, Neubauer J, Herzel H (2002) Calls out of chaos: the adaptive significance of nonlinear phenomena in mammalian vocal production. Anim Behav 63:407–418
Funnell WRJ, Decraemer WF (1996) On the incorporation of moiré shape measurements in finite-element models of the cat eardrum. J Acoust Soc Am 100:925–932
Gea SLR, Decraemer WF, Funnell RWJ, Dirckx JJJ, Maier H (2010) Tympanic membrane boundary deformations derived from static displacements observed with computerized tomography in human and gerbil. JARO - J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 11:1–17
Guinan JJJ, Peake WT (1967) Middle-ear characteristics of anesthetized cats. J Acoust Soc Am 41:1237–1261
Huang S, Olson E (2011) Auditory nerve excitation via a non-traveling wave mode of basilar membrane motion. JARO—J Assoc Res Otolaryngol 12:559–575
Keilson SE, Teich MC, Khanna SM (1989a) Models of nonlinear vibration. I. Oscillator with bilinear resistance. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 467:241–248
K.eilson SE, Teich MC, Khanna SM (1989b) Models of nonlinear vibration. III. Oscillator with bilinear mass. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 467:257–264
Kobrak HG (1948) Construction material of the sound conduction system of the human ear. J Acoust Soc Am 20:125–130
Moore BCJ, Stone MA, Fullgrabe C, Glasberg BR, Puria S (2008) Spectro-temporal characteristics of speech at high frequencies, and the potential for restoration of audibility to people with mild-to-moderate hearing loss. Ear Hear 29:907–922
Olson ES (1998) Observing middle and inner ear mechanics with novel intracochlear pressure sensors. J Acoust Soc Am 103:3445–3463
Olson ES (2001) Intracochlear pressure measurements related to cochlear tuning. J Acoust Soc Am 110:349–367
Pong W, Marcaccio W (1963) Nonlinearity of the middle ear as a possible source of subharmonics. J Acoust Soc Am 35:679–681
Puria S (2003) Measurements of human middle ear forward and reverse acoustics: implications for otoacoustic emissions. J Acoust Soc Am 113:2773–2789
Rosowski JJ, Cheng JT, Ravicz ME, Hulli N, Hernandez-Montes M, Harrington E, Furlong C (2009) Computer-assisted time-averaged holograms of the motion of the surface of the mammalian tympanic membrane with sound stimuli of 0.4–25 kHz. Hear Res 253:83–96
Ruggero MA, Narayan SS, Temchin AN, Recio A (2000) Mechanical bases of frequency tuning and neural excitation at the base of the cochlea: Comparison of basilar-membrane vibrations and auditory-nerve-fiber responses in chinchilla. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:11744–11750
Slama MCC, Ravicz ME, Rosowski JJ (2010) Middle ear function and cochlear input impedance in chinchilla. J Acoust Soc Am 127:1397–1410
Suthers RA, Narins PM, Lin W-Y, Schnitzler H-U, Denzinger A, Xu C-H, Feng AS (2006) Voices of the dead: complex nonlinear vocal signals from the larynx of an ultrasonic frog. J Exp Biol 209:4984–4993
Teich MC, Keilson SE, Khanna SM (1989) Models of nonlinear vibration. II. Oscillator with bilinear stiffness. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 467:249–256
Teich M, Heneghan C, Khanna S, Flock Å, Ulfendahl M, Brundin L (1995) Investigating routes to chaos in the guinea-pig cochlea using the continuous wavelet transform and the short-time Fourier transform. Ann Biomed Eng 23:583–607
Thompson JMT, Stewart HB (2002) Nonlinear dynamics and chaos. Wiley, New York
Tonndorf J, Khanna SM (1972) Tympanic-membrane vibrations in human cadaver ears studied by time-averaged holography. J Acoust Soc Am 52:1221–1233
Usanov D, Mareev O, Skripal’ A, Mareev G, Kamyshanskiĭ A (2007) Acoustic pressure induced period-doubling bifurcations in tympanic membrane oscillations. Tech Phys Lett 33:939–940
von Gierke HE (1950) Subharmonics generated in human and animal ears by intense sound. J Acoust Soc Am 22:675–675
von Unge M, Decraemer WF, Bagger-Sjöbäck D, Dirckx JJ (1993) Displacement of the gerbil tympanic membrane under static pressure variations measured with a real-time differential moire interferometer. Hear Res 70:229–242
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the reviewers and JARO editor for their constructive comments and to Willem F. Decraemer for contributing to the discussion on asymmetric stiffness. These studies were supported by a grant from the NIDCD.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, S., Dong, W. & Olson, E.S. Subharmonic Distortion in Ear Canal Pressure and Intracochlear Pressure and Motion. JARO 13, 461–471 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10162-012-0326-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10162-012-0326-3