Abstract
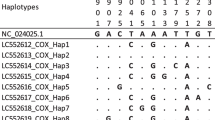
The New World screwworm (NWS) Cochliomyia hominivorax (Coquerel) is one of the major myiasis-causing flies that injures livestock and leads to losses of ~US$ 2.7 billions/year in the Neotropics. Ivermectin (IVM), a macrocyclic lactone (ML), is the most used preventive insecticide for this parasite and targets the glutamate-gated chloride (GLUCLα) channels. Several authors have associated altered GluClα homologues to MLs resistance in invertebrates, although studies about resistance in NWS are limited to other genes. Here, we aimed to characterise the NWS GluClα (ChGluClα) cDNA and to search for alterations associated with IVM resistance in NWS larvae from a bioassay. The open reading frame of the ChGluClα comprised 1,359 bp and encoded a sequence of 452 amino acids. The ChGluClα cDNAs of the bioassay larvae showed different sequences that could be splice variants, which agree with the occurrence of alternative splicing in GluClα homologues. In addition, we found cDNAs with premature stop codons and the K242R SNP, which occurred more frequently in the surviving larvae and was located close to mutation (L256F) involved in ML resistance. Although these alterations were in low frequency, the ChGluClα sequencing will allow further studies to find alterations in the gene of resistant natural populations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215(3):403–410
Bartos M, Corradi J, Bouzat C (2009) Structural basis of activation of cys-loop receptors: the extracellular-transmembrane interface as a coupling region. Mol Neurobiol 40(3):236–252
Baxter SW, Chen M, Dawson A, Zhao JZ, Vogel H, Shelton AM et al (2010) Mis-spliced transcripts of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha6 are associated with field evolved spinosad resistance in Plutella xylostella (L.). PLoS Genet. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000802
Carvalho RA, Azeredo-Espin AM, Torres TT (2010) Deep sequencing of New World screw-worm transcripts to discover genes involved in insecticide resistance. BMC Genom. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-11-695
Cascio M (2006) Modulating inhibitory ligand-gated ion channels. AAPS J 8(2):E353–E361
Cederholm JM, Schofield PR, Lewis TM (2009) Gating mechanisms in Cys-loop receptors. Eur Biophys J 39(1):37–49
Cleland TA (1996) Inhibitory glutamate receptor channels. Mol Neurobiol 13(2):97–136
Cully DF, Vassilatis DK, Liu KK, Paress PS, Van der Ploeg LH, Schaeffer JM et al (1994) Cloning of an avermectin-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channel from Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 371(6499):707–711
Dent JA, Smith MM, Vassilatis DK, Avery L (2000) The genetics of ivermectin resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(6):2674–2679
Dermauw W, Ilias A, Riga M, Tsagkarakou A, Grbic M, Tirry L et al (2012) The cys-loop ligand-gated ion channel gene family of Tetranychus urticae: implications for acaricide toxicology and a novel mutation associated with abamectin resistance. Insect Biochem Mol 42(7):455–465
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hall M, Wall R (1995) Myiasis of humans and domestic animals. Adv Parasit 35:257–334
Hibbs RE, Gouaux E (2011) Principles of activation and permeation in an anion-selective Cys-loop receptor. Nature 474(7349):54–60
Hsu J-C, Feng H-T, Wu W-J, Geib SM, Mao C-H, Vontas J (2012) Truncated transcripts of nicotinic acetylcholine subunit gene Bdα6 are associated with spinosad resistance in Bactrocera dorsalis. Insect Biochem Mol 42(10):806–815
Huang X, Madan A (1999) CAP3: A DNA sequence assembly program. Genome Res 9(9):868–877
Jensen ML, Schousboe A, Ahring PK (2005) Charge selectivity of the Cys-loop family of ligand-gated ion channels. J Neurochem 92:217–225
Jones AK, Sattelle DB (2006) The cys-loop ligand-gated ion channel superfamily of the honeybee, Apis mellifera. Invertebr Neurosci 6(3):123–132
Jones AK, Sattelle DB (2007) The cys-loop ligand-gated ion channel gene superfamily of the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. BMC Genomics. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-8-327
Jones AK, Bera AN, Lees K, Sattelle DB (2010) The cys-loop ligand-gated ion channel gene superfamily of the parasitoid wasp, Nasonia vitripennis. Heredity 104(3):247–259
Kane NS, Hirschberg B, Qian S, Hunt D, Thomas B, Brochu R et al (2000) Drug-resistant Drosophila indicate glutamate-gated chloride channels are targets for the antiparasitics nodulisporic acid and ivermectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(25):13949–13954
Knipple DC, Soderlund DM (2010) The ligand-gated chloride channel gene family of Drosophila melanogaster. Pestic Biochem Phys 97(2):140–148
Kwon DH, Yoon KS, Clark JM, Lee SH (2010) A point mutation in a glutamate-gated chloride channel confers abamectin resistance in the two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae Koch. Insect Mol Biol 19(4):583–591
Lee WY, Free CR, Sine SM (2009) Binding to gating transduction in nicotinic receptors: Cys-loop energetically couples to pre-M1 and M2-M3 regions. J Neurosci 29(10):3189–3199
Marygold SJ, Leyland PC, Seal RL, Goodman JL, Thurmond J, Strelets VB et al (2013) FlyBase: improvements to the bibliography. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D751–D757
McCavera S, Rogers AT, Yates DM, Woods DJ, Wolstenholme AJ (2009) An ivermectin-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channel from the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus. Mol Pharmacol 75(6):1347–1355
Njue AI, Hayashi J, Kinne L, Feng XP, Prichard RK (2004) Mutations in the extracellular domains of glutamate-gated chloride channel alpha3 and beta subunits from ivermectin-resistant Cooperia oncophora affect agonist sensitivity. J Neurochem 89(5):1137–1147
Omura S, Crump A (2004) The life and times of ivermectin—a success story. Nat Rev Microbiol 2(12):984–989
Ortells MO, Lunt GG (1995) Evolutionary history of the ligand-gated ion-channel superfamily of receptors. Trends Neurosci 18(3):121–127
Petersen TN, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2011) SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat Methods 8(10):785–786
Pierleoni A, Indio V, Savojardo C, Fariselli P, Martelli PL, Casadio R (2011) MemPype: a pipeline for the annotation of eukaryotic membrane proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 39:W375–W380
Rice P, Longden I, Bleasby A (2000) EMBOSS: the European molecular biology open software suite. Trends Genet 16(6):276–277
Robertson JL (2007) Bioassays with arthropods. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Robertson JL, Smith KC, Savin NE, Lavigne RJ (1984) Effects of dose selection and sample size on the precision of lethal dose estimates in dose-mortality regression. J Econ Entomol 77:833–837
Semenov EP, Pak WL (1999) Diversification of Drosophila chloride channel gene by multiple posttranscriptional mRNA modifications. J Neurochem 72(1):66–72
Sigrist CJ, Cerutti L, de Castro E, Langendijk-Genevaux PS, Bulliard V, Bairoch A et al (2010) PROSITE, a protein domain database for functional characterization and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res 38:D161–D166
Sine SM, Engel AG (2006) Recent advances in Cys-loop receptor structure and function. Nature 440(7083):448–455
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25(24):4876–4882
Vargas ME, Espin AM (1995) Genetic variability in mitochondrial DNA of the screwworm, Cochliomyia hominivorax (Diptera: Calliphoridae) from Brazil. Biochem Genet 33(7–8):237–256
Vargas-Terán M, Hofmann HC, Tweddle NE (2005) Impact of screwworm eradication programmes using the sterile insect technique. In: Dyck VA, Hendrichs J, Robinson AS (eds) Sterile insect technique. Springer, Netherlands, pp 629–650
Watson GB, Chouinard SW, Cook KR, Geng C, Gifford JM, Gustafson GD et al (2010) A spinosyn-sensitive Drosophila melanogaster nicotinic acetylcholine receptor identified through chemically induced target site resistance, resistance gene identification, and heterologous expression. Insect Biochem Mol 40(5):376–384
Welch J, Hall MJR (2008) New World screwworm (Cochliomyia hominivorax) and Old World screwworm (Chrysomya bezziana). In: OIE Biological Standards Commission (ed) Manual of diagnostic tests and vaccines for terrestrial animals. World Organisation for Animal Health, Paris, pp 265–275
Wilkins MR, Gasteiger E, Bairoch A, Sanchez JC, Williams KL, Appel RD et al (1999) Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. In: Link AJ (ed) 2-D proteome analysis protocols. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 531–552
Wolstenholme AJ, Rogers AT (2005) Glutamate-gated chloride channels and the mode of action of the avermectin/milbemycin anthelmintics. Parasitology 131:S85–S95
Yamaguchi M, Sawa Y, Matsuda K, Ozoe F, Ozoe Y (2012) Amino acid residues of both the extracellular and transmembrane domains influence binding of the antiparasitic agent milbemycin to Haemonchus contortus AVR-14B glutamate-gated chloride channels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 419(3):562–566
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by Grants from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (# 2011/01030-5). We would like to thank Rosângela Rodrigues for the technical assistance and Salete Couto Campos for the help with the bioassay and NWS strain maintenance. We are grateful to Dr. Thiago Mastrângelo for advices in preparing the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lopes, A.M.M., de Carvalho, R.A. & de Azeredo-Espin, A.M.L. Glutamate-gated chloride channel subunit cDNA sequencing of Cochliomyia hominivorax (Diptera: Calliphoridae): cDNA variants and polymorphisms. Invert Neurosci 14, 137–146 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10158-014-0172-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10158-014-0172-6