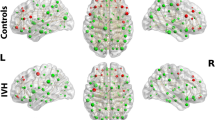
Abstract
Optimizing the treatment of hydrocephalus remains a major challenge in adult and pediatric neurosurgery. Currently, clinical treatment relies heavily on anatomic imaging of ventricular size and clinical presentation. The emergence of functional and structural brain connectivity imaging has provided the basis for a new paradigm in the management of hydrocephalus. Here we review the pertinent advances in this field. Following PRISMA-ScR guidelines for scoping reviews, we searched PubMed for relevant literature from 1994 to April 2023 using hydrocephalus and MRI-related terms. Included articles reported original MRI data on human subjects with hydrocephalus, while excluding non-English or pre-1994 publications that didn't match the study framework. The review identified 44 studies that investigated functional and/or structural connectivity using various MRI techniques across different hydrocephalus populations. While there is significant heterogeneity in imaging technology and connectivity analysis, there is broad consensus in the literature that 1) hydrocephalus is associated with disruption of functional and structural connectivity, 2) this disruption in cerebral connectivity can be further associated with neurologic compromise 3) timely treatment of hydrocephalus restores both cerebral connectivity and neurologic compromise. The robustness and consistency of these findings vary as a function of patient age, hydrocephalus etiology, and the connectivity region of interest studied. Functional and structural brain connectivity imaging shows potential as an imaging biomarker that may facilitate optimization of hydrocephalus treatment. Future research should focus on standardizing regions of interest as well as identifying connectivity analysis most pertinent to clinical outcome.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Adam R, Ghahari D, Morton JB, Eagleson R, de Ribaupierre S (2022) Brain network connectivity and executive function in children with infantile hydrocephalus. Brain Connect 12:784–798
Air EL, Yuan W, Holland SK, Jones BV, Bierbrauer K, Altaye M, Mangano FT (2010) Longitudinal comparison of pre- and postoperative diffusion tensor imaging parameters in young children with hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg Pediatr 5:385–391
Akbari SHA, Limbrick DD Jr, McKinstry RC, Altaye M, Ragan DK, Yuan W, Mangano FT, Holland SK, Shimony JS (2015) Periventricular hyperintensity in children with hydrocephalus. Pediatr Radiol 45:1189–1197
Assaf Y, Ben-Sira L, Constantini S, Chang LC, Beni-Adani L (2006) Diffusion tensor imaging in hydrocephalus: initial experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1717–1724
Babaeeghazvini P, Rueda-Delgado LM, Gooijers J, Swinnen SP, Daffertshofer A (2021) Brain structural and functional connectivity: a review of combined works of diffusion magnetic resonance imaging and electro-encephalography. Front Hum Neurosci 15:721206
Balédent O, Capel C, Metanbou S, Bouzerar R (2021) Diffusion and flow MR imaging to investigate hydrocephalus patients before and after endoscopic third ventriculostomy. Acta Neurochir Suppl 131:303–306
Bastos AM, Schoffelen J-M (2015) A tutorial review of functional connectivity analysis methods and their interpretational pitfalls. Front Syst Neurosci 9:175
Ben-Sira L, Goder N, Bassan H, Lifshits S, Assaf Y, Constantini S (2015) Clinical benefits of diffusion tensor imaging in hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg Pediatr 16:195–202
Bir SC, Patra DP, Maiti TK, Sun H, Guthikonda B, Notarianni C, Nanda A (2016) Epidemiology of adult-onset hydrocephalus: institutional experience with 2001 patients. Neurosurg Focus 41:E5
Buckley RT, Yuan W, Mangano FT, Phillips JM, Powell S, McKinstry RC, Rajagopal A, Jones BV, Holland S, Limbrick DD Jr (2012) Longitudinal comparison of diffusion tensor imaging parameters and neuropsychological measures following endoscopic third ventriculostomy for hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg Pediatr 9:630–635
Caligiuri ME, Quattrone A, Mechelli A, La Torre D, Quattrone A (2022) Semi-automated assessment of the principal diffusion direction in the corpus callosum: differentiation of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus from neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurol 269:1978–1988
Fabbro S, Piccolo D, Vescovi MC, Bagatto D, Tereshko Y, Belgrado E, Maieron M, De Colle MC, Skrap M, Tuniz F (2023) Resting-state functional-MRI in iNPH: can default mode and motor networks changes improve patient selection and outcome? Preliminary report. Fluids Barriers CNS 20:7
Froudist-Walsh S, Karolis V, Caldinelli C, Brittain PJ, Kroll J, Rodríguez-Toscano E, Tesse M, Colquhoun M, Howes O, Dell’Acqua F, Thiebaut de Schotten M, Murray RM, Williams SCR, Nosarti C (2015) Very early brain damage leads to remodeling of the working memory system in adulthood: a combined fMRI/Tractography study. J Neurosci 35:15787–15799
Fukuhara T, Luciano MG, Liu JZ, Yue GH (2001) Functional magnetic resonance imaging before and after ventriculoperitoneal shunting for hydrocephalus–case report. Neurol Med Chir 41:626–630
Ghaffari-Rafi A, Mehdizadeh R, Ghaffari-Rafi S, Leon-Rojas J (2020) Inpatient diagnoses of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus in the United States: demographic and socioeconomic disparities. J Neurol Sci 418:117152
Griffa A, Bommarito G, Assal F, Herrmann FR, Van De Ville D, Allali G (2020) Dynamic functional networks in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: alterations and reversibility by CSF tap test. Hum Brain Mapp 42:1485–1502
Huang W, Fang X, Li S, Mao R, Ye C, Liu W, Deng Y, Lin G (2024) Abnormal characteristic static and dynamic functional network connectivity in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. CNS Neurosci Ther 30(3):e14178
Huang W, Fang X, Li S, Mao R, Ye C, Liu W, Lin G (2021) Preliminary exploration of the sequence of nerve fiber bundles involvement for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a correlation analysis using diffusion tensor imaging. Front Neurosci 15:794046
Isaacs AM, Riva-Cambrin J, Yavin D, Hockley A, Pringsheim TM, Jette N, Lethebe BC, Lowerison M, Dronyk J, Hamilton MG (2018) Age-specific global epidemiology of hydrocephalus: Systematic review, metanalysis and global birth surveillance. PLoS ONE 13:e0204926
Isaacs AM, Smyser CD, Lean RE, Alexopoulos D, Han RH, Neil JJ, Zimbalist SA, Rogers CE, Yan Y, Shimony JS, Limbrick DD Jr (2019) MR diffusion changes in the perimeter of the lateral ventricles demonstrate periventricular injury in post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus of prematurity. Neuroimage Clin 24:102031
Jang SH, Chang CH, Jung YJ, Lee HD (2017) Recovery of akinetic mutism and injured prefronto-caudate tract following shunt operation for hydrocephalus and rehabilitation: a case report. Medicine 96:e9117
Jang S, Lee H (2018) Change of ascending reticular activating system following shunt operation for hydrocephalus in a subarachnoid hemorrhage patient. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg 80:62–66
Kahle KT, Kulkarni AV, Limbrick DD Jr, Warf BC (2015) Hydrocephalus in children. Lancet 387:788–799
Kalpakidou AK, Allin MPG, Walshe M, Giampietro V, McGuire PK, Rifkin L, Murray RM, Nosarti C (2014) Functional neuroanatomy of executive function after neonatal brain injury in adults who were born very preterm. PLoS ONE 9:e113975
Kanno S, Ogawa K-I, Kikuchi H, Toyoshima M, Abe N, Sato K, Miyazawa K, Oshima R, Ohtomo S, Arai H, Shibuya S, Suzuki K (2021) Reduced default mode network connectivity relative to white matter integrity is associated with poor cognitive outcomes in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. BMC Neurol 21:353
Keong NC, Lock C, Soon S, Hernowo AT, Czosnyka Z, Czosnyka M, Pickard JD, Narayanan V (2022) Diffusion tensor imaging profiles can distinguish diffusivity and neural properties of white matter injury in hydrocephalus vs. non-hydrocephalus using a strategy of a periodic table of DTI elements. Front Neurol 13:868026
Kestle JR (2003) Pediatric hydrocephalus: current management. Neurol Clin 21:883–95.vii
Khoo HM, Kishima H, Tani N, Oshino S, Maruo T, Hosomi K, Yanagisawa T, Kazui H, Watanabe Y, Shimokawa T, Aso T, Kawaguchi A, Yamashita F, Saitoh Y, Yoshimine T (2015) Default mode network connectivity in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg 124:350–358
Kulesz PA, Ware AL, Orkisz JS, Williams VJ, Juranek J, Fletcher JM (2019) Are primary and secondary types of brain anomalies exclusive factors affecting the attention networks in individuals with spina bifida? Neuropsychology 33:1057–1064
Kulkarni AV, Donnelly R, Mabbott DJ, Widjaja E (2015) Relationship between ventricular size, white matter injury, and neurocognition in children with stable, treated hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg Pediatr 16:267–274
Lean RE, Han RH, Smyser TA, Kenley JK, Shimony JS, Rogers CE, Limbrick DD Jr, Smyser CD (2019) Altered neonatal white and gray matter microstructure is associated with neurodevelopmental impairments in very preterm infants with high-grade brain injury. Pediatr Res 86:365–374
Lenfeldt N, Larsson A, Nyberg L, Andersson M, Birgander R, Eklund A, Malm J (2008) Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: increased supplementary motor activity accounts for improvement after CSF drainage. Brain 131:2904–2912
Lenfeldt N, Larsson A, Nyberg L, Birgander R, Eklund A, Malm J (2011) Diffusion tensor imaging reveals supplementary lesions to frontal white matter in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 68:1586–1593 (discussion 1593)
Li Y, Zhao C, Tan Z, Wang Y, Zhang H, Wang J, Guo H, Zeng B, Huang W (2015) Longitudinal changes in the brain following third ventriculostomy in a child with hydrocephalus: a case report. Medicine 94:e2095
Lockwood Estrin G, Kyriakopoulou V, Makropoulos A, Ball G, Kuhendran L, Chew A, Hagberg B, Martinez-Biarge M, Allsop J, Fox M, Counsell SJ, Rutherford MA (2016) Altered white matter and cortical structure in neonates with antenatally diagnosed isolated ventriculomegaly. Neuroimage Clin 11:139–148
Mangano FT, Altaye M, McKinstry RC, Shimony JS, Powell SK, Phillips JM, Barnard H, Limbrick DD Jr, Holland SK, Jones BV, Dodd J, Simpson S, Mercer D, Rajagopal A, Bidwell S, Yuan W (2016) Diffusion tensor imaging study of pediatric patients with congenital hydrocephalus: 1-year postsurgical outcomes. J Neurosurg Pediatr 18:306–319
Mangano FT, Stevenson CB, Nagaraj U, Conley A, Yuan W (2019) Abnormal anisotropic diffusion properties in pediatric myelomeningocele patients treated with fetal surgery: an initial DTI study. Childs Nerv Syst 36:827–833
Marumoto K, Koyama T, Hosomi M, Kodama N, Miyake H, Domen K (2012) Diffusion tensor imaging in elderly patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus or Parkinson’s disease: diagnosis of gait abnormalities. Fluids Barriers CNS 9:20
Ogata Y, Ozaki A, Ota M, Oka Y, Nishida N, Tabu H, Sato N, Hanakawa T (2017) Interhemispheric resting-state functional connectivity predicts severity of idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Front Neurosci 11:470
Ou X, Snow JH, Byerley AK, Hall JJ, Glasier CM (2011) Decreased activation and increased lateralization in brain functioning for selective attention and response inhibition in adolescents with spina bifida. Child Neuropsychol 19:23–36
Park C-H, Ryu H, Kim C-H, Joa K-L, Kim M-O, Jung H-Y (2020) Injury of corticospinal tract in a patient with subarachnoid hemorrhage as determined by diffusion tensor tractography: a case report. Brain Sci 10(3):177
Smyser CD, Snyder AZ, Shimony JS, Blazey TM, Inder TE, Neil JJ (2013) Effects of white matter injury on resting state fMRI measures in prematurely born infants. PLoS ONE 8:e68098
Tallus J, Mohammadian M, Kurki T, Roine T, Posti JP, Tenovuo O (2023) A comparison of diffusion tensor imaging tractography and constrained spherical deconvolution with automatic segmentation in traumatic brain injury. Neuroimage Clin 37:103284
Tang Y, Yuan X, Duan J, Zhang X, Chen J, Zhou Y, Song F, Zhou D (2021) White matter characteristics of cognitive impairment in tap-test positive idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a diffusion tensor tract-based spatial study. Front Neurosci 15:774638
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, Moher D, Peters MDJ, Horsley T, Weeks L, Hempel S, Akl EA, Chang C, McGowan J, Stewart L, Hartling L, Aldcroft A, Wilson MG, Garritty C, Lewin S, Godfrey CM, Macdonald MT, Langlois EV, Soares-Weiser K, Moriarty J, Clifford T, Tunçalp Ö, Straus SE (2018) PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med 169:467–473
Wright Z, Larrew TW, Eskandari R (2016) Pediatric hydrocephalus: current state of diagnosis and treatment. Pediatr Rev 37:478–490
Yang X, Li H, He W, Lv M, Zhang H, Zhou X, Wei H, Xu B, Chen J, Ma H, Xia J, Yang G (2022) Quantification of changes in white matter tract fibers in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus based on diffusion spectrum imaging. Eur J Radiol 149:110194
Yuan W, Holland SK, Shimony JS, Altaye M, Mangano FT, Limbrick DD, Jones BV, Nash T, Rajagopal A, Simpson S, Ragan D, McKinstry RC (2015) Abnormal structural connectivity in the brain networks of children with hydrocephalus. Neuroimage Clin 8:483–492
Yuan W, Mangano FT, Air EL, Holland SK, Jones BV, Altaye M, Bierbrauer K (2009) Anisotropic diffusion properties in infants with hydrocephalus: a diffusion tensor imaging study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1792–1798
Yuan W, McKinstry RC, Shimony JS, Altaye M, Powell SK, Phillips JM, Limbrick DD Jr, Holland SK, Jones BV, Rajagopal A, Simpson S, Mercer D, Mangano FT (2012) Diffusion tensor imaging properties and neurobehavioral outcomes in children with hydrocephalus. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 34:439–445
Yuan W, Stevenson CB, Altaye M, Jones BV, Leach J, Lovha M, Rennert N, Mangano FT (2021) Diffusion tensor imaging in children following prenatal myelomeningocele repair and its predictive value for the need and timing of subsequent CSF diversion surgery for hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg Pediatr 27(4):391–399
Zhang H, He W-J, Liang L-H, Zhang H-W, Zhang X-J, Zeng L, Luo S-P, Lin F, Lei Y (2021) Diffusion spectrum imaging of corticospinal tracts in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Front Neurol 12:636518
Zhao C, Li Y, Cao W, Xiang K, Zhang H, Yang J, Gan Y (2016) Diffusion tensor imaging detects early brain microstructure changes before and after ventriculoperitoneal shunt in children with high intracranial pressure hydrocephalus. Medicine 95:e5063
Zhao S-X, Xiao Y-H, Lv F-R, Zhang Z-W, Sheng B, Ma H-L (2017) Lateral ventricular volume measurement by 3D MR hydrography in fetal ventriculomegaly and normal lateral ventricles. J Magn Reson Imaging 48:266–273
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the Masonic Institute of the Developing Brain for the ongoing support in pediatric connectivity studies.
Funding
There were no funding sources for this scoping review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
IPP, CSG made substantial contributions to the conception an design of the work, IPP, CSG, EF, RAM, CCC participated in the acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data; IPP, CSG, RAM, CCC drafted the work and revised it critically for important intellectual content; IPP, CSG, EF, RAM, CCC approved the version to be published and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Peña Pino, I., Fellows, E., McGovern, R.A. et al. Structural and functional connectivity in hydrocephalus: a scoping review. Neurosurg Rev 47, 201 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-024-02430-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-024-02430-z