Abstract
Background
Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is characterized by jolts of pain along the distribution of the trigeminal nerve. If patients fail conservative management, microvascular decompression (MVD) is the next step in treatment. MVD is largely done by placing implant pads between the nerve and compressing vessels. We conducted a literature review to assess effectiveness and safety of Teflon™ and Ivalon® sponges for treatment of TN with MVD.
Methods
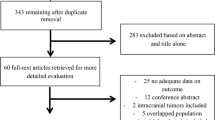
In January 2019, PubMed was searched for manuscripts published in English using permutations of “Microvascular decompression”, “Teflon”, “Ivalon”, “Granuloma”, “Polytetrafluoroethylene”, “Trigeminal Neuralgia”, and “Exploration”. Success and relapse rates, causes of relapse, and complication rates were analyzed. We analyzed for relationships with ANCOVA at an alpha threshold of .05.
Results
Thirty-six studies representing 4273 patients fit inclusion criteria. Twenty-five dealt with initial MVD, 12 with re-do MVD. Initial MVD initial success rates were 85% in patients receiving Teflon™ (57–100%*) and 91% in patients receiving Ivalon® (79–100%*). Recurrence rates were 12% in Teflon™ patients (0*–30%) and 9.1% in Ivalon® patients (0*–19%). In patients with relapses, implants were the cause in 49% of Teflon™ patients (0*–100%*) and 50% of Ivalon® patients (0*–100%*). Complication rates for patients receiving Teflon™ were 12% (0*–34%) and 19% for patients receiving Ivalon® (0*–40%).
Conclusion
Teflon™ and Ivalon® are two materials used in MVD for TN. It is an effective treatment with long-term symptom relief and recurrence rates of 1–5% each year. Ivalon® has been used less than Teflon™ though is associated with similar success rates and similar complication rates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apfelbaum RI (1983) Surgery for tic douloureux. Clin Neurosurg 31:351–368
Arksey H, O'Malley L (2005) Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. Int J Soc Res Methodol 8:19–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/1364557032000119616
Ashkan K, Marsh H (2004) Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia in the elderly: a review of the safety and efficacy. Neurosurgery 55:840–848 discussion 848-850
Barker FG 2nd, Jannetta PJ, Bissonette DJ, Larkins MV, Jho HD (1996) The long-term outcome of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. N Engl J Med 334:1077–1083. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199604253341701
Bishnoi I, Singh D, Bishnoi S, Mewada T, Sachdeva D, Mittal A, Odugora SH (2018) Ring graft technique for microvascular decompression. Neurol India 66:1687–1691. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.246282
Bond AE, Zada G, Gonzalez AA, Hansen C, Giannotta SL (2010) Operative strategies for minimizing hearing loss and other major complications associated with microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. World Neurosurg 74:172–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2010.05.001
Broggi G, Ferroli P, Franzini A, Servello D, Dones I (2000) Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia: comments on a series of 250 cases, including 10 patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 68:59–64
Burchiel KJ, Clarke H, Haglund M, Loeser JD (1988) Long-term efficacy of microvascular decompression in trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 69:35–38. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1988.69.1.0035
Capelle HH, Brandis A, Tschan CA, Krauss JK (2010) Treatment of recurrent trigeminal neuralgia due to Teflon granuloma. J Headache Pain 11:339–344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10194-010-0213-4
Chen J, Lee S, Lui T, Yeh Y, Chen T, Tzaan W (2000) Teflon granuloma after microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Surg Neurol 53:281–287
Cho DY, Chang CG, Wang YC, Wang FH, Shen CC, Yang DY (1994) Repeat operations in failed microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery 35:665–669 discussion 669-670
Eldridge PR, Sinha AK, Javadpour M, Littlechild P, Varma TR (2003) Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia in patients with multiple sclerosis. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 81:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1159/000075105
El-Garem HF, Badr-El-Dine M, Talaat AM, Magnan J (2002) Endoscopy as a tool in minimally invasive trigeminal neuralgia surgery. Otology & neurotology : official publication of the American Otological Society. American Neurotology Society [and] European Academy of Otology and Neurotology 23:132–135
El-Ghandour NM (2010) Microvascular decompression in the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia caused by vertebrobasilar ectasia. Neurosurgery 67:330–337. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.Neu.0000371978.86528.60
Feng BH, Zheng XS, Liu M, Wang XQ, Wang XH, Ying TT, Li ST (2015) Microvascular Decompression for Trigeminal Neuralgia: Zone Exploration and Decompression Techniques. J Craniofac Surg 26:2381–2384. https://doi.org/10.1097/scs.0000000000002147
Feng BH, Wang XH, Li ST (2018) Posterior Fossa Re-Exploration for Recurrent Trigeminal Neuralgia: Operative Findings and Surgical Techniques. J Craniofac Surg 29:1284–1286. https://doi.org/10.1097/scs.0000000000004576
Goya T, Wakisaka S, Kinoshita K (1990) Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia with special reference to delayed recurrence. Neurol Med Chir 30:462–467
Gu W, Zhao W (2014) Microvascular decompression for recurrent trigeminal neuralgia. Journal of clinical neuroscience : official journal of the Neurosurgical Society of Australasia 21:1549–1553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2013.11.042
Jannetta PJ (1967) Arterial compression of the trigeminal nerve at the pons in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. J Neurosurg 26(Suppl):159–162. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1967.26.1part2.0159
Jannetta PJ, Bissonette DJ (1985) Management of the failed patient with trigeminal neuralgia. Clin Neurosurg 32:334–347
Jiao Y, Yan Z, Che S, Wang C, Wang J, Wang X, Wang H, Qi W, Feng Y (2018) Improved Microvascular Decompression in Treating Trigeminal Neuralgia: Application of Nest-Shaped Teflon Fibers. World Neurosurg 110:e1–e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.09.138
Kabatas S, Karasu A, Civelek E, Sabanci AP, Hepgul KT, Teng YD (2009) Microvascular decompression as a surgical management for trigeminal neuralgia: long-term follow-up and review of the literature. Neurosurg Rev 32:87–93; discussion 93-84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-008-0171-3
Katusic S, Williams DB, Beard CM, Bergstralh EJ, Kurland LT (1991) Epidemiology and clinical features of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia and glossopharyngeal neuralgia: similarities and differences, Rochester, Minnesota, 1945-1984. Neuroepidemiology 10:276–281. https://doi.org/10.1159/000110284
Li ST, Pan Q, Liu N, Shen F, Liu Z, Guan Y (2004) Trigeminal neuralgia: what are the important factors for good operative outcomes with microvascular decompression. Surg Neurol 62:400–404; discussion 404-405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2004.02.028
Liao JJ, Cheng WC, Chang CN, Yang JT, Wei KC, Hsu YH, Lin TK (1997) Reoperation for recurrent trigeminal neuralgia after microvascular decompression. Surg Neurol 47:562–568 discussion 568-570
Matsushima T, Yamaguchi T, Inoue TK, Matsukado K, Fukui M (2000) Recurrent trigeminal neuralgia after microvascular decompression using an interposing technique. Teflon felt adhesion and the sling retraction technique. Acta Neurochir 142:557–561
Oiwa Y, Nakai K, Takayama M, Naka D, Itakura T (2004) Microvascular decompression of cranial nerves using sheets of a dural substitute--technical note. Neurol Med Chir 44:94–100 discussion 100-101
Premsagar IC, Moss T, Coakham HB (1997) Teflon-induced granuloma following treatment of trigeminal neuralgia by microvascular decompression. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg 87:454–457. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1997.87.3.0454
Rath SA, Klein HJ, Richter HP (1996) Findings and long-term results of subsequent operations after failed microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery 39:933–938 discussion 938-940
Revuelta-Gutierrez R, Lopez-Gonzalez MA, Soto-Hernandez JL (2006) Surgical treatment of trigeminal neuralgia without vascular compression: 20 years of experience. Surg Neurol 66:32–36; discussion 36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2005.10.018
Sandell T, Eide PK (2008) Effect of microvascular decompression in trigeminal neuralgia patients with or without constant pain. Neurosurgery 63:93–99; discussion 99-100. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.Neu.0000335075.16858.Ef
Sekula RF Jr, Frederickson AM, Jannetta PJ, Quigley MR, Aziz KM, Arnone GD (2011) Microvascular decompression for elderly patients with trigeminal neuralgia: a prospective study and systematic review with meta-analysis. J Neurosurg 114:172–179. https://doi.org/10.3171/2010.6.Jns10142
Sindou M, Leston J, Howeidy T, Decullier E, Chapuis F (2006) Micro-vascular decompression for primary Trigeminal Neuralgia (typical or atypical). Long-term effectiveness on pain; prospective study with survival analysis in a consecutive series of 362 patients. Acta Neurochir 148:1235–1245; discussion 1245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-006-0809-2
Siwawetpikul P, Leing-Udom A (2016) A "Reposition Technique" Microvascular Decompression in Trigeminal Neuralgia: Clinical Outcomes and Complications. J Med Assoc Thai = Chotmaihet thangphaet 99(Suppl 3):S39–S46
Ugwuanyi UC, Kitchen ND (2010) The operative findings in re-do microvascular decompression for recurrent trigeminal neuralgia. Br J Neurosurg 24:26–30. https://doi.org/10.3109/02688690903507489
Wu M, Fu X, Ji Y, Ding W, Deng D, Wang Y, Jiang X, Niu C (2018) Microvascular Decompression for Classical Trigeminal Neuralgia Caused by Venous Compression: Novel Anatomic Classifications and Surgical Strategy. World Neurosurg 113:e707–e713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.02.130
Yang DB, Jiang DY, Chen HC, Wang ZM (2015) Second microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia in recurrent cases after microvascular decompression. J Craniofac Surg 26:491–494. https://doi.org/10.1097/scs.0000000000001523
Zheng X, Feng B, Hong W, Zhang W, Yang M, Tang Y, Zhong J, Hua X, Li S (2012) Management of intraneural vessels during microvascular decompression surgery for trigeminal neuralgia. World Neurosurg 77:771–774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2011.08.031
Zhong J, Li ST, Zhu J, Guan HX, Zhou QM, Jiao W, Ying TT, Yang XS, Zhan WC, Hua XM (2012) A clinical analysis on microvascular decompression surgery in a series of 3000 cases. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 114:846–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2012.01.021
Shulev YA, Gordienko KS, Trashin AV, Pechiborshch DA, Rzayev DA (2016) [Venous compression as a cause of trigeminal neuralgia]. Zh Vopr Neirokhir Im N N Burdenko 80:21-30.https://doi.org/10.17116/neiro201680421-30
Funding
Our scoping review received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. In addition, of the sources of evidence included in this article, the ones that disclosed a source of funding and the funding received are as follows: Feng et al. (2015) were supported by a grant from the National Science Foundation of China, a grant from the Health Commission of Shanghai, and 2 grants from the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai.[16] Wu et al. were supported by a grant from the Science and Technology Project of Anhui Province, China.[37] Feng et al. (2018) were supported by a grant from Shanghai Jiao Tong University cross fund for medical engineering.[15]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
As this was a literature review and no patient records were accessed or under study, ethical approval from an overseeing board was not sought.
Informed consent
As this was a literature review and no patient records were accessed or under study, no informed consent was sought.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pressman, E., Jha, R.T., Zavadskiy, G. et al. Teflon™ or Ivalon®: a scoping review of implants used in microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurg Rev 43, 79–86 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-019-01187-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-019-01187-0