Abstract
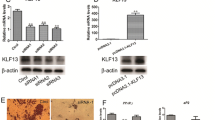
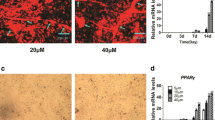
As a key component of Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) pathway, Smad2 has many crucial roles in a variety of cellular processes, but it cannot bind DNA without complex formation with Smad4. In the present study, the molecular mechanism in the progress of myogenesis underlying transcriptional regulation of SMAD2 and SMAD4 had been clarified. The result showed the inhibition between SMAD2 and SMAD4, which promotes and inhibits bovine myoblast differentiation, respectively. Further, the characterization of promoter region of SMAD2 and SMAD4 was analyzed, and identified C/EBPβ directly bound to the core region of both SMAD2 and SMAD4 genes promoter and stimulated the transcriptional activity. However, C/EBPβ has lower expression in myoblasts which plays vital function in the transcriptional networks controlling adipogenesis, while the overexpression of C/EBPβ gene in myoblasts significantly increased SMAD2 and SMAD4 gene expression, induced the formation of lipid droplet in bovine myoblasts, and promoted the expression of adipogenesis-specific genes. Collectively, our results showed that C/EBPβ may play an important role in the trans-differentiation and dynamic equilibrium of myoblasts into adipocyte cells via promoting an increase in SMAD2 and SMAD4 gene levels. These results will provide an important basis for further understanding of the TGFβ pathway and C/EBPβ gene during myogenic differentiation.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data are available within the manuscript. The authors acknowledge that all relevant data presented in this study are contained within the article/material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
References
Alter J, Bengal E (2011) Stress-induced C/EBP homology protein (CHOP) represses MyoD transcription to delay myoblast differentiation. PLoS ONE 6:e29498
Anderson MS, Kunkel LM (1992) The molecular and biochemical basis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Trends Biochem Sci 17:289–292
Calva D, Dahdaleh FS, Woodfield G, Weigel RJ, Carr JC, Chinnathambi S, Howe JR (2011) Discovery of SMAD4 promoters, transcription factor binding sites and deletions in juvenile polyposis patients. Nucleic Acids Res 39:5369–5378
Davison JM, Hartman DA, Singhi AD, Choudry HA, Ahrendt SA, Zureikat AH, Ramalingam L, Nikiforova M, Pai RK (2014) Loss of SMAD4 protein expression is associated with high tumor grade and poor prognosis in disseminated appendiceal mucinous neoplasms. Am J Surg Pathol 38:583–592
Derynck R, Zhang Y, Feng XH (1998) Smads: transcriptional activators of TGF-beta responses. Cell 95:737–740
Droguett R, Cabello-Verrugio C, Santander C, Brandan E (2010) TGF-beta receptors, in a Smad-independent manner, are required for terminal skeletal muscle differentiation. Exp Cell Res 316:2487–2503
Feng XH, Derynck R (2005) Specificity and versatility in tgf-beta signaling through Smads. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 21:659–693
Florini JR, Roberts AB, Ewton DZ, Falen SL, Flanders KC, Sporn MB (1986) Transforming growth factor-beta. A very potent inhibitor of myoblast differentiation, identical to the differentiation inhibitor secreted by Buffalo rat liver cells. J Biol Chem 261:16509–16513
Gao L, Yang M, Wang X, Yang L, Bai C, Li G (2019) Mstn knockdown decreases the trans-differentiation from myocytes to adipocytes by reducing Jmjd3 expression via the SMAD2/SMAD3 complex. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 83:2090–2096
He SM, Zhao ZW, Wang Y, Zhao JP, Wang L, Hou F, Gao GD (2011) Reduced expression of SMAD4 in gliomas correlates with progression and survival of patients. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 30:70
Heino J, Massague J (1990) Cell adhesion to collagen and decreased myogenic gene expression implicated in the control of myogenesis by transforming growth factor beta. J Biol Chem 265:10181–10184
Hirai S, Matsumoto H, Hino N, Kawachi H, Matsui T, Yano H (2007) Myostatin inhibits differentiation of bovine preadipocyte. Domest Anim Endocrinol 32:1–14
Hu E, Tontonoz P, and Spiegelman BM (1995) Transdifferentiation of myoblasts by the adipogenic transcription factors PPAR gamma and C/EBP alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:9856-60
Kim HS, Liang L, Dean RG, Hausman DB, Hartzell DL, Baile CA (2001) Inhibition of preadipocyte differentiation by myostatin treatment in 3T3-L1 cultures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 281:902–906
Kim SW, Her SJ, Kim SY, Shin CS (2005) Ectopic overexpression of adipogenic transcription factors induces transdifferentiation of MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 327:811–819
Kim TH and Dekker J (2018) ChIP-Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (ChIP-qPCR). Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2018
Langley B, Thomas M, Bishop A, Sharma M, Gilmour S, Kambadur R (2002) Myostatin inhibits myoblast differentiation by down-regulating MyoD expression. J Biol Chem 277:49831–49840
Lee JH, Kim SS, Lee HS, Hong S, Rajasekaran N, Wang LH, Choi JS, Shin YK (2017) Upregulation of SMAD4 by MZF1 inhibits migration of human gastric cancer cells. Int J Oncol 50:272–282
Lee KP, Shin YJ, Panda AC, Abdelmohsen K, Kim JY, Lee SM, Bahn YJ, Choi JY, Kwon ES, Baek SJ, Kim SY, Gorospe M, Kwon KS (2015) miR-431 promotes differentiation and regeneration of old skeletal muscle by targeting Smad4. Genes Dev 29:1605–1617
Liu D, Black BL, Derynck R (2001) TGF-beta inhibits muscle differentiation through functional repression of myogenic transcription factors by Smad3. Genes Dev 15:2950–2966
Liu D, Kang JS, Derynck R (2004) TGF-beta-activated Smad3 represses MEF2-dependent transcription in myogenic differentiation. EMBO J 23:1557–1566
Liu N, Qi D, Jiang J, Zhang J, Yu C (2020) Expression pattern of p-Smad2/Smad4 as a predictor of survival in invasive breast ductal carcinoma. Oncol Lett 19:1789–1798
Liu S, Wang Y, Wang L, Wang N, Li Y, Li H (2010) Transdifferentiation of fibroblasts into adipocyte-like cells by chicken adipogenic transcription factors. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 156:502–508
Liu Z, Lin X, Cai Z, Zhang Z, Han C, Jia S, Meng A, Wang Q (2011) Global identification of SMAD2 target genes reveals a role for multiple co-regulatory factors in zebrafish early gastrulas. J Biol Chem 286:28520–28532
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
Luo J, Deng ZL, Luo X, Tang N, Song WX, Chen J, Sharff KA, Luu HH, Haydon RC, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, He TC (2007) A protocol for rapid generation of recombinant adenoviruses using the AdEasy system. Nat Protoc 2:1236–1247
Marchildon F, Lala N, Li G, St-Louis C, Lamothe D, Keller C, Wiper-Bergeron N (2012) CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta is expressed in satellite cells and controls myogenesis. Stem Cells 30:2619–2630
Marchildon F, Lamarche E, Lala-Tabbert N, St-Louis C, Wiper-Bergeron N (2015) Expression of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein beta in muscle satellite cells inhibits myogenesis in cancer cachexia. PLoS ONE 10:e0145583
Martin JF, Li L, Olson EN (1992) Repression of myogenin function by TGF-beta 1 is targeted at the basic helix-loop-helix motif and is independent of E2A products. J Biol Chem 267:10956–10960
Massague J (2000) How cells read TGF-beta signals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 1:169–178
Massague J, Wotton D (2000) Transcriptional control by the TGF-beta/Smad signaling system. EMBO J 19:1745–1754
Nerlov C (2007) The C/EBP family of transcription factors: a paradigm for interaction between gene expression and proliferation control. Trends Cell Biol 17:318–324
Park SH, Yu M, Kim J, Moon Y (2017) C/EBP homologous protein promotes NSAID-activated gene 1-linked pro-inflammatory signals and enterocyte invasion by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Microbes Infect 19:110–121
Pessah M, Marais J, Prunier C, Ferrand N, Lallemand F, Mauviel A, Atfi A (2002) c-Jun associates with the oncoprotein Ski and suppresses Smad2 transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem 277:29094–29100
Qiu X, Gao G, Du L, Wang J, Wang Q, Yang F, Zhou X, Long D, Huang J, Liu Z, Qi R (2022) Time-series clustering of lncRNA-mRNA expression during the adipogenic transdifferentiation of porcine skeletal muscle satellite cells. Curr Issues Mol Biol 44:2038–2053
Quinn ZA, Yang CC, Wrana JL, McDermott JC (2001) Smad proteins function as co-modulators for MEF2 transcriptional regulatory proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 29:732–742
Reddy KC, Dunbar TL, Nargund AM, Haynes CM, Troemel ER (2016) The C. elegans CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein gamma is required for surveillance immunity. Cell Rep 14:1581–1589
Siersbaek R, Mandrup S (2011) Transcriptional networks controlling adipocyte differentiation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 76:247–255
Trendelenburg AU, Meyer A, Rohner D, Boyle J, Hatakeyama S, Glass DJ (2009) Myostatin reduces Akt/TORC1/p70S6K signaling, inhibiting myoblast differentiation and myotube size. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 296:C1258–C1270
Wang H, Cheng G, Fu C, Wang H, Yang W, Wang H, Zan L (2014) Sequence analysis of bovine C/EBPdelta gene and its adipogenic effects on fibroblasts. Mol Biol Rep 41:251–257
Wedel A, Ziegler-Heitbrock HW (1995) The C/EBP family of transcription factors. Immunobiology 193:171–185
Wei D, Raza SHA, Wang X, Khan R, Lei Z, Zhang G, Zhang J, Luoreng Z, Ma Y, Alamoudi MO, Aloufi BH, Alshammari AM, Abd El-Aziz AH, Alhomrani M, Alamri AS (2022a) Tissue expression analysis, cloning, and characterization of the 5’-regulatory region of the bovine LATS1 gene. Front Vet Sci 9:853819
Wei D, Zhang J, Raza SHA, Song Y, Jiang C, Song X, Wu H, Alotaibi MA, Albiheyri R, Al-Zahrani M, Makhlof RTM, Alsaad MA, Abdelnour SA, Quan G (2022b) Interaction of MyoD and MyoG with Myoz2 gene in bovine myoblast differentiation. Res Vet Sci 152:569–578
Welle SL (2009) Myostatin and muscle fiber size. Focus on “Smad2 and 3 transcription factors control muscle mass in adulthood” and “Myostatin reduces Akt/TORC1/p70S6K signaling, inhibiting myoblast differentiation and myotube size.” Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 296:C1245–C1247
Whitman M (1998) Smads and early developmental signaling by the TGFbeta superfamily. Genes Dev 12:2445–2462
Wu X, Ji P, Zhang L, Bu G, Gu H, Wang X, Xiong Y, Zuo B (2015) The expression of porcine Prdx6 gene is up-regulated by C/EBPbeta and CREB. PLoS One 10:e0144851
Xu X, Zheng L, Hang N, Zhu G, Mao W, Fan Y, Tao K (2020) The transcription factor c-Jun regulates Smad4 expression by upregulating pre-miR-183 expression to promote invasion and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 56:550–558
Yang JH, Chang MW, Pandey PR, Tsitsipatis D, Yang X, Martindale JL, Munk R, De S, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M (2020) Interaction of OIP5-AS1 with MEF2C mRNA promotes myogenic gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res 48:12943–12956
Ying Z, Tian H, Li Y, Lian R, Li W, Wu S, Zhang HZ, Wu J, Liu L, Song J, Guan H, Cai J, Zhu X, Li J, Li M (2017) CCT6A suppresses SMAD2 and promotes prometastatic TGF-beta signaling. J Clin Invest 127:1725–1740
Zauberman A, Lapter S, Zipori D (2001) Smad proteins suppress CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) beta- and STAT3-mediated transcriptional activation of the haptoglobin promoter. J Biol Chem 276:24719–24725
Zhang J, Raza SHA, Wei D, Yaping S, Chao J, Jin W, Almohaimeed HM, Batarfi MA, Assiri R, Aggad WS, Ghalib SH, Ageeli AA (2022) Roles of MEF2A and MyoG in the transcriptional regulation of bovine LATS2 gene. Res Vet Sci 152:417–426
Zhang L, Ning Y, Li P, Zan L (2019) Smad3 influences Smad2 expression via the transcription factor C/EBPalpha and C/EBPbeta during bovine myoblast differentiation. Arch Biochem Biophys 671:235–244
Zhang L, Zhao Y, Ning Y, Wang H, Zan L (2017) Ectopical expression of FABP4 gene can induce bovine muscle-derived stem cells adipogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 482:352–358
Zhao S, Nan L, Wang Y, Wei L, Mo S (2021) Effects of Smad4 on the expression of caspase3 and Bcl2 in human gingival fibroblasts cultured on 3D PLGA scaffolds induced by compressive force. Int J Mol Med 47:1
Funding
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (82260285, 32202641 and 31960672), the Natural Science Foundation of Ningxia (2021AAC05007), the Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (2021JQ-622), the Key R & D projects in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (2023BCF01006), the Yan’an University Doctoral Research Initiation Project (YDBK2018-28), the National Modern Agriculture (Beef and Yak) Technology System (CARS-37), and the Scientific Research Plan Projects of Shaanxi Education Department (20JK0444).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dawei Wei and Le Zhang: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, software, validation, writing — original draft, writing—review and editing.
Sayed Haidar Abbas Raza and Zhao Juan: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, software, validation, writing — review and editing.
Guijie Zhang: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, methodology, software, validation. Hadba Al-Amrah: formal analysis, writing — review and editing. Waleed Al Abdulmonem: data curation, formal analysis. Yousef Mesfer Alharbi: data curation, formal writing — review and editing, methodology. Jiupan Zhang: supervision, software, methodology, visualization. Xiaojun Liang: conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, resources, supervision, visualization, writing — review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, D., Zhang, L., Raza, S.H.A. et al. Interaction of C/EBPβ with SMAD2 and SMAD4 genes induces the formation of lipid droplets in bovine myoblasts. Funct Integr Genomics 23, 191 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01115-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-023-01115-y