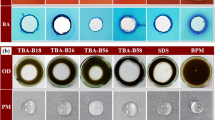
Abstract
Biosurfactants are amphiphilic compounds with extensive applications in oily contaminated environments to remove hydrocarbons. Moreover, enzymes such as laccase and manganese peroxidase are responsible for the oxidation of a variety of phenolic compounds and aromatic amines. Therefore, in the present study, bacteria with the potential to produce biosurfactants and enzymes (namely, laccase, manganese peroxidase, and endoglucanase carboxymethyl cellulose (CMCase)) were isolated from petroleum oil-contaminated soil. From 15 isolated bacteria, three isolates were selected as the best producers of biosurfactants according to the related tests, such as tests for surface tension reduction. These three bacteria indicated tolerance to a salinity test and were classified as resistant and very resistant. The isolates 3, 12, 13, and 14 showed positive results for the degradation of guaiacol, phenol red, and carboxymethylcellulose, as well as the decoloration of methylene blue by the creation of a clear halo around the bacterial colony. Upon the quantitation of the laccase and manganese peroxidase activities, 22.58 U/L and 21.81 U/L, respectively, were measured by isolate 13. Furthermore, CMCase activity was recorded with 0.057436 U/ml belonging to isolate 14. Bacterial strains with appreciable laccase, peroxidase, CMCase activity, and biosurfactant production potentials were identified through 16S rDNA sequence analysis as Bacillus sp. (isolate 3), Bacillus toyonensis (isolate 12), Bacillus cereus (isolate 13), and Bacillus tropicus (isolate 14), and their nucleotide sequences were deposited in the GenBank. The potentials for the industrial applicability of the biosurfactants and enzymes abound, and production needs to be optimized by the selected bacterial strains.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ECe:
-
Electrical conductivity (EC) of a saturated soil paste extract
- TPHs:
-
Total petroleum hydrocarbons
- CTAB:
-
Cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide
- MSM:
-
Minimal salt medium
- CFS:
-
Cell-free supernatant
- MnP:
-
Manganese peroxidase
- DNS:
-
3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid
- ABTS:
-
2,2′-Azino-bis 3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid
References
Abbasnezhad H, Gray M, Foght JM (2011) Influence of adhesion on aerobic biodegradation and bioremediation of liquid hydrocarbons. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92:653–675
Bodour AA, Maier RM (1998) Application of a modified dropcollapse technique for surfactant quantification and screening of biosurfactant-producing microorganisms. J Microbiol Methods 32:273–280
Cappicino JG, Sherman N (1998) Microbiology: a laboratory manual, The Benjamin Cummings publishinig company, INC.39. Bridge parkway Redwood City, California, 94065
Chandra R, Singh R (2012) Decolourisation and detoxification of rayon grade pulp paper mill effluent by mixed bacterial culture isolated from pulp paper mill effluent polluted site. Biochem Eng J 61:49–58
Cooper DG, Goldenberg BG (1987) Surface-active agents from two Bacillus species. Appl Environ Microbiol 53(2):224–229
Dashti N, Salamah S, Khanafer M, Al-Shamy G, Al-Awadhi H, Radwan SS (2019) Culture-independent analysis of hydrocarbonoclastic bacterial communities in environmental samples during oil-bioremediation. Microbiology Open 8(2):e00630
De Almeida DG, Soares DA, Silva RDCF, Luna JM, Rufino RD, Santos VA, Banat IM, Sarubbo LA (2016) Biosurfactants: promising molecules for petroleum biotechnology advances. Front Microbiol 7:1718
De Giani A, Zampolli J, Di Gennaro P (2021) Recent trends on biosurfactants with antimicrobial activity produced by bacteria associated with human health: different perspectives on their properties, challenges, and potential applications. Front Microbiol 12:655150
Deng Z, Jiang Y, Chen K, Gao F, Liu X (2020) Petroleum depletion property and microbial community shift after bioremediation using Bacillus halotolerans T-04 and Bacillus cereus 1–1. Front Microbiol 11:353
Desai JD, Banat IM (1997) Microbial production of surfactants and their commercial potential. Microbial Mol Biol Rev 61:47–64
Dhasayan A, Selvin J, Kiran S (2015) Biosurfactant production from marine bacteria associated with sponge Callyspongia diffusa. 3 Biotech 5(4):443–54
Drakontis CE, Amin S (2020) Biosurfactants: formulations, properties, and applications. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 48:77–90
D’Souza DT, Tiwari R, Sah AK, Raghukumar C (2006) Enhanced production of laccase by a marine fungus during treatment of colored effluents and synthetic dyes. Enzyme Microb Technol 38(3–4):504–511
Enayatzamir K, Alikhani HA, Couto SR (2009) Simultaneous production of laccase and decolouration of the diazo dye Reactive Black 5 in a fixed-bed bioreactor. J Hazard Mater 164(1):296–300
Enayatzamir K, Alikhani HA, Yakhchali B, Tabandeh F, Rodríguez-Couto S (2010) Decolouration of azo dyes by Phanerochaete chrysosporium immobilised into alginate beads. Environ Sci Pollut Res 17(1):145–153
Falade AO, Eyisi OA, Mabinya LV, Nwodo UU, Okoh AI (2017) Peroxidase production and ligninolytic potentials of fresh water bacteria Raoultella ornithinolytica and Ensifer adhaerens. Biotechnol Rep 16:12–17
Ferradji FZ, Mnif S, Badis A, Rebbani S, Fodil D, Eddouaouda K et al (2014) Naphthalene and crude oil degradation by biosurfactant producing Streptomyces spp. isolated from Mitidja plain soil (North of Algeria). Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 86:300–308
Ferreira-Leitao VS, de Carvalho MEA, Bon EP (2007) Lignin peroxidase efficiency for methylene blue decolouration: comparison to reported methods. Dyes Pigm 74(1):230–236
Gayathiri E, Prakash P, Karmegam N, Varjani S, Awasthi MK, Ravindran B (2022) Biosurfactants: potential and eco-friendly material for sustainable agriculture and environmental safety-a review. Agronomy 12(3):662
Gudiña EJ, Fernandes EC, Rodrigues AI, Teixeira JA, Rodrigues LR (2015) Biosurfactant production by Bacillus subtilis using corn steep liquor as culture medium. Front Microbiol 6:59
Hassanshahian M, Giti E, Simone C (2011) Isolation and characterization of crude-oil-degrading bacteria from the Persian Gulf and the Caspian Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 64(1):7–12
Hussain AA, Abdel-Salam MS, Abo-Ghalia HH, Hegazy WK, Hafez SS (2017) Optimization and molecular identification of novel cellulose degrading bacteria isolated from Egyptian environment. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 15(1):77–85
Ibrahim HM (2018) Characterization of biosurfactants produced by novel strains of Ochrobactrum anthropi HM-1 and Citrobacter freundii HM-2 from used engine oil-contaminated soil. Egypt J Pet 27(1):21–29
Ibrahim ML, Ijah UJJ, Manga SB, Bilbis LS, Umar S (2013) Production and partial characterization of biosurfactant produced by crude oil degrading bacteria. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 81:28–34
Joshi SJ, Al-Wahaibi YM, Al-Bahry SN, Elshafie AE, Al-Bemani AS, Al-Bahri A, Al-Mandhari MS (2016) Production, characterization, and application of Bacillus licheniformis W16 biosurfactant in enhancing oil recovery. Front Microbiol 7:1853
Joy S, Rahman PKSM, Sharma S (2017) Biosurfactant production and concomitant hydrocarbon degradation potentials of bacteria isolated from extreme and hydrocarbon contaminated environments. Chem Eng J 317:232–241
Kaczorek E, Pijanowska A, Olszanowski A (2008) Yeast and bacteria cell hydrophobicity and hydrocarbon biodegradation in the presence of natural surfactants: rhamnolipides and saponins. Bioresour Technol 99(10):4285–4291
Kasana RC, Salwan R, Dhar H, Dutt S, Gulati A (2008) A rapid and easy method for the detection of microbial cellulases on agar plates using Gram’s iodine. Curr Microbiol 57(5):503–507
Krasowska A, Sigler K (2014) How microorganisms use hydrophobicity and what does this mean for human needs? Front Cell Infect Microbiol 4:112
Kumar A, Chandra R (2020) Ligninolytic enzymes and its mechanisms for degradation of lignocellulosic waste in environment. Heliyon 6(2):e03170
Kuwahara M, Glenn JK, Morgan MA, Gold MH (1984) Separation and characterization of two extracelluar H2O2-dependent oxidases from ligninolytic cultures of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. FEBS Lett 169(2):247–250
Liang YL, Zhang Z, Wu M, Wu Y, Feng JX (2014) Isolation, screening, and identification of cellulolytic bacteria from natural reserves in the subtropical region of China and optimization of cellulase production by Paenibacillus terrae ME27–1. BioMed Res Int 1–13
Lima JMS, Pereira JO, Batista IH, Junior RCP, dos Santos BH, Neto PDQC, Matsuura ABJ, de Castro FS, Azevedo JL (2017) Biosurfactants produced by Microbacterium sp, isolated from aquatic macrophytes in hydrocarbon-contaminated area in the Rio Negro, Manaus. Amazonas. Acta Scientiarum Biol Sci 39(1):13–20
Luo JC, Long H, Zhang J, Zhao Y, Sun L (2021) Characterization of a deep sea Bacillus toyonensis isolate: genomic and pathogenic features. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 11:107
Mandels M, Reese ET (1975) Induction of cellulase in Trichoderma viride as influenced by carbon sources and metals. J Bacteriol 73(2):269–278
Mohammadipour Z, Enayatizamir N, Ghezelbash G, Moezzi A (2021) Bacterial diversity and chemical properties of wheat straw-based compost leachate and screening of cellulase producing bacteria. Waste Biomass Valorization 12(3):1293–1302
Mohanty S, Mukherji S (2012) Alteration in cell surface properties of Burkholderia spp. during surfactant-aided biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94(1):193–204
Nakamura K, Kitamura K (1982) Isolation and identification of crystalline cellulose hydrolyzing bacterium and its enzymatic properties. J Ferment Technol 60(4):343–348
Niku-Paavola ML, Raaska L, Itävaara M (1990) Detection of white-rot fungi by a non-toxic stain. Mycol Res 94:27–31
Noparat P, Maneerat S, Saimmai A (2014) Application of biosurfactant from Sphingobacterium spiritivorum AS43 in the biodegradation of used lubricating oil. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 172:3949–3969
Pacwa-Płociniczak M, Płaza GA, Piotrowska-Seget Z, Cameotra SS (2011) Environmental applications of biosurfactants: recent advances. Int J Mol Sci 12(1):633–654
Pang R, Li M, Zhang C (2015) Degradation of phenolic compounds by laccase immobilized on carbon nanomaterials: diffusional limitation investigation. Talanta 131:38–45
Peixoto FBS, da Cunha Peixoto JC, Motta DCL, Peixoto ATM, Pereira JO, Astolfi-Filho S (2018) Assessment of petroleum biodegradation for Bacillus toyonensis by the using redox indicator 2, 6 dichlorophenol indophenol. Acta Scientiarum J Biol Sci 40:e35640–e35640
Phulpoto IA, Yu Z, Hu B, Wang Y, Ndayisenga F, Li J, Liang H, Qazi MA (2020) Production and characterization of surfactin-like biosurfactant produced by novel strain Bacillus nealsonii S2MT and it’s potential for oil contaminated soil remediation. Microb Cell Fact 19(1):1–12
Pirhadi M, Enayatizamir N, Motamedi H, Sorkheh K (2016) Screening of salt tolerant sugarcane endophytic bacteria with potassium and zinc for their solubilizing and antifungal activity. Biosci Biotechnol Res Commun 93:530–538
Raj A, Kumar A, Dames JF (2021) Tapping the role of microbial biosurfactants in pesticide remediation: an eco-friendly approach for environmental sustainability. Front Microbiol 12:791723–791723
Rosenberg M, Gutnick D, Rosenberg E (1980) Adherence of bacteria to hydrocarbons: A simple method for measuring cell- surface hydrophobicity. FEMS Microbiol Lett 9(1):29–33
Sabine J, Zeidler S, Nig P, Ngu ND, Scholz A, Averhoff B et al (2018) Salt induction and activation of MtlD, the key enzyme in the synthesis of the compatible solute mannitol in Acinetobacter baumannii. Microbiol Open 9:55–78
Sachdev DP, Cameotra SS (2013) Biosurfactants in agriculture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(3):1005–1016
Saini JK, Saini R, Tewari L (2015) Lignocellulosic agriculture wastes as biomass feedstocks for second-generation bioethanol production: concepts and recent developments. 3 Biotech 5(4):337–353
Sasikumar V, Priya V, Shankar CS, Sekar SD (2014) Isolation and preliminary screening of lignin degrading microbes. J Acad Ind Res 3(6):291–294
Sayed K, Baloo L, Kutty SRB, Makba F (2021) Potential biodegradation of Tapis light crude petroleum oil, using palm oil mill effluent final discharge as biostimulant for isolated halotolerant Bacillus strains. Mar Pollut Bull 172:112863
Shaoping K, Zhiwei D, Bingchen W, Huihui W, Jialiang L, Hongbo S (2021) Changes of sensitive microbial community in oil polluted soil in the coastal area in Shandong. China for Ecorestoration Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 207:111551
Shibulal B, Al-Bahry SN, Al-Wahaibi YM, Elshafie AE, Al-Bemani AS, Joshi SJ (2018) Microbial-enhanced heavy oil recovery under laboratory conditions by Bacillus firmus BG4 and Bacillus halodurans BG5 isolated from heavy oil fields. Colloids Interfaces 2(1):1
Shin CS, Lee JP, Lee JS, Park SC (2000) Enzyme production of Trichoderma reesei Rut C-30 on various lignocellulosic substrates. In Twenty-first symposium on biotechnology for fuels and chemicals (pp. 237–245). Humana Press, Totowa, NJ.
Shivanand P, Mugeraya G (2011) Halophilic bacteria and their compatible solutes–osmoregulation and potential applications. Curr Sci 1516–1521
Silva-Dias A, Miranda IM, Branco J, Monteiro-Soares M, Pina-Vaz C, Rodrigues AG (2015) Adhesion, biofilm formation, cell surface hydrophobicity, and antifungal planktonic susceptibility: relationship among Candida spp. Front Microbiol 6:205
Stancu MM (2020) Biosurfactant production by a Bacillus megaterium strain. Open Life Sci 15(1):629–637
Sun JQ, Xu L, Liu XY, Zhao GF, Cai H, Nie Y, Wu XL (2018a) Functional genetic diversity and culturability of petroleum-degrading bacteria isolated from oil-contaminated soils. Front Microbiol 9:1332
Sun W, Cao W, Jiang M, Saren G, Liu J, Cao J, Ali I, Yu X, Peng C, Naz I (2018) Isolation and characterization of biosurfactant-producing and diesel oil degrading Pseudomonas sp. CQ2 from Changqing oil field. China RSC advances 8(69):39710–39720
Supaphol S, Panichsakpatana S, Trakulnaleamsai S, Tungkananuruk N, Roughjanajirapa P, O’Donnell AG (2006) The selection of mixed microbial inocula in environmental biotechnology: Example using petroleum contaminated tropical soils. J Microbiol Methods 65(3):432–441
Tathonga S, Muangchindaa C, Kongsuwanb C, Khondeec N, Luepromchaib E, Soonglerdsongphae S, Ruangchainikome C, Pinyakongb O (2022) Production of lipopeptide biosurfactant by Bacillus subtilis GY19 and its application as oil-contaminated surface cleaning agent. ScienceAsia 48(1):43–50
Tian JH, Pourcher AM, Peu P (2016) Isolation of bacterial strains able to metabolize lignin and lignin-related compounds. Lett Appl Microbiol 63(1):30–37
Verma M, Ekka A (2015) Kraft lignin degradation through bacterial strain isolated from soils of timber areas. IOSR J Environ Sci Toxicol Food Technol 1(6):28–32
Viramontes-Ramos S, Portillo-Ruiz MC, Ballinas-Casarrubias MDL, Torres-Muñoz JV, Rivera-Chavira BE, Nevárez-Moorillón GV (2010) Selection of biosurfactan/bioemulsifier-producing bacteria from hydrocarbon-contaminated soil. Braz J Microbiol 41:668–675
Vollenbroich D, Pauli G, Ozel M, Vater J (1997) Antimycoplasma properties and application in cell culture of surfactin, a lipopeptide antibiotic from Bacillus subtilis. Appl Environ Microbiol 63(1):44–49
Yadav M, Yadav HS (2015) Applications of ligninolytic enzymes to pollutants, wastewater, dyes, soil, coal, paper and polymers. Environ Chem Lett 13(3): 309–318
Yamamura S, Yamashita M, Fujimoto N, Kuroda M, Kashiwa M, Sei K, Fujita M, Ike M (2007) Bacillus selenatarsenatis sp. nov, a selenate-and arsenate-reducing bacterium isolated from the effluent drain of a glass-manufacturing plant. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57(5):1060–1064
Youssef N, Duncan K, Nagle D, Savage K, Knapp R, McInerney M (2004) Comparison of methods to detect biosurfactant production by diverse microorganisms. J Microbiol Methods 56(3):339–347
Zhang C, Jia L, Wang S, Qu J, Li K, Xu L, Shi Y, Yan Y (2010) Biodegradation of beta-cypermethrin by two Serratia spp. with different cell surface hydrophobicity. Bioresour Technol 101(10):3423–3429
Zhang J, Xue Q, Gao H, Lai H, Wang P (2016) Production of lipopeptide biosurfactants by Bacillus atrophaeus 52a and their potential use in microbial enhanced oil recovery. Microb Cell Factories 15(1):1–11
Zhang J, Lai H, Gao H, Hu S, Xue Q (2018) Prevention and mitigation of paraffin deposition by biosurfactant-producing and paraffin-degrading Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain 6–2c. Chem Eng J 335:510–519
Zhou L, Li H, Zhang Y, Han S, Xu H (2016) Sphingomonas from petroleum-contaminated soils in Shenfu, China and their PAHs degradation abilities. Braz J Microbiol 47:271–278
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources University of Khuzestan, for the support of this study and Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz.
Funding
This study was supported by the Iran National Science Foundation, grant no. 99022578.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Lab work: Sara Valizadeh, supervision: Naeimeh Enayatizamir and Habibolah Nadian Ghomsheh, advisors: Hossein Motamedi and Bijan Khalili Moghadam. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Valizadeh, S., Enayatizamir, N., Ghomsheh, H.N. et al. Characterization of the biosurfactant production and enzymatic potential of bacteria isolated from an oil-contaminated saline soil. Int Microbiol 26, 529–542 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-022-00318-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-022-00318-w