Abstract
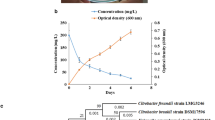
Ibuprofen (IBU) is the third most commonly used analgesic drug in the world. It enters the water system as a result of human excretion-based wastewater discharges. Hence, it attracts the attention of environmentalists for its ecological fate and degradation behavior. In this study, the two IBU degrading bacterial strains, Citrobacter freundii strain PYI-2 (MT039504) and Citrobacter portucalensis strain YPI-2 (MN744335), were isolated from industrial wastewater samples using an enrichment culture method, identified, and characterized. Physiological and batch culture degradation studies have indicated that these strains involved in IBU degradation and the intermediates produced during the process were analyzed. These strains degrade IBU in the batch culture. The optimum pH was reported for degradation of the PYI2 strain (6.9) and YPI2 strain (5.8), and the optimum temperatures were 42°C and 32°C, respectively. Biomass kinetic analysis of these strains was performed based on physical parameters (temperature, pH, and rpm) and confirmed by the experimental study. As indicated in the GC-MS chromatogram peaks, viz., hydroxyibuprofen, 2-(4-hydroxyphenylpropionic acid), 1,4-hydroquinone, and 2-hydroxy-1,4-quinol various intermediates compounds of degradation pathway were observed. Finally, through the GC-MS data, the metabolic pathway for degradation was predicted. In the study, it was confirmed that Citrobacter freundii strain PYI-2 and Citrobacter portucalensis strain YPI-2 exhibit metabolic potential for the biodegradation of IBU and can be further deployed in bioremediation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaij C, Borst P (1972) The gel electrophoresis of DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Nucleic Acids Protein Synth 269:192–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2787(72)90426-1
Aguilar-Romero I, De la Torre-Zúñiga J, Quesada JM, Haïdour A, O'Connell G, McAmmond BM, Van Hamme JD, Romero E, Wittich RM, van Dillewijn P (2021) Effluent decontamination by the ibuprofen-mineralizing strain, Sphingopyxisgranuli RW412: metabolic processes. Environ Pollut (Barking, Essex :1987) 274:116536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116536
Alben KT (2002) Books and software: design, analyze, and optimize with Design-expert. ACS publications. 222-A
Almeida B, Kjeldal H, Lolas I et al (2013a) Quantitative proteomic analysis of ibuprofen-degrading Patulibacter sp. strain I11. Biodegradation 24:615–630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-012-9610-5
Almeida B, Kjeldal H, Lolas I, Knudsen AD, Carvalho G, Nielsen KL et al (2013b) Quantitative proteomic analysis of ibuprofen-degrading Patulibactersp. strain I11. Biodegradation 24:615–630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-012-9610-5
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25(17):3389–3402. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Aulestia M, Flores A, Mangas EL, Pérez-Pulido AJ, Santero E, Camacho EM (2021) Isolation and genomic characterization of the ibuprofen-degrading bacterium Sphingomonas strain MPO218. Environ Microbiol 23(1):267–280. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.15309
Aus der Beek T, Weber FA, Bergmann A, Hickmann S, Ebert I, Hein A et al (2016) Pharmaceuticals in the environment–global occurrences and perspectives. Environ Toxicol Chem 35:823–835. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3339
Balciunas EM, Kappelmeyer U, Harms H, Heipieper HJ (2020) Increasing ibuprofen degradation in constructed wetlands by bioaugmentation with gravel containing biofilms of an ibuprofen-degrading Sphingobium yanoikuyae. Eng Life Sci 20:160–167. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.201900097
Barbosa MO, Moreira NFF, Ribeiro AR et al (2016) Occurrence and removal of organic micropollutants: an overview of the watch list of EU Decision 2015/495. Water Res 94:257–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.02.047
Chandra R, Ghosh A, Jain RK, Singh S (2006) Isolation and characterization of two potential pentachlorophenol degrading aerobic bacteria from pulp paper effluent sludge. J Gen Appl Microbiol 52:125–130. https://doi.org/10.2323/jgam.52.125
Chen Y, Rosazza JP (1994) Microbial transformation of ibuprofen by a Nocardia species. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:1292–1296. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.60.4.1292-1296.1994
Chopra S, Kumar D (2020a) Ibuprofen as an emerging organic contaminant in environment, distribution and remediation. Heliyon 6:e04087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04087
Chopra S, Kumar D (2020b) Characterization, optimization and kinetics study of acetaminophen degradation by Bacillus drentensis strain S1 and waste water degradation analysis. Bioresour Bioprocess 7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-020-0297-x
Chopra S, Kumar D (2020c) Characterization, optimization and kinetic study of diclofenac degradation by novel bacterial strains and their synthetic consortia. Bioremediat J 24(12):1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/10889868.2020.1793723
Daughton CG, Ternes TA (1999) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: agents of subtle change? Environ Health Perspect 107:907–938. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.99107s6907
Deblonde T, Cossu-Leguille C, Hartemann P (2011) Emerging pollutants in wastewater: a review of the literature. Int J Hyg Environ Health 214:442–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheh.2011.08.002
Deschenes LA, of Texas A (2000) Origin 6.0: Scientific data analysis and graphing software Origin Lab Corporation (formerly Microcal Software, Inc.). Web site: www.originlab.com. Commercial price: 595. Academic Press: 446
Ellis JB (2006) Pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) in urban receiving waters. Environ Pollut 144:184–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.12.018
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution (N Y) 39:783–791. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x
Fent K, Weston AA, Caminada D (2006) Ecotoxicology of human pharmaceuticals. Aquat Toxicol 76:122–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.AQUATOX.2005.09.009
Fortunato MS, Fuentes Abril NP, Martinefski M, Trıpodi V, Papalia M, Radice M et al (2016) Aerobic degradation of ibuprofen in batch and continuous reactors by an indigenous bacterial community. Environ Technol 37:2617–2626. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2016.1156773
Gorashi NE, Tripathi M, Kalia V, Gujar GT (2014) Identification and characterization of the Sudanese Bacillus thuringiensis and related bacterial strains for their efficacy against Helicoverpa armigera and Tribolium castaneum. Indian J Exp Biol 52(6):637–649
Guzik U, Wojcieszyńska D (2019) Biodegradation of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and their influence on soil microorganisms. In: Kumar A, Sharma S (eds) Microbes and Enzymes in Soil Health and Bioremediation. Springer, Singapore, pp 379–401. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-9117-0_16
Halden RU, Halden BG, Dwyer DF (1997) A kinetic analysis of dioxin degradation in bioaugmented soils. Abstr Annu Meet Am Soc Microbiol, poster Q-381
Hanlon GW, Kooloobandi A, Hutt AJ (1994) Microbial metabolism of 2-arylpropionic acids: effect of environment on the metabolism of ibuprofen by Verticillium lecanii. J Appl Bacteriol 76:442–447. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.1994.tb01100.x
Hasan M, Alfredo K, Murthy S, Riffat R (2021) Biodegradation of salicylic acid, acetaminophen and ibuprofen by bacteria collected from a full-scale drinking water biofilter. J Environ Manag 295:113071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113071
Hoffmann G, Aramaki S, Blum-Hoffmann E et al (1989) Quantitative analysis for organic acids in biological samples: batch isolation followed by gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis. Clin Chem 35:587–595
Huang CY, Fu LH, Sung MH, Huang CF, Wu JP, Kuo HW (2020) Ibuprofen biodegradation by hospital, municipal, and distillery activated sludges. Environ Technol 41(2):171–180. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1493146
Hucker GJ, Conn HJ (1923) Methods of gram staining, Vol; 93 of Technical bulletin. Agricultural Experiment Station Geneva, NY New York
Ivshina IB, Tyumina E, Kuzmina MV, Vikhareva EV (2019) Features of diclofenac biodegradation by Rhodococcusruber IEGM 346. Sci Rep. 9:9159. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45732-9
Ivshina IB, Tyumina EA, Bazhutin GA, Vikhareva EV (2021) Response of Rhodococcuscerastii IEGM 1278 to toxic effects of ibuprofen. PLoS ONE 16(11):e0260032. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0260032
Jahanshahi M, Sanati MH, Babaei Z (2008) Optimization of parameters for the fabrication of gelatin nanoparticles by the Taguchi robust design method. J Appl Stat 35:1345–1353
Jardim WF, Moraes SG, Takiyama MMK (1997) Photocatalytic degradation of aromatic chlorinated compounds using TiO2: Toxicity of intermediates. Water Res 31:1728–1732. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(96)00349-1
Jia Y, Yin L, Khanal SK, Zhang H, Oberoi AS, Lu H (2020) Biotransformation of ibuprofen in biological sludge systems: investigation of performance and mechanisms. Water Res 170:115303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.115303
Joss A, Zabczynski S, Göbel A et al (2006) Biological degradation of pharmaceuticals in municipal wastewater treatment: proposing a classification scheme. Water Res 40:1686–1696. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2006.02.014
Jurado A, Vàzquez-Suñé E, Carrera J et al (2012) Emerging organic contaminants in groundwater in Spain: a review of sources, recent occurrence and fate in a European context. Sci Total Environ 440:82–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2012.08.029
Kesur BR, Salunkhe VR, Magdum CS (2012) Development and validation of UV spectrophotometric method for simultaneous estimation of ibuprofen and famotidine in bulk and formulated tablet dosage form. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 4:271–274
Khoshayand MR, Abdollahi H, Shariatpanahi M, Saadatfard A, Mohammadi A (2008) Simultaneous spectrophotometric determination of paracetamol, ibuprofen and caffeine in pharmaceuticals by chemometric methods. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 70(3):491–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SAA.2007.07.033
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01731581
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
la Farré M, Pérez S, Kantiani L (2008) Fate and toxicity of emerging pollutants, their metabolites and transformation products in the aquatic environment. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 27:991–1007. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TRAC.2008.09.010
Langenhoff A, Inderfurth N, Veuskens T, Schraa G, Blokland M, Kujawa-Roeleveld K et al (2013) Microbial removal of the pharmaceutical compounds ibuprofen and diclofenac from wastewater. Biomed Res Int 2013:325806. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/325806
Li T, Rosazza JP (1997) Purification, characterization, and properties of an aryl aldehyde oxidoreductase from Nocardia sp. strain NRRL 5646. J Bacteriol 179:3482 LP–3483487. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.179.11.3482-3487.1997
Maheshwari RK, Prasad S, PandeyP WG (2010) Novel spectrophotometric analysis of piroxicam tablets using ibuprofen sodium as hydrotropic solubilizing agents. IntJ Pharma SciDrug Res 2(3):210–212 http://www.ijpsdr.com/pdf/vol2-issue3/9.pdf
Marchlewicz A, Guzik U, Wojcieszyńska D (2015) Over-the-counter monocyclic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in environment - sources, risks, biodegradation. Water Air Soil Pollut 226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2622-0
Marchlewicz A, Guzik U, Hupert-Kocurek K et al (2017a) Toxicity and biodegradation of ibuprofen by Bacillus thuringiensis B1(2015b). Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:7572–7584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8372-3
Marchlewicz A, Guzik U, Smułek W, Wojcieszyńska D (2017b) Exploring the degradation of ibuprofen by bacillus thuringiensis B1(2015b): the new pathway and factors affecting degradation. Molecules 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101676
Marco-Urrea E, Pérez-Trujillo M, Blánquez P et al (2010a) Biodegradation of the analgesic naproxen by Trametes versicolor and identification of intermediates using HPLC-DAD-MS and NMR. Bioresour Technol 101:2159–2166. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2009.11.019
Marco-Urrea E, Pérez-Trujillo M, Cruz-Morató C et al (2010b) White-rot fungus-mediated degradation of the analgesic ketoprofen and identification of intermediates by HPLC–DAD–MS and NMR. Chemosphere 78:474–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.10.009
Murdoch RW, Hay AG (2005) Formation of catechols via removal of acid side chains from ibuprofen and related aromatic acids. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:6121–6125. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.10.6121-6125.2005
Murdoch RW, Hay AG (2013) Genetic and chemical characterization of ibuprofen degradation by Sphingomonas Ibu-2. Microbiology 159:621–632. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.062273-0
Murdoch RW, Hay AG (2015) The biotransformation of ibuprofen to trihydroxyibuprofen in activated sludge and by Variovorax Ibu-1. Biodegradation 26:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-015-9719-4
Murray KE, Thomas SM, Bodour AA (2010) Prioritizing research for trace pollutants and emerging contaminants in the freshwater environment. Environ Pollut 158:3462–3471
Muthukumar M, Mohan D, Rajendran M (2003) Optimization of mix proportions of mineral aggregates using Box Behnken design of experiments. Cem Concr Compos 25:751–758
Nguyen PY, Carvalho G, Reis M, Oehmen A (2021) A review of the biotransformations of priority pharmaceuticals in biological wastewater treatment processes. Water Res 188:116446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116446
Norris JR, Ribbons DW (1972) Methods in microbiology. Academic Press
Ogata H, Goto S, Fujibuchi W, Kanehisa M (1998) Computation with the KEGG pathway database. Biosystems 47:119–128
Onesios KM, Yu JT, Bouwer EJ (2009) Biodegradation and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in treatment systems: a review. Biodegradation 20:441–466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-008-9237-8
Pal A, Gin KY-H, Lin AY-C, Reinhard M (2010) Impacts of emerging organic contaminants on freshwater resources: review of recent occurrences, sources, fate and effects. Sci Total Environ 408:6062–6069
Palyzova A, Marešova H, Novák J, Zahradník J, Řezanka T (2020) Effect of the anti-inflammatory drug diclofenac on lipid composition of bacterial strain Raoultellasp. KDF8. Folia Microbiol 65:763–773. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12223-020-00790-9
Panikov NS (1995) Microbial growth kinetics. Springer Science & Business Media
Peters NE, Meybeck M (2000) Water quality degradation effects on freshwater availability: impacts of human activities. Water Int 25:185–193
Quintana JB, Weiss S, Reemtsma T (2005) Pathways and metabolites of microbial degradation of selected acidic pharmaceutical and their occurrence in municipal wastewater treated by a membrane bioreactor. Water Res 39:2654–2664. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.WATRES.2005.04.068
Rastogi A, Tiwari MK, Ghangrekar MM (2021) A review on environmental occurrence, toxicity and microbial degradation of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). J Environ Manage 300:113694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113694
Rivera-Utrilla J, Sánchez-Polo M, Ferro-García MA, Prados-Joya G, Ocampo-Pérez R (2013) Pharmaceuticals as emerging contaminants and their removal from water. A review. Chemosphere. 93:1268–1287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.07.059
Rodil R, Quintana JB, Concha-Graña E et al (2012) Emerging pollutants in sewage, surface and drinking water in Galicia (NW Spain). Chemosphere 86:1040–1049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.11.053
Rutere C, Knoop K, Posselt M et al (2020) Ibuprofen degradation and associated bacterial communities in hyporheic zone sediments. Microorganisms:8. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081245
Salgado R, Brito D, Noronha JP, Almeida B, Bronze MR, Oehmen A et al (2020a) Metabolite identification of ibuprofen biodegradation by Patulibactermedicamentivoransunder aerobic conditions. Environ Technol 41:450–465. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1502362
Salgado R, Brito D, Noronha JP et al (2020b) Metabolite identification of ibuprofen biodegradation by Patulibacter medicamentivorans under aerobic conditions. Environ Technol (United Kingdom) 41:450–465. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1502362
Santos LH, Araújo AN, Fachini A et al (2010) Ecotoxicological aspects related to the presence of pharmaceuticals in the aquatic environment. J Hazard Mater 175:45–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.10.100
Sharma K, Kaushik G, Thotakura N et al (2019a) Fate of ibuprofen under optimized batch biodegradation experiments using Micrococcus yunnanensis isolated from pharmaceutical sludge. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:8315–8328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02400-9
Sharma K, Kaushik G, Thotakura N, Raza K, Sharma N, Nimesh S (2019b) Fate of ibuprofen under optimized batch biodegradation experiments using Micrococcus yunnanensisisolated from pharmaceutical sludge. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:8315–8328. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02400-9
Smith K, Diggle MA, Clarke SC (2003) Comparison of commercial DNA extraction kits for extraction of bacterial genomic DNA from whole-blood samples. J Clin Microbiol 41:2440–2443. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.41.6.2440-2443.2003
Swift HF (1921) Preservation of stock cultures of bacteria by freezing and drying. J Exp Med 33:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.33.1.69
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/22.22.4673
Wallis Y, Morrell N (2011) Automated DNA sequencing. In: PCR mutation detection protocols. Springer, pp 173–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60761-947-5_12
Wang Y, Wang Q, Wang Y et al (2017) Statistical optimization for the production of recombinant cold-adapted superoxide dismutase in E. coli using response surface methodology. Bioengineered 8:693–699. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2017.1303589
Wang Y, Lu J, Engelstädter J, Zhang S, Ding P, Mao L et al (2020) Non-antibiotic pharmaceuticals enhance the transmission of exogenous antibiotic resistance genes through bacterial transformation. ISME J. 14:2179–2196. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-020-0679-2
Wilson K (2001) Preparation of Genomic DNA from Bacteria. Curr Protoc Mol Biol 56:2.4.1–2.4.5. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142727.mb0204s56
Żur J, Piński A, Marchlewicz A, Hupert-Kocurek K, Wojcieszyńska D, Guzik U (2018) Organic micropollutants paracetamol and ibuprofen-toxicity, biodegradation, and genetic background of their utilization by bacteria. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25(22):21498–21524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2517-x
Zwiener C, Seeger S, Glauner T, Frimmel F (2002) Metabolites from the biodegradation of pharmaceutical residues of ibuprofen in biofilm reactors and batch experiments. Anal Bioanal Chem 372:569–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-001-1210-x
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the sample analysis DNA sequencing at Eurofins Genomics India Pvt Ltd and Advanced Instrumentation Research Facility (AIRF), JNU, New Delhi, India, for GC-MS analysis. The author, S. Chopra, wishes to thank the University Grants Commission New Delhi, India, for providing a research assistantship in the form of an RGNF fellowship. The authors are thankful to the Department of Biotechnology, Deenbandhu Chhotu Ram University of Science and Technology Murthal-131039 Sonepat, Haryana, India, for providing the necessary facilities to conduct this study.
Availability of data and material
The 16S rRNA sequence data of the two IBU degrading Citrobacter freundii strain PYI-2 and Citrobacter portucalensis strain YPI-2, was deposited to NCBI GenBank with accession number(s), MT039504 and MN74433, respectively.
Code availability
Not applicable
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Both authors were involved in the manuscript.
Consent for publication
The authors have consent for the publication and approved the final draft of the manuscript.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 16 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chopra, S., Kumar, D. Characteristics and growth kinetics of biomass of Citrobacter freundii strains PYI-2 and Citrobacter portucalensis strain YPI-2 during the biodegradation of Ibuprofen. Int Microbiol 25, 615–628 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-022-00248-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-022-00248-7