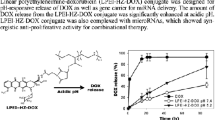
Abstract
Efficient intracellular delivery of protein drugs is critical for protein therapy. The combination of protein drugs with chemotherapeutics represents a promising strategy in enhancing anti-cancer effect. However, co-delivery systems for efficient delivery of these two kinds of drugs are still lacking because of their different properties. Herein, we show a well-designed delivery system based on dynamic covalent bond for efficient intracellular co-delivery of ribonuclease A (RNase A) and doxorubicin (DOX). Two polymers, PEG-b-P(Asp-co-AspDA) and PAE-b-P(Asp-co-AspPBA), and two 2-acetylphenylboronic acid (2-APBA)-functionalized drugs, 2-APBA-RNase A and 2-APBA-DOX, self-assemble into mixed-shell nanoparticles (RNase A/DOX@MNPs) via dynamic phenylboronic acid (PBA)-catechol bond between PBA and dopamine (DA) moieties. The PBA-catechol bond endows the nanoparticles with high stability and excellent stimulus-responsive drug release behavior. Under the slight acidic environment at tumor tissue, RNase A/DOX@MNPs are positively charged, promoting their endocytosis. Upon cellular uptake into endosome, further protonation of PAE chains leads to the rupture of endosomes because of the proton sponge effect and the cleavage of PBA-catechol bond promotes the release of two drugs. In cytoplasm, the high level of GSH removed the modification of 2-APBA on drugs. The restored RNase A and DOX show a synergistic and enhanced antic-cancer effect. This system may be a promising platform for intracellular co-delivery of protein drugs and chemotherapeutics.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. The author’s contact information: shilinqi@nankai.edu.cn (LQ.S.), marujiang@nankaiiedu.cn (R.J.M.)
References
Chung, J. E.; Tan, S.; Gao, S. J.; Yongvongsoontorn, N.; Kim, S. H.; Lee, J. H.; Choi, H. S.; Yano, H.; Zhuo, L.; Kurisawa, M.; Ying, J. Y. Self-assembled micellar nanocomplexes comprising green tea catechin derivatives and protein drugs for cancer therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 907–912.
Leader, B.; Baca, Q. J.; Golan, D. E. Protein therapeutics: a summary and pharmacological classification. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 21–39.
Vermonden, T.; Censi, R.; Hennink, W. E. Hydrogels for protein delivery. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2853–2888.
Yang, Z. C.; Li, Y. C.; Li, F.; Huang, Q. R.; Zhang, G.; Shi, T. F. Design and preparation of pH-responsive curdlan hydrogels as a novel protein delivery vector. Chinese J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 34, 280–287.
Stewart, M. P.; Langer, R.; Jensen, K. F. Intracellular delivery by membrane disruption: mechanisms, strategies, and concepts. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 7409–7531.
Fu, L. Y.; Hua, X. W.; Jiang, X. Y.; Shi, J. J. Multistage systemic and cytosolic protein delivery for effective cancer treatment. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 111–118.
Nischan, N.; Herce, H. D.; Natale, F.; Bohlke, N.; Budisa, N.; Cardoso, M. C.; Hackenberger, C. P. R. Covalent attachment of cyclic TAT peptides to GFP results in protein delivery into live cells with immediate bioavailability. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 1950–1953.
Antonio, J. P. M.; Russo, R.; Carvalho, C. P.; Cal, P. M. S. D.; Gois, P. M. P. Boronic acids as building blocks for the construction of therapeutically useful bioconjugates. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 3513–3536.
Qin, X. F.; Yu, C. M.; Wei, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, C. W.; Wu, Q.; Liu, J. H.; Yao, S. Q.; Huang, W. Rational design of nanocarriers for intracellular protein delivery. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1902791.
Dutta, K.; Hu, D.; Zhao, B.; Ribbe, A. E.; Zhuang, J. M.; Thayumanavan, S. Templated self-assembly of a covalent polymer network for intracellular protein delivery and traceless release. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 5676–5679.
Ren, L. F.; Lv, J.; Wang, H.; Cheng, Y. Y. A coordinative dendrimer achieves excellent efficiency in cytosolic protein and peptide delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 4711–4719.
Kretzmann, J. A.; Luther, D. C.; Evans, C. W.; Jeon, T.; Jerome, W.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Lee, Y.; Norret, M.; Iyer, K. S.; Rotello, V. M. Regulation of proteins to the cytosol using delivery systems with engineered polymer architecture. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 4758–4765.
Scaletti, F.; Hardie, J.; Lee, Y. W.; Luther, D. C.; Ray, M.; Rotello, V. M. Protein delivery into cells using inorganic nanoparticle-protein supramolecular assemblies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 3421–3432.
He, C. L.; Tang, Z. H.; Tian, H. Y.; Chen, X. S. Co-delivery of chemotherapeutics and proteins for synergistic therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 98, 64–76.
Rubinfeld, B.; Upadhyay, A.; Clark, S. L.; Fong, S. E.; Smith, V.; Koeppen, H.; Ross, S.; Polakis, P. Identification and immunotherapeutic targeting of antigens induced by chemotherapy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 205–209.
Giantonio, B. J.; Catalano, P. J.; Meropol, N. J.; O’Dwyer, P. J.; Mitchell, E. P.; Alberts, S. R.; Schwartz, M. A.; Benson, A. B. I. Bevacizumab in combination with oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin (FOLFOX4) for previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer: results from the eastern cooperative oncology group study E3200. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 1539–1544.
Kim, C. S.; Mout, R.; Zhao, Y. L.; Yeh, Y.; Tang, R.; Jeong, Y.; Duncan, B.; Hardy, J. A.; Rotello, V. M. Co-delivery of protein and small molecule therapeutics using nanoparticle-stabilized nanocapsules. Bioconjugate Chem. 2015, 26, 950–954.
Phua, S. Z. F.; Yang, G. B.; Lim, W. Q.; Verma, A.; Chen, H. Z.; Thanabalu, T.; Zhao, Y. L. Catalase-integrated hyaluronic acid as nanocarriers for enhanced photodynamic therapy in solid tumor. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 4742–4751.
Ng, D. Y. W.; Arzt, M.; Wu, Y. Z.; Kuan, S. L.; Lamla, M.; Weil, T. J. Constructing hybrid protein zymogens through protective dendritic assembly. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 324–328.
Sangsuwan, R.; Tachachartvanich, P.; Francis, M. B. Cytosolic delivery of proteins using amphiphilic polymers with 2-pyridinecarboxaldehyde groups for site-selective attachment. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 2376–2383.
Liu, C. Y.; Wan, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Ping, Y.; Cheng, Y. Y. A boronic acid-rich dendrimer with robust and unprecedented efficiency for cytosolic protein delivery and CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaaw8992.
Huang, S.; Kong, X.; Xiong, Y. S.; Zhang, X. R.; Chen, H.; Jiang, W. Q.; Niu, Y. Z.; Xu, W. L.; Ren, C. G. An overview of dynamic covalent bonds in polymer material and their applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 141, 110094.
Chakma, P.; Konkolewicz, D. Dynamic covalent bonds in polymeric materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 9682–9695.
Chen, H.; Cui, L. Y.; Li, Y. F.; Liu, Y.; Ma, R. J.; Shi, L. Q. Phenylboronic acid functionalized polymer nanocarriers for intracellular delivery of protein drugs. Acta Polymerica Sinica (in Chinese) 2023, 54, 451–466.
Zhou, Y.; Zhai, Z. H.; Yao, Y. M.; Stant, J. C.; Landrum, S. L.; Bortner, M. J.; Frazier, C. E.; Edgar, K. J. Oxidized hydroxypropyl cellulose/carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogels permit pH-responsive, targeted drug release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 300, 120213.
Liu, C. Y.; Shen, W. W.; Li, B. N.; Li, T. F.; Chang, H.; Cheng, Y. Y. Natural polyphenols augment cytosolic protein delivery by a functional polymer. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 1956–1965.
Su, S.; Wang, Y. Y.; Du, F. S.; Lu, H.; Li, Z. C. Dynamic covalent bond-assisted programmed and traceless protein release: high loading nanogel for systemic and cytosolic delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1805287.
Cal, P. M. S. D.; Vicente, J. B.; Pires, E.; Coelho, A. V.; Veiros, L. F.; Cordeiro, C.; Gois, P. M. P. Iminoboronates: a new strategy for reversible protein modification. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 10299–10305.
Ding, X. Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, P.; Jin, E.; Xiao, C. S.; Chen, X. S. Injectable self-healing hydrogel wound dressing with cysteine-specific on-demand dissolution property based on tandem dynamic covalent bonds. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2011230.
Chen, D. Y.; Jin, Z. K.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Y. S.; He, Q. J. MBene as a theranostic nanoplatform for photocontrolled intratumoral retention and drug release. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2008089.
Springsteen, G.; Wang, B. H. Alizarin red S. as a general optical reporter for studying the binding of boronic acids with carbohydrates. Chem. Commun. 2001, 58, 1608–1609.
Ma, R. J.; Wang, B. L.; Sun, P. C.; Shi, L. Q. 11B 3Q MAS NMR study on glucose-responsive micelles self-assembled from PEG-b-P(AA-co-AAPBA). Chin. J. Chem 2014, 32, 97–102.
Ren, J.; Zhang, Y. X.; Zhang, J.; Gao, H. J.; Liu, G.; Ma, R. J.; An, Y. G.; Kong, D.; Shi, L. Q. pH/Sugar dual responsive core-cross-linked PIC micelles for enhanced intracellular protein delivery. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 3434–3443.
Zhang, Y. X.; Fu, H.; Chen, J. J.; Xu, L. L.; An, Y. L.; Ma, R. J.; Zhu, C. L.; Liu, Y.; Ma, F. H.; Shi, L. Q. Holdase/foldase mimetic nanochaperone improves antibody-based cancer immunotherapy. Small Methods 2022, 7, 2201051.
Cheng, T. J.; Zhang, Y. M.; Liu, J. J.; Ding, Y. X.; Ou, H. L.; Huang, F.; An, Y. G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J. F.; Shi, L. Q. Ligand-switchable micellar nanocarriers for prolonging circulation time and enhancing targeting efficiency. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5296–5304.
Yan, M.; Du, J. J.; Gu, Z.; Liang, M.; Hu, Y. F.; Zhang, W. J.; Priceman, S.; Wu, L.; Zhou, Z. H.; Liu, Z.; Segura, T.; Tang, Y.; Lu, Y. F. A novel intracellular protein delivery platform based on single-protein nanocapsules. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 48–53.
Cui, L. Y.; Liu, S. N.; Wu, F.; Chen, H.; Li, Y. F.; Shi, L. Q.; Liu, Y.; Ma, R. J. Pottein@PP-Zn nanocomplex assembled by coordination of zinc ions used for intracellular protein delivery. Sci. China Chem. 2023, 66, 2354–2362.
Mosquera, J.; Garcia, I.; Liz-Marzan, L. M. Cellular uptake of nanoparticles versus small molecules: a matter of size. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2305–2313.
Ruan, L. F.; Chen, J.; Du, C. C.; Lu, H. R.; Zhang, J. Y.; Cai, X. M.; Dou, R.; Lin, W. C.; Chai, Z. F.; Nie, G. J.; Hu, Y. Mitochondrial temperature-responsive drug delivery reverses drug resistance in lung cancer. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 13, 191–199.
Ye, M. Z.; Han, Y. X.; Tang, J. B.; Piao, Y.; Liu, X. R.; Zhou, Z. X.; Gao, J. Q.; Rao, J. H.; Shen, Y. Q. A tumor-specific cascade amplification drug release nanoparticle for overcoming multidrug resistance in cancers. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702342.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Nos. 2022YFA1205703 and 2022YFA1205702), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51773099, 51933006 and 52103183) and Haihe Laboratory of Sustainable Chemical Transformations (No. YYJC202102).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no interest conflict.
Electronic Supplementary Information
10118_2024_3090_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
A Dynamic Covalent Bonding-based Nanoplatform for Intracellular Co-Delivery of Protein Drugs and Chemotherapeutics with Enhanced Anti-Cancer Effect
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, SN., Meng, JH., Cui, LY. et al. A Dynamic Covalent Bonding-based Nanoplatform for Intracellular Co-Delivery of Protein Drugs and Chemotherapeutics with Enhanced Anti-Cancer Effect. Chin J Polym Sci (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-024-3090-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-024-3090-z