Abstract
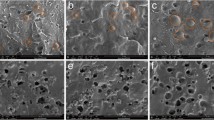
Polymer/conductive filler composites have been widely used for the preparation of self-limiting heating cables with the positive temperature coefficient (PTC) effect. The control of conductive filler distribution and network in polymer matrix is the most critical for performance of PTC materials. In order to compensate for the destruction of the filler network structure caused by strong shearing during processing, an excessive conductive filler content is usually added into the polymer matrix, which in turn sacrifices its processability and mechanical properties. In this work, a facile post-treatment of the as-extruded cable, including thermal and electrical treatment to produce high-density polyethylene (HDPE)/carbon black (CB) cable with excellent PTC effect, is developed. It is found for the as-extruded sample, the strong shearing makes the CB particles disperse uniformly in HDPE matrix, and 25 wt% CB is needed for the formation of conductive paths. For the thermal-treated sample, a gradually aggregated CB filler structure is observed, which leads to the improvement of PTC effect and the notable reduction of CB content to 20 wt%. It is very interesting to see that for the sample with combined thermal and electrical treatment, CB particles are agglomerated and oriented along the electric field direction to create substantial conductive paths, which leads to a further decrease of CB content down to 15 wt%. In this way, self-limiting heating cables with excellent processability, mechanical properties and PTC effect have simultaneously been achieved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gras, R.; Luong, J.; Pursch, M.; Shellie, R. A. Positive temperature coefficient compensating heating for analytical devices. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 6426–6430.
Kang, H. S.; Sim, S.; Shin, Y. H. A numerical study on the lightweight design of PTC heater for an electric vehicle heating system. Energies 2018, 11, 1276.
Shin, Y. H.; Ahn, S. K.; Kim, S. C. Performance characteristics of PTC elements for an electric vehicle heating system. Energies 2016, 9, 813.
Feng, X. M.; Ai, X. P.; Yang, H. X. A positive-temperature-coefficient electrode with thermal cut-off mechanism for use in rechargeable lithium batteries. Electrochem. Commun. 2004, 6, 1021–1024.
Zhong, H.; Kong, C.; Zhan, H.; Zhan, C. M.; Zhou, Y. H. Safe positive temperature coefficient composite cathode for lithium ion battery. J. Power Sources 2012, 216, 273–280.
Wan, Q.; Li, Q. H.; Chen, Y. J.; Wang, T. H.; He, X. L.; Gao, X. G.; Li, J. P. Positive temperature coefficient resistance and humidity sensing properties of Cd-doped ZnO nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 3085–3087.
Chu, K.; Lee, S. C.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.; Moon, C.; Park, S. H. Smart conducting polymer composites having zero temperature coefficient of resistance. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 471–478.
Xu, H. P.; Wu, Y. H.; Yang, D. D.; Wang, J. R.; Xie, H. Q. Study on theories and influence factors of PTC property in polymer-based conductive composites. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2011, 27, 173–183.
Lee, J. H.; Kim, S. K.; Kim, N. H. Effects of the addition of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on the positive temperature coefficient characteristics of carbon-black-filled high-density polyethylene nanocomposites. Scripta. Mater. 2006, 55, 1119–1122.
Li, Q.; Siddaramaiah; Kim, N. H.; Yoo, G. H.; Lee, J. H. Positive temperature coefficient characteristic and structure of graphite nanofibers reinforced high density polyethylene/carbon black nanocomposites. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2009, 40, 218–224.
Zeng, Y.; Lu, G. X.; Wang, H.; Du, J. H.; Ying, Z.; Liu, C. Positive temperature coefficient thermistors based on carbon nanotube/polymer composites. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6684.
Ferrara, M.; Neitzert, H. C.; Sarno, M.; Gorrasi, G.; Sannino, D.; Vittoria, V.; Ciambelli, P. Influence of the electrical field applied during thermal cycling on the conductivity of LLDPE/CNT composites. Physica E 2007, 37, 66–71.
Tsai, C. S.; Liu, C. I.; Tsao, K. Y.; Chen, K. N.; Yeh, J. T.; Huang, C. Y. Effect of Initiator on the over-voltage positive temperature coefficient of linear low density polyethylene/carbon black nano composites. Macromol. Symp. 2009, 286, 125–134.
Bystrov, V. S.; Bdikin, I. K.; Silibin, M. V.; Meng, X. J.; Lin, T.; Wang, J. L.; Karpinsky, D. V.; Bystrova, A. V.; Paramonova, E. V. Pyroelectric properties of ferroelectric composites based on polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) with graphene and graphene oxide. Ferroelectrics 2019, 541, 17–24.
He, L. X.; Tjong, S. C. Electrical behavior and positive temperature coefficient effect of graphene/polyvinylidene fluoride composites containing silver nanowires. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 375.
Jiang, S. L.; Yu, Y.; Xie, J. J.; Wang, L. P.; Zeng, Y. K.; Fu, M.; Li, T. Positive temperature coefficient properties of multiwall carbon nanotubes/poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 838–842.
Liu, Y. W.; Wang, B. M.; Zhan, Q. F.; Tang, Z. H.; Yang, H. L.; Liu, G.; Zuo, Z. H.; Zhang, X. S.; Xie, Y. L.; Zhu, X. J.; Chen, B.; Wang, J. L.; Li, R. W. Positive temperature coefficient of magnetic anisotropy in polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF)-based magnetic composites. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6615.
Li, G. J.; Hu, C.; Zhai, W.; Zhao, S. G.; Zheng, G. Q.; Dai, K.; Liu, C. T.; Shen, C. Y. Particle size induced tunable positive temperature coefficient characteristics in electrically conductive carbon nanotubes/polypropylene composites. Mater. Lett. 2016, 182, 314–317.
Zhao, S. G.; Li, G. J.; Liu, H.; Dai, K.; Zheng, G. Q.; Yan, X. R.; Liu, C. T.; Chen, J. B.; Shen, C. Y.; Guo, Z. H. Positive temperature coefficient (PTC) evolution of segregated structural conductive polypropylene nanocomposites with visually traceable carbon black conductive network. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1700265.
Li, Q.; Park, O. K.; Lee, J. H. Positive temperature coefficient behavior of HDPE/EVA blends filled with carbon black. Adv. Mater. Res. 2009, 79–82, 2267–2270.
Yu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zeng, H. M.; Hou, Y. H.; Zhang, H. B. Conductive polymer blends filled with carbon black: positive temperature coefficient behavior. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1999, 39, 1678–1688.
Ding, X. J.; Wang, J. W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Li, S. Q. Carbon black-filled polypropylene as a positive temperature coefficient material: effect of filler treatment and heat treatment. Polym. Bull. 2016, 73, 369–383.
Zhang, R.; Tang, P.; Shi, R.; Cheng, T. Y.; Bin, Y. Z.; Hu, S. F. Improved electrical heating properties for polymer nanocomposites by electron beam irradiation. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 2847–2863.
Zhang, X.; Zheng, S. D.; Zou, H. Z.; Zheng, X. F.; Liu, Z. Y.; Yang, W.; Yang, M. B. Two-step positive temperature coefficient effect with favorable reproducibility achieved by specific “island-bridge” electrical conductive networks in HDPE/PVDF/CNF composite. Compos. Part A-Appl. S 2017, 94, 21–31.
Bin, Y.; Xu, C.; Agari, Y.; Matsuo, M. Morphology and electrical conductivity of ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene-low-molecular-weight polyethylene-carbon black composites prepared by gelation crystallization from solutions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1999, 277, 452–461.
Jeon, J.; Lee, H. B. R.; Bao, Z. Flexible wireless temperature sensors based on Ni microparticle-filled binary polymer composites. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 850–855.
Yin, C. L.; Liu, Z. Y.; Gao, Y. J.; Yang, M. B. Effect of compounding procedure on morphology and crystallization behavior of isotactic polypropylene/high-density polyethylene/carbon black ternary composites. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2012, 23, 1112–1120.
Jong, Y. S.; Han, S. H.; Park, E. S. Effects of thermal aging on morphology, resistivity, and thermal properties of extruded high-density polyethylene/carbon black heating elements. Polym. Compos. 2011, 32, 1049–1061.
Liang, J. Z.; Yang, Q. Q. Resistivity relaxation behavior of carbon black filled high-density polyethylene conductive composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 1104–1108.
Lee, M. G.; Nho, Y. C. Electrical resistivity of carbon black filled high-density polyethylene composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 83, 2440–2446.
Seo, M. K.; Rhee, K. Y.; Park, S. J. Influence of electro-beam irradiation on PTC/NTC behaviors of carbon blacks/HDPE conducting polymer composites. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2011, 11, 428–433.
Ren, D. Q.; Zheng, S. D.; Huang, S. L.; Liu, Z. Y.; Yang, M. B. Effect of the carbon black structure on the stability and efficiency of the conductive network in polyethylene composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 3382–3389.
Song, Y. H.; Zheng, Q. Effect of voltage on the conduction of a high-density polyethylene/carbon black composite at the NTC region. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 907–912.
Tai, X. Y.; Wu, G. Z.; Yui, H.; Asai, S.; Sumita, M. Dynamics of electric field induced particle alignment in nonpolar polymer matrix. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 3791–3793.
Prasse, T.; Flandin, L.; Schulte, K.; Bauhofer, W. In situ observation of electric field induced agglomeration of carbon black in epoxy resin. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 72, 2903–2905.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no interest conflict.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, TH., Wu, T. & Fu, Q. Preparation of Self-limiting Heating Cables with Excellent Processability, Mechanical Properties and PTC Effect via Thermal and Electrical Treatments. Chin J Polym Sci 42, 511–520 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-024-3074-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10118-024-3074-z