Abstract
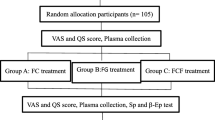
This study aimed to explore the safety and clinical efficacy of light emitting diode (LED) golden light combined with acyclovir in treating herpes zoster (HZ). According to the random number table, 54 inpatients with HZ were divided into control group, golden-light group, and red-light group, with 18 cases in each group. The control group received acyclovir intravenous drip, while the patients in the red-light group received acyclovir intravenous drip and red-light LED phototherapy, and the golden-light group received acyclovir intravenous drip and golden-light LED phototherapy. Primary assessments included herpes stopping time, incrustation time, decrustation time, pain visual analog scale scores (VAS), and incidence of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) on the 30th and 90th days. Golden-light group and red-light group showed a shorter herpes stopping time, incrustation time, and decrustation time (P < 0.05) compared to the control group (P < 0.05), while the golden-light group showed a shorter incrustation time and decrustation time than the red light group (all P < 0.05). After treatment VAS scores, the golden-light group showed a significant improvement compared to the control group. The golden-light group showed a better PHN incidence than the control group at 30 days follow-up. Compared with the comprehensive curative effect, the total effective rates of the golden-light group, red-light group, and control group were 88.89%, 77.78%, and 72.22%, respectively, and the efficacy of the golden-light group was better than that of the control group and red-light group. Golden light combined with acyclovir can shorten the course of HZ, relieve pain, and reduce the occurrence of PHN, and the effect is better than that of the red-light group and the control group.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Le P, Rothberg M (2019) Herpes zoster infection. BMJ (Clinical research ed) 364:k5095
Schmader K (2018) Herpes zoster. Ann Intern Med 169(3):ITC19–ITC31
Zhou H, Wang Z, Jin H, Chen X, Lei L (2021) A systematic review and meta-analysis of independent risk factors for postherpetic neuralgia. Ann Palliat Med 10(12):12181–12189
Oster G, Harding G, Dukes E, Edelsberg J, Cleary PD (2005) Pain, medication use, and health-related quality of life in older persons with postherpetic neuralgia: results from a population-based survey. J Pain 6(6):356–363
Malfliet A, Coppieters I, Van Wilgen P, Kregel J, De Pauw R, Dolphens M, Ickmans K (2017) Brain changes associated with cognitive and emotional factors in chronic pain: a systematic review. Eur J Pain 21(5):769–786
Wang J, Bao J (2011) WX: A clinical investigation on postherpetic neuralgia ( PHN). Chinese J Pain Med 17(04):198–200
Consensus Workgroup on Herpes Zoster CDA (2018) Chinese consensus on herpes zoster. Chin J Dermatol 51(06):403–408
Lane N (2006) Cell biology: power games. Nature 443(7114):901–903
Lim W, Lee S, Kim I, Chung M, Kim M, Lim H, Park J, Kim O, Choi H (2007) The anti-inflammatory mechanism of 635 nm light-emitting-diode irradiation compared with existing COX inhibitors. Lasers Surg Med 39(7):614–621
Sadick N (2008) Handheld LED array device in the treatment of acne vulgaris. J Drugs Dermatol : JDD 7(4):347–350
Zhao X, Li S, Ding J, Wei J, Tian P, Wei H, Chen T (2021) Combination of an engineered Lactococcus lactis expressing CXCL12 with light-emitting diode yellow light as a treatment for scalded skin in mice. Microb Biotechnol 14(5):2090–2100
Jiang M, Wang W, Zeng X (2013) Efficacy of LED red light and yellow light irradiation combined with collagen dressing therapy for facial dermatitis. Chin J Derm Venereol 27(02):223–224
Niu W, Xu Z, Xiao W, Liu Y, Hu F, Wang G, Zhang J, He Z, Yu S, Shi J et al (2022) Phosphor-free golden light LED array for 5.4-Gbps visible light communication using MIMO Tomlinson-Harashima precoding. J Lightwave Technol 40(15):5031–5040
Peng L, Du B, Sun L, Zhao Y, Zhang X (2019) Short-term efficacy and safety of prednisone in herpes zoster and the effects on IL-6 and IL-10. Exp Ther Med 18(4):2893–2900
Gross G, Eisert L, Doerr H, Fickenscher H, Knuf M, Maier P, Maschke M, Müller R, Pleyer U, Schäfer M et al (2020) S2k guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia. Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft = J German Soc Dermatol: JDDG 18(1):55–78
Lin J, Ding X, Hong C, Pang Y, Chen L, Liu Q, Zhang X, Xin H, Wang X (2019) Several biological benefits of the low color temperature light-emitting diodes based normal indoor lighting source. Sci Rep 9(1):7560
Shiva S, Gladwin MT (2009) Shining a light on tissue NO stores: near infrared release of NO from nitrite and nitrosylated hemes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 46(1):1–3
Park KY, Han TY, Kim IS, Yeo IK, Kim BJ, Kim MN (2013) The effects of 830 nm light-emitting diode therapy on acute herpes zoster ophthalmicus: a pilot study. Ann Dermatol 25(2):163–167
Chabert R, Fouque L, Pinacolo S, Garcia-Gimenez N, Bonnans M, Cucumel K, Domloge N (2015) Evaluation of light-emitting diodes (LED) effect on skin biology (in vitro study). Skin Res Technol 21(4):426–436
Liu Z (2019) To observe the efficacy of ganciclovir combined with LED red light in the treatment of herpes zoster. J Dermatology and Venereology 41(05):758–759
Hamblin MR (2017) Mechanisms and applications of the anti-inflammatory effects of photobiomodulation. AIMS Biophys 4(3):337–361
de Brito SK, Rodrigues M, de Souza SD, Mesquita-Ferrari RA, Nunes FD (2020) de Fatima Teixeira da Silva D, Bussadori SK, Fernandes KPS: Differential expression of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory mediators by M1 and M2 macrophages after photobiomodulation with red or infrared lasers. Lasers Med Sci 35(2):337–343
Yang F, Yu S, Fan B, Liu Y, Chen YX, Kudel I, Concialdi K, DiBonaventura M, Hopps M, Hlavacek P et al (2019) The epidemiology of herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia in China: results from a cross-sectional study. Pain Ther 8(2):249–259
Chen Y, Wang H, Wang T, Li Y, Chen T (2016) Early application of low-level laser may reduce the incidence of postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). J Am Acad Dermatol 75(3):572–577
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all study participants for their contributions to the study.
Funding
Science and Technology Research Project of Education Department of Jiangxi Province (No. GJJ200230), Jiangxi Provincial Science and Technology Plan Project (No. 20152ACG70015), The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University Young Talent Research Incubation Program (No. YFYPY202147), and Health Commission Jiangxi Provincial of China (No. 202130178).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study adheres to the ethical guidelines of the Helsinki Declaration, and the experiments conducted in this study were authorized by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University. All participants in this study—patients or guardians—signed consent forms containing complete clinical information.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Xiao, Z., Wang, D. et al. Clinical efficacy of LED golden light combined with acyclovir in the treatment of herpes zoster: a single-center prospective study. Lasers Med Sci 38, 157 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-023-03817-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-023-03817-y