Abstract
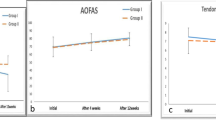
The application of laser therapy on soft tissue is used for pain relief, anti-inflammation action and biostimulation. The efficiency of High Energy Laser Therapy has not yet been studied on Achilles tendinopathy. The aim of the study is to evaluate the effectiveness of a flow of Cold air and High Energy Laser Therapy (CHELT) versus Extracorporeal Shock Waves Therapy (ESWT) in the treatment of Achilles tendinopathy. In this prospective, clinical trial, 60 subjects affected by insertional Achilles tendinopathy were enrolled and randomized to CHELT (30 subjects) or to ESWT (30 subjects). In CHELT group the patients received ten daily sessions of 1,200 J and 12 W of laser therapy (wavelength of 1,084, 810 and 980 nm) added to a flow of cold air at −30 °C. In the ESWT group, the patients received three sessions at 3- to 4-day intervals of 1,600 impulses with an energy flux density (EFD) of 0.05–0.07 mJ/mm2. Both groups of participants performed stretching and eccentric exercises over a 2-month period. The visual analogue scale (VAS), the Ankle–Hindfoot Scale, and the Roles and Maudsley Score were measured before treatment (T0), and at end of the treatment session (T1) and 2 (T2) and 6 months (T3) after treatment during the follow-up examinations. In both groups, we found a statistically significant improvement of the VAS at T1, T2 and T3 (p < 0.01). The difference between the two groups was statistically significant in favour of the CHELT group (p < 0.001). At 2 months, the CHELT group was statistically better for Ankle–Hindfoot Scale and the Roles and Maudsley Score (p < 0.05) and at 6 months only for the Roles and Maudsley Score (p < 0.001). High Energy Laser Therapy gave quicker and better pain relief. It also gave the patient a full functional recovery and greater satisfaction.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holmes GB, Lin J (2006) Etiologic factors associated with symptomatic Achilles tendinopathy. Foot Ankle Int 27:952–959
Paavola M, Kannus P, Jarvinen TA, Jarvinen TL, Jozsa L, Jarvinen M (2002) Treatment of tendon disorders: is there a role for corticosteroid injection? Foot Ankle Clin 7:501–513
Ohberg L, Lorentzon R, Alfredson H (2001) Neovascularisation in Achilles tendons with painful tendinosis but not in normal tendons: an ultrasonographic investigation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 9:233–238
Alfredson H, Forsgren S, Thorsen K, Fahlstrom M, Johansson H, Lorentzon R (2001) Glutamate NMDAR1 receptors localised to nerves in human Achilles tendons: implications for treatment? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 9:123–126
Lian O, Scott A, Engebretsen L, Bahr R, Duronio V, Khan K (2007) Excessive apoptosis in patellar tendinopathy in athletes. Am J Sports Med 35:605–611
Rompe JD, Furia JP, Maffulli N (2008) Mid-portion Achilles tendinopathy—current options for treatment. Disabil Rehabil 30:1666–1676
Yu J, Park D, Lee G (2013) Effect of eccentric strengthening on pain, muscle strength, endurance, and functional fitness factors in male patients with Achilles tendinopathy. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 92(1):68–76
Kingma JJ, de Knikker R, Wittink HM, Takken T (2007) Eccentric overload training in patients with chronic Achilles tendinopathy: a systematic review. Br J Sports Med 41(6):e3
Furia JP (2005) Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in the treatment of chronic insertional Achilles tendinopathy. Orthopade 34:571–578
Vulpiani MC, Trischitta D, Trovato P, Vetrano M, Ferretti A, Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) in Achilles tendinopathy (2009) A long-term follow-up observational study. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 49:171–176
Costa ML, Shepstone L, Donell ST, Thomas TL (2005) Shock wave therapy for chronic Achilles tendon pain: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res 440:199–204
Paoloni JA, Appleyard RC, Nelson J, Murrell GA (2004) Topical glyceryl trinitrate treatment of chronic noninsertional achilles tendinopathy. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86-A(5):916–922
Paoloni JA, Murrell GA (2007) Three-year follow-up study of topical glyceryl trinitrate treatment of chronic noninsertional Achilles tendinopathy. Foot Ankle Int 28(10):1064–1068
Bjordal JM, Lopes-Martins RA, Iversen VV (2006) A randomised, placebo controlled trial of low level laser therapy for activated Achilles tendinitis with microdialysis measurement of peritendinous prostaglandin E2 concentrations. Br J Sports Med 40:76–80
Stergioulas A, Stergioula M, Aarskog R, Lopes-Martins RAB, Bjordal JM (2008) Effects of low-level laser therapy and eccentric exercises in the treatment of recreational athletes with chronic Achilles tendinopathy. Am J Sports Med 36:881–887
Akizuki K, Gartman EJ, Nisonson B, Ben-Avi S, McHugh MP (2001) The relative stress on the Achilles tendon during ambulation in an ankle immobiliser: implications for rehabilitation after Achilles tendon repair. Br J Sports Med 35:329–334
McAleenan M, McVeigh JG, Cullen M, Sayers M, McCrea K, Baxter D (2010) The effectiveness of night splints in Achilles tendinopathy: a pilot study. Physiotherapy Ireland 31:29–33
Koenig MJ, Torp-Pedersen S, Qvistgaard E, Terslev L, Bliddal (2004) Preliminary results of colour Doppler-guided intratendinous glucocorticoid injection for Achilles tendonitis in five patients. Scand J Med Sci Sports 14(2):100–106
Maquirriain J (2013) Surgical treatment of chronic Achilles tendinopathy: long-term results of the endoscopic technique. J Foot Ankle Surg 52(4):451–455
Chung B, Wiley JP (2002) Extracorporeal shockwave therapy: a review. Sports Med 32:851–865
Furia JP (2006) High energy extracorporal shock wave therapy as a treatment for insertional Achilles tendinopathy. Am J Sports Med 34:733–740
Furia JP (2006) Extracorporeal shockwave therapy in the treatment of chronic noninsertional Achilles tendinopathy. Am J Sports Med 34(5):502–508
Rasmussen S, Christensen M, Mathiesen I, Simonson O (2008) Shockwave therapy for chronic Achilles tendinopathy: a double-blind, randomized clinical trial of efficacy. Acta Orthop 79(2):249–256
Marcos RL, Leal-Junior EC, Arnold G, Magnenet V, Rahouadj R, Wang X, Demeurie F, Magdalou J, de Carvalho MH, Lopes-Martins RÁ (2012) Low-level laser therapy in collagenase-induced Achilles tendinitis in rats: analyses of biochemical and biomechanical aspects. J Orthop Res 30(12):1945–1951
Carcia CR, Martin RL, Houck J, Wukich DK (2010) Achilles pain, stiffness, and muscle power deficits: Achilles tendinitis. J Orhop Sports Phys Ther 40:A1–A26
Basford JR (1995) Low intensity laser therapy: still not an established clinical tool. Lasers Surg Med 16(4):331–342
Ohshiro T, Calderhead RG (1991) Development of low reactive-level laser therapy and its present status. J Clin Laser Med Surg 9(4):267–275
Santamato A, Solfrizzi V, Panza F, Tondi G, Frisardi V, Leggin BG, Ranieri M, Fiore P (2009) Short-term effects of high-intensity laser therapy versus ultrasound therapy in the treatment of people with subacromial impingement syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. Phys Ther 89(7):643–652
Fiore P, Panza F, Cassatella G, Russo A, Frisardi V, Solfrizzi V, Ranieri M, Di Teo L, Santamato A (2011) Short-term effects of high-intensity laser therapy versus ultrasound therapy in the treatment of low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med 47(3):367–373
Rowe V, Hemmings S, Barton C, Malliaras P, Maffulli N, Morrissey (2012) Conservative management of midportion Achilles tendinopathy: a mixed methods study, integrating systematic review and clinical reasoning. Sports Med 1;42(11):941–67.
Williams JG (1986) Achilles tendon lesions in sport. Sports Med 3:114–135
Maffulli N, Kenward MG, Testa V, Capasso G, Regine R, King JB (2003) Clinical diagnosis of Achilles tendinopathy with tendinosis. Clin J Sport Med 13:11–15
Kaux JF, Forthomme B, Le Goff C, Crielaard JM, Croisier JL (2011) Current opinions of tendinopathy. J Sports Sci Med 10:238–253
Patil UA, Dhami LD (2008) Overview of lasers. Indian J Plast Surg 41(Suppl):S101–S113
Tiele R (2009) New guidelines for ESWT. Newsletter ISMST 5:20
Rompe JD, Furia J, Maffulli N (2009) Eccentric loading versus eccentric loading plus shock-wave treatment for midportion Achilles tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med 37:463–470
Ohberg L, Alfredson H (2004) Effects on neovascularization behind the good results with eccentric training in chronic Achilles tendinosis? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 12:465–470
Myles PS, Troedel S, Boquest M, Reeves M (1999) The pain visual analog scale: is it linear or nonlinear? Anesth Analg 89:1517–1520
Kitaoka HB, Alexander IJ, Adelaar RS, Nunley JA, Myerson MS, Sanders M (1994) Clinical rating systems for the ankle–hindfoot, midfoot, hallux, and lesser toes. Foot Ankle Int 15:349–353
Roles NC, Maudsley RH (1972) Radial tunnel syndrome: resistant tennis elbow as a nerve entrapment. J Bone Joint Surg Br 54:499–508
Farrar JT, Young JP Jr, LaMoreaux L, Werth JL, Poole RM (2001) Clinical importance of changes in chronic pain intensity measured on an 11-point numerical pain rating scale. Pain 94:149–158
Kearney R, Costa ML (2010) Insertional Achilles tendinopathy management: a systematic review. Foot Ankle Int 31(8):689–694
Mitchell AW, Lee JC, Healy JC (2009) The use of ultrasound in the assessment and treatment of Achilles tendinosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 91(11):1405–1409
Lake JE, Ishikawa SN (2009) Conservative treatment of Achilles tendinopathy: emerging techniques. Foot Ankle Clin 14(4):663–674
Tumilty S, Munn J, McDonough S, Hurley DA, Basford JR, Baxter GD (2010) Low level laser treatment of tendinopathy: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Photomed Laser Surg 28(1):3–16
IPG312 Extracorporeal shockwave therapy for refractory Achilles tendinopathy: guidance 07 April 2011.
Waynant, Ronald; Tata, Darrell B (Eds.) (2008) Proceedings of light-activated tissue regeneration and therapy Conference, Springer
Rompe JD, Kirkpatrick CJ, Kullmer K, Schwitalle M, Krischnek O (1998) Dose-related effects of shock waves on rabbit tendon Achilles: a sonographic and histological study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 80-B:546–552
Staudenraus J (1995) In vivo Strasswllenmessung. In Chaussy (Hrsg). Die Stosswelle in Forschung und Kinik. Attempto Verlag, S21–S26.
Mariotto S, de Prati AC, Cavalieri E, Amelio E, Marlinghaus E, Suzuki H (2009) Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in inflammatory diseases: molecular mechanism that triggers anti-inflammatory action. Curr Med Chem 16(19):2366–2372
Martini L, Giavaresi G, Fini M, Torricelli P, Borsari V, Giardino R, De Pretto M, Remondini D, Castellani GC (2005) Shock wave therapy as an innovative technology in skeletal disorders: study on transmembrane current in stimulated osteoblast-like cells. Int J Artif Organs 28(8):841–847
Wang CJ, Yang KD, Ko JY, Huang CC, Huang HY, Wang FS (2009) The effects of shockwave on bone healing and systemic concentrations of nitric oxide (NO), TGF-beta1, VEGF and BMP-2 in long bone non-unions. Nitric Oxide 20(4):298–303
Bolt DM, Burba DJ, Hubert JD, Pettifer GR, Giselle L (2004) Hosgood evaluation of cutaneous analgesia after non-focused extracorporeal shock wave application over the 3rd metacarpal bone in horses. Can J Vet Res 68(4):288–292
Frigo L, Fávero GM, Lima HJ, Maria DA, Bjordal JM, Joensen J, Iversen VV, Marcos RL, Parizzoto NA, Lopes-Martins RA (2010) Low-level laser irradiation (InGaAlP-660 nm) increases fibroblast cell proliferation and reduces cell death in a dose-dependent manner. Photomed Laser Surg 28(Suppl 1):S151–S156
Pires D, Xavier M, Araújo T, Silva JA Jr, Aimbire F, Albertini R (2011) Low-level laser therapy (LLLT; 780 nm) acts differently on mRNA expression of anti- and pro-inflammatory mediators in an experimental model of collagenase-induced tendinitis in rat. Lasers Med Sci 26(1):85–94
Lievens PC (1991) The effect of the combined HeNe and IR laser treatment on the regeneration of the lymphatic system during the process of wound healing. Lasers Med 6:189–191
Wakabayashi H, Hamba M (1993) Matsumoto K. Tachibana H. Effect of irradiation by semiconductor laser on responses evoked in trigeminal caudal neurons by tooth pulp stimulation. Lasers Surg Med 13:605–610
Allen RJ (2006) Physical agents used in the management of chronic pain by physical therapists. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 17:315–345
Tsukya K, Kawatani M, Takeshige C, Matsumoto I (1994) Laser irradiation abates neuronal responses to nociceptive stimulation of rat-paw skin. Brain Res Bull 34:369–374
Nicolau RA, Martinez MS, Rigau J, Tomàs J (2004) Neurotransmitter release changes induced by low power 830 nm diode laser irradiation on the neuromuscular junctions of the mouse. Lasers Surg Med 35:236–241
Laakso EL (1994) Plasma ACTH and B-endorfin levels in response to low level laser therapy (LLLT) for myofascial trigger points. Laser Therapy 6:133–142
Bjordal J, Couppé C, Ljunggreen A (2001) Low level laser therapy for tendinopathy. Evidence of a dose-response pattern. Physical Therapy Reviews 6:91–99
Stiglić-Rogoznica N, Stamenković D, Frlan-Vrgoc L, Avancini-Dobrović V, Vrbanić TS (2011) Analgesic effect of high intensity laser therapy in knee osteoarthritis. Coll Antropol 35(Suppl 2):183–185
Lopes-Martins R, Penna SC, Joensen J, Iversen VV, Bjordal JM (2007) Low level laser therapy (LLLT) in inflammatory and rheumatic diseases: a review of therapeutic mechanisms. Current Rheumatology Reviews 3:147–154
Farouk AH, Al W, Zhang XJ (2004) The comparaison of effects between pulsed and CW lasers on wound healing. Clin Laser Med Surg 22(1):15–18
Bjordal JM, Johnson MI, Iversen V, Aimbire F, Lopes-Martins RA (2006) Low-level laser therapy in acute pain: a systematic review of possible mechanisms of action and clinical effects in randomized placebo-controlled trials. Photomed Laser Surg 24(2):158–168
Hirvonen HE, Mikkelsson MK, Kautiainen H, Pohjolainen TH, Leirisalo-Repo M (2006) Effectiveness of different cryotherapies on pain and disease activity in active rheumatoid arthritis. A randomised single blinded controlled trial. Clin Exp Rheumatol 24(3):295–301
Bélanger A (2002) Evidence-based guide to therapeutic physical agents. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 263–298
Knobloch K, Grasemann R, Spies M, Vogt PM (2008) Midportion achilles tendon microcirculation after intermittent combined cryotherapy and compression compared with cryotherapy alone: a randomized trial. Am J Sports Med 36(11):2128–2138
Autrata R, Senková K, Holousová M, Helmanová I, Pyrochtová S (2008) Combined treatment with laser photocoagulation and cryotherapy for threshold retinopathy of prematurity. Eur J Ophthalmol 18(1):112–117
Chow RT, Johnson MI, Lopes-Martins RA, Bjordal JM (2009) Efficacy of low-level laser therapy in the management of neck pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised placebo or active-treatment controlled trials. Lancet 374(9705):1897–1908
Corona SA, Nascimento TN, Catirse AB, Lizarelli RF, Dinelli W, Palma-Dibb RG (2003) Clinical evaluation of low-level laser therapy and fluoride varnish for treating cervical dentinal hypersensitivity. J. Oral Rehabil 30:1183–1189
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Notarnicola, A., Maccagnano, G., Tafuri, S. et al. CHELT therapy in the treatment of chronic insertional Achilles tendinopathy. Lasers Med Sci 29, 1217–1225 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-013-1510-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-013-1510-3