Abstract
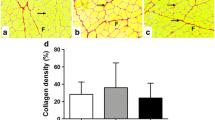
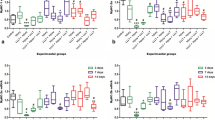
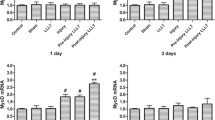
This work investigated the effect of gallium arsenide (GaAs) irradiation (power: 5 mW; intensity: 77.14 mW/cm2, spot: 0.07 cm2) on regenerating skeletal muscles damaged by crotoxin (CTX). Male C57Bl6 mice were divided into six groups (n = 5 each): control, treated only with laser at doses of 1.5 J or 3 J, CTX-injured and, CTX-injured and treated with laser at doses of 1.5 J or 3 J. The injured groups received a CTX injection into the tibialis anterior (TA) muscle. After 3 days, TA muscles were submitted to GaAs irradiation at doses of 1.5 or 3 J (once a day, during 5 days) and were killed on the eighth day. Muscle histological sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) in order to determine the myofiber cross-sectional area (CSA), the previously injured muscle area (PIMA) and the area density of connective tissue. The gene expression of MyoD and myogenin was detected by real-time PCR. GaAs laser at a dose of 3 J, but not 1.5 J, significantly increased the CSA of regenerating myofibers and reduced the PIMA and the area density of intramuscular connective tissue of CTX-injured muscles. MyoD gene expression increased in the injured group treated with GaAs laser at a dose of 1.5 J. The CTX-injured, 3-J GaAs laser-treated, and the CTX-injured and treated with 3-J laser groups showed an increase in myogenin gene expression when compared to the control group. Our results suggest that GaAs laser treatment at a dose of 3 J improves skeletal muscle regeneration by accelerating the recovery of myofiber mass.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hawke TJ, Garry DJ (2001) Myogenic satellite cells: physiology to molecular biology. J Appl Physiol 91:534–551
Ten Broek RW, Grefte S, Von den Hoff JW (2010) Regulatory factors and cell populations involved in skeletal muscle regeneration. J Cell Physiol 224:7–16
Mester E, Spiry T, Szende B, Tota JG (1971) Effect of laser rays on wound healing. Am J Surg 122:532–535
Mester E, Mester AF, Mester A (1985) The biomedical effects of laser application. Lasers Surg Med 5:31–39
Yaakobi T, Maltz L, Oron U (1996) Promotion of bone repair in the cortical bone of the tibia in rats by low-energy laser (He-Ne) irradiation. Calcif Tissue Int 59:297–300
Luger EJ, Rochkind S, Wollman Y, Kogan G, Dekel S (1998) Effect of low-power laser irradiation on the mechanical properties of bone fracture healing in rats. Lasers Surg Med 22:97–102
Rochkind S, Ouaknine GE (1992) New trend in neuroscience: low-power laser effect on peripheral and central nervous system (basic science, preclinical and clinical studies). Neurol Res 14:2–11
Van Breugel HH, Bar PR (1993) He-Ne laser irradiation affects proliferation of cultured rat Schwann cells in a dose-dependent manner. J Neurocytol 22:185–190
Bibikova A, Belkin V, Oron U (1994) Enhancement of angiogenesis in regenerating gastrocnemius muscle of the toad (Bufo viridis) by low-energy laser irradiation. Anat Embryol (Berl) 190:597–602
Bibikova A, Oron U (1995) Regeneration in denervated toad (Bufo viridis) gastrocnemius muscle and the promotion of the process by low-energy laser irradiation. Anat Rec 241:123–128
Oliveira NM, Parizzotto NA, Salvini TF (1999) GaAs (904-nm) laser radiation does not affect muscle regeneration in mouse skeletal muscle. Lasers Surg Med 25:13–21
Servetto N, Cremonezzi D, Simes JC, Moya M, Soriano F, Palma JA, Campana VR (2010) Evaluation of inflammatory biomarkers associated with oxidative stress and histological assessment of low-level laser therapy in experimental myopathy. Lasers Surg Med 42:577–583
Leal Junior EC, Lopes-Martins RA, Frigo L, De Marchi T, Rossi RP, de Godoi V, Tomazoni SS, Silva DP, Basso M, Filho PL, de Valls Corsetti F, Iversen VV, Bjordal JM (2010) Effects of low-level laser therapy (LLLT) in the development of exercise-induced skeletal muscle fatigue and changes in biochemical markers related to postexercise recovery. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther 40:524–532
Karu T (1989) Laser biostimulation: a photobiological phenomenon. J Photochem Photobiol B 3:638–640
da Silva JP, da Silva MA, Almeida AP, Lombardi Junior I, Matos AP (2010) Laser therapy in the tissue repair process: a literature review. Photomed Laser Surg 28:17–21
Basford JR (1993) Laser therapy: scientific basis and clinical role. Orthopedics 16:541–547
Basford JR (1995) Low intensity laser therapy: still not an established clinical tool. Lasers Surg Med 16:331–342
Nakano J, Kataoka H, Sakamoto J, Origuchi T, Okita M, Yoshimura T (2009) Low-level laser irradiation promotes the recovery of atrophied gastrocnemius skeletal muscle in rats. Exp Physiol 94:1005–1015
Hotta PT, Hotta TH, Bataglion C, Bataglion SA, de Souza Coronatto EA, Siessere S, Regalo SC (2010) Emg analysis after laser acupuncture in patients with temporomandibular dysfunction (TMD). Implications for practice. Complement Ther Clin Pract 16:158–160
Weiss N, Oron U (1992) Enhancement of muscle regeneration in the rat gastrocnemius muscle by low energy laser irradiation. Anat Embryol (Berl) 186:497–503
Bibikova A, Oron U (1993) Promotion of muscle regeneration in the toad (Bufo viridis) gastrocnemius muscle by low-energy laser irradiation. Anat Rec 235:374–380
Ben-Dov N, Shefer G, Irintchev A, Wernig A, Oron U, Halevy O (1999) Low-energy laser irradiation affects satellite cell proliferation and differentiation in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta 1448:372–380
Dourado DM, Favero S, Baranauskas V, da Cruz-Hofling MA (2003) Effects of the Ga-As laser irradiation on myonecrosis caused by Bothrops Moojeni snake venom. Lasers Surg Med 33:352–357
Mester E (1982) Biostimulating effect of laser beams. Z Exp Chir 15:67–74
World Association of Laser Therapy (WALT) (2006) Consensus agreement on the design and conduct of clinical studies with low-level laser therapy and light therapy for musculoskeletal pain and disorders. Photomed Laser Surg 24:761–762
Conte TC, Franco DV, Baptista IL, Bueno CR Jr, Selistre-de-Araujo HS, Brum PC, Moriscot AS, Miyabara EH (2008) Radicicol improves regeneration of skeletal muscle previously damaged by crotoxin in mice. Toxicon 52:146–155
Mathieu O, Cruz-Orive LM, Hoppeler H, Weibel ER (1981) Measuring error and sampling variation in stereology: comparison of the efficiency of various methods for planar image analysis. J Microsc 121:75–88
Warrell DA (1996) Clinical features of envenoming by snake bites. In: Bon C, Goyffon M (eds) Envenomings and their treatments. Fondation Marcel Me´rieux, Lyon, pp 63–76
Gutierrez JM, Ownby CL (2003) Skeletal muscle degeneration induced by venom phospholipases A2: insights into the mechanisms of local and systemic myotoxicity. Toxicon 42:915–931
Duguez S, Bihan MC, Gouttefangeas D, Feasson L, Freyssenet D (2003) Myogenic and nonmyogenic cells differentially express proteinases, Hsc/Hsp70, and BAG-1 during skeletal muscle regeneration. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285:E206–E215
Fillipin LI, Mauriz JL, Vedovelli K, Moreira AJ, Zettler CG, Lech O, Marroni NP, Gonzalez-Gallego J (2005) Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) prevents oxidative stress and reduces fibrosis in rat traumatized Achilles tendon. Lasers Surg Med 37:293–300
Shefer G, Barash I, Oron U, Halevy O (2003) Low-energy laser irradiation enhances de novo protein synthesis via its effects on translation-regulatory proteins in skeletal muscle myoblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta 1593:131–139
Leal Junior EC, Lopes-Martins RA, de Almeida P, Ramos L, Iversen VV, Bjordal JM (2010) Effect of low-level laser therapy (GaAs 904 nm) in skeletal muscle fatigue and biochemical markers of muscle damage in rats. Eur J Appl Physiol 108:1083–1088
Shefer G, Partridge TA, Heslop L, Gross JG, Oron U, Halevy O (2002) Low-energy laser irradiation promotes the survival and cell cycle entry of skeletal muscle satellite cells. J Cell Sci 115:1461–1469
Oron U (2006) Photoengineering of tissue repair in skeletal and cardiac muscles. Photomed Laser Surg 24:111–120
Iyomasa DM, Garavelo I, Iyomasa MM, Watanabe IS, Issa JP (2009) Ultrastructural analysis of the low-level laser therapy effects on the lesioned anterior tibial muscle in the gerbil. Micron 40:413–418
Dourado DM, Favero S, Matias R, Carvalho Pde T, da Cruz-Hofling MA (2011) Low-level laser therapy promotes vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 expression in endothelial and nonendothelial cells of mice gastrocnemius exposed to snake venom. Photochem Photobiol 87:418–426
Acknowledgments
The authors dedicate this work to the co-author and great friend Dr. Cláudio A. Toledo, who passed away recently. This study was supported by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP). LHS, MTS, and TCC received scholarships from FAPESP (grants# 2009/50198-6, 2009/54240-7 and 2007/56879-0, respectively).
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lucila H. Silva and Meiricris T. Silva contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Silva, L.H., Silva, M.T., Gutierrez, R.M. et al. GaAs 904-nm laser irradiation improves myofiber mass recovery during regeneration of skeletal muscle previously damaged by crotoxin. Lasers Med Sci 27, 993–1000 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-011-1031-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-011-1031-x