Abstract
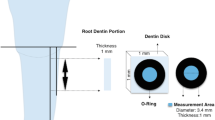
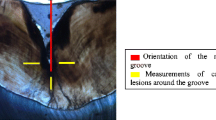
The purpose of this in vitro study was to compare the effects of a self-etch adhesive system and neodymium:yttrium–aluminum–garnet (Nd:YAG) laser application on the dentinal permeability of the furcation area of primary molars. After endodontic access, 39 extracted human deciduous molars were divided into three groups: control group (CG), no treatment; adhesive group (AG), self-etching adhesive was applied to the furcation area; laser group (LG), specimens were irradiated with Nd:YAG laser. To evaluate dentin permeability of the furcation area, we immersed the specimens in 0.5 % methylene blue dye for 4 h. Then, they were longitudinally sectioned into two halves and photographed. The images were analyzed by two qualified evaluators using TpsDig software to calculate the percentage of the dye penetration area in comparison with the total furcation area. Additional analyses by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were performed. The analysis of variance (ANOVA), complemented by Student’s t-test, showed that mean dye penetration in the LG was statistically significant lower than that in all the other groups (P < 0.05). The SEM analysis showed mostly dentinal tubules obliterated by smear layer in the CG; in the AG the smear layer was modified by the adhesive, and, in the LG, melted surfaces were observed. It can be concluded that the Nd:YAG laser was capable of reducing the dentinal permeability of the furcation area of deciduous molars.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Paras LG, Rapp R, Piesco NP, Zeichner SJ, Zullo TG (1993) An investigation of accessory foramina in furcation areas of human primary molars.. Part 1: SEM observations of frequency, size and location of accessory foramina in the internal and external furcation areas. J Clin Pediatr Dent 17:65–69
Messer LB, Cline JT, Korf NW (1980) Long term effects of primary molar pulpotomies on succedaneous bicuspids. J Dent Res 59:116–123
Ringelstein D, Seow WK (1989) The prevalence of furcation foramina in primary molars. Pediatr Dent 11:198–202
Wrbas KT, Kielbassa AM, Hellwig E (1997) Microscopic studies of accessory canals in primary molar furcations. ASDC J Dent Child 64:118–122
Moss SJ, Addelston H, Goldsmith ED (1965) Histologic study of pulpal floor of deciduous molars. J Am Dent Assoc 70:372–379
Morabito A, Defabianis P (1992) A SEM investigation on pulpal-periodontal connections in primary teeth. ASDC J Dent Child 59:53–57
Kramer PF, Faraco I, Meira R (2003) A SEM investigation of accessory foramina in the furcation areas of primary molars. J Clin Pediatr Dent 27:157–161
Miserendino LJ, Levy GC, Rizoiu IM (1995) Effects of Nd:YAG laser on the permeability of root canal wall dentin. J Endod 21:83–87
Lee BS, Lin FH, Lan WH (2002) Ultrastructural changes of human dentin after irradiation by Nd:YAG laser. Lasers Surg Med 30:246–252
Birang R, Poursamimi J, Gutknecht N, Lampert F, Mir M (2007) Comparative evaluation of the effects of Nd:YAG and Er:YAG laser in dentin hypersensitivity treatment. Lasers Med Sci 22:21–24
Moritz A, Jakolitsch S, Goharkhay K, Schoop U, Kluger W, Mallinger R, Sperr W, Georgopoulos A (2000) Morphologic changes correlating to different sensitivities of Escherichia coli and enterococcus faecalis to Nd:YAG laser irradiation through dentin. Lasers Surg Med 26:250–261
Christensen GJ (2002) Preventing postoperative tooth sensitivity in class I, II and V restorations. J Am Dent Assoc 133:229–231
Myers DR, Battenhouse MR, Barenie JT, McKinney RV, Singh B (1987) Histopathology of furcation lesions associated with pulp degeneration in primary molars. Pediatr Dent 9:279–282
Obersztyn A (1963) Experimental investigation of factors causing resorption of deciduous teeth. J Dent Res 42:660–674
Haralabakis NB, Yiagtzis SC, Toutountzakis NM (1994) Premature or delayed exfoliation of deciduous teeth and root resorption and formation. Angle Orthod 64:151–157
Nakabayashi N, Saimi Y (1996) Bonding to intact dentin. J Dent Res 75:1706–1715
Grégoire G, Millas A (2005) Microscopic evaluation of dentin interface obtained with 10 contemporary self-etching systems: correlation with their pH. Oper Dent 30:481–491
Tay FR, Pashley DH (2001) Aggressiveness of contemporary self-etching systems. I. Depth of penetration beyond dentin smear layers. Dent Mater 17:296–308
Perdigão J, Lopes MM, Gomes G (2008) In vitro bonding performance of self-etch adhesives: II— ultramorphological evaluation. Oper Dent 33:534–549
Bolaños-Carmona V, González-López S, Haro-Muñoz C, Briones-Luján MT (2008) Interfacial morphology and bond strength of self-etching adhesives to primary dentin with or without acid etching. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 87:499–507
Agostini FG, Kaaden C, Powers JM (2001) Bond strength of self-etching primers to enamel and dentin of primary teeth. Pediatr Dent 23:481–486
da Silva Telles PD, Moreira Machado MAA, Nör JE (2001) SEM study of a self-etching primer adhesive system used for dentin bonding in primary and permanent teeth. Pediatr Dent 23:315–320
Sardella TN, de Castro FL, Sanabe ME, Hebling J (2005) Shortening of primary dentin etching time and its implication on bond strength. J Dent 33:355–362
Soares FZM, Rocha RO, Raggio DP, Sadek FT, Cardoso PEC (2005) Microtensile bond strength of different adhesive systems to primary and permanent dentin. Pediatr Dent 27:457–462
De Munck J, Vargas M, Iracki J et al (2005) One-day bonding effectiveness of new self-etch adhesives to bur-cut enamel and dentin. Oper Dent 30:39–49
Koibuchi H, Yasuda N, Nakabayashi N (2001) Bonding to dentin with a self-etching primer: the effect of smear layers. Dent Mater 17:122–126
Uekusa S, Yamaguchi K, Miyazaki M, Tsubota K, Kurokawa H, Hosoya Y (2006) Bonding efficacy of single-step self-etch systems to sound primary and permanent tooth dentin. Oper Dent 31:569–576
Can-Karabulut DC, Oz FT, Karabulut B, Batmaz I, Ilk O (2009) Adhesion to primary and permanent dentin and a simple model approach. Eur J Dent 3:32–41
Nör JE, Feigal RJ, Dennison JB, Edwards CA (1996) Dentin bonding: SEM comparison of the resin-dentin interface in primary and permanent teeth. J Dent Res 75:1396–1403
Schoop U, Kluger W, Dervisbegovic S, Goharkhay K, Wernisch J, Georgopoulos A, Sperr W, Moritz A (2006) Innovative wavelengths in endodontic treatment. Lasers Surg Med 38:624–630
Dederich DN, Zakariasen KL, Tulip J (1984) Scanning electron microscopic analysis of canal wall dentin following neodymium-yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser irradiation. J Endod 10:428–431
Hardee MW, Miserendino LJ, Kos W, Walia H (1994) Evaluation of the antibacterial effects of intracanal Nd:YAG laser irradiation. J Endod 20:377–380
Lopes-Silva AM, Lage-Marques JL (2003) Evaluation of the permeability of the furcation area of deciduous molars conditioned with Er:YAG laser and cyanoacrylate. Pesqui Odontol Bras 17:212–216
Lizarelli RFZ, Moriyama T, Bagnato VS (2002) Ablation rate and micromorphological aspects with Nd:YAG picosecond pulsed laser on primary teeth. Lasers Surg Med 31:177–185
Lizarelli RFZ, Kurachi C, Misoguti L, Bagnato VS (1999) Characterization of enamel and dentin response to Nd:YAG picosecond laser ablation. J Clin Laser Med Surg 17:127–131
Lizarelli RFZ, Moriyama T, Jorge JRP, Bagnato VS (2006) Comparative ablation rate from a Er:YAG laser on enamel and dentin of primary and permanent teeth. Laser Phys 16:849–858
Soares F, Varella CH, Pileggi R, Adewumi A, Guelmann M (2008) Impact of Er,Cr:YSGG laser therapy on the cleanliness of the root canal walls of primary teeth. J Endod 34:474–477
Anic I, Segovic S, Katanec D, Prskalo K, Najzar-Fleger D (1998) Scanning electron microscopic study of dentin lased with argon, CO2 and Nd:YAG laser. J Endod 24:77–81
Ramsköld LO, Fong CD, Strömberg T (1997) Thermal effects and antibacterial properties of energy level required to sterilize stained root canals with an Nd:YAG laser. J Endod 23:96–100
Eriksson AR, Albrektsson T (1983) Temperature threshold levels for heat-induced bone tissue injury: a vital-microscopic study in the rabbit. J Prosthet Dent 50:101–107
Gutknecht N, Kaiser F, Hassan A, Lampert F (1996) Long-term evaluation of endodontically treated teeth by Nd:YAG lasers. J Clin Laser Med Surg 14:7–11
Liu JF (2006) Effects of Nd:YAG laser pulpotomy on human primary molars. J Endod 32:404–407
Pinheiro SL, Schenka AA, Neto AA, de Souza CP, Rodriguez HM, Ribeiro MC (2009) Photodynamic therapy in endodontic treatment of deciduous teeth. Lasers Med Sci 24:521–526
Bergmans L, Moisiadis P, Teughels W, Van Meerbeek B, Quirynen M, Lambrechts P (2006) Bactericidal effect of Nd:YAG laser irradiation on some endodontic pathogens ex vivo. Int Endod J 39:547–557
Wang QQ, Zhang CF, Yin XZ (2007) Evaluation of the bactericidal effect of Er, Cr:YSGG, and Nd:YAG lasers in experimentally infected root canals. J Endod 33:830–832
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their gratitude to: LELO (Special Laboratory of Lasers in Dentistry), University of São Paulo, Brazil and FAPESP (Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo, grant 2007/55487-0), for providing the Nd:YAG laser; to Professor Victor E. Arana-Chavez, from the Oral Biology Laboratory, Department of Dental Materials, School of Dentistry, University of São Paulo, Brazil, for his assistance in the preparation of the samples for the scanning electron microscope, and to PhD student Nilton Azambuja, Department of Restorative Dentistry, for his assistance in taking the electron micrographs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guglielmi, C.A.B., Müller Ramalho, K., Scaramucci, T. et al. Evaluation of the furcation area permeability of deciduous molars treated by neodymium:yttrium–aluminum–garnet laser or adhesive. Lasers Med Sci 25, 873–880 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-009-0730-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10103-009-0730-z