Abstract
Microalgae paves the way towards a negative emission technology; however, single-pot systems combining nutrient removal and wastewater treatment are scarce in the literature. In this study, three different types of wastewater (university, municipality, and dairy industries) were studied using microalgae towards treatment and nutrient removal using Scenedesmus sp. and Chlorella sp. The experiments were carried out in 20 L reactors, for 9 days, where in achieving a maximum of algal growth rate of 770 and 725 mg/L for Scenedesmus sp. and Chlorella sp., respectively. Of the three wastewaters, dairy wastewater had the highest influent COD (3488 mg/L), which was reduced by 92% after 9 days. The pigment content was highest after 6 days (0.22 ± 0.03%), and there was no significant improvement after 9 days, suggesting a trade-off between nutrient removal, photosynthetic performance, and COD reduction. Microalgae act as a sustainable solution and negative emission technology to solve the crisis of wastewater treatment, nutrient removal and production of high-value products.
Graphical abstract

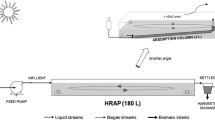
Single-pot microalage-based nutrient removal and wastewater treatment system



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The article does not include any kind of unauthorized, restricted and illegal material and data.
Abbreviations
- ASP:
-
Activated sludge process
- CEPT:
-
Common effluent treatment plant
- COD:
-
Chemical oxygen demand
- DCW:
-
Dry cell weight
- DWW:
-
Dairy wastewater
- HRT:
-
Hydraulic retention time
- MFC:
-
Microbial fuel cell
- MLD:
-
Million litre per day
- MWW:
-
Municipal wastewater
- N:
-
Nitrogen
- NPK:
-
Nitrogen phosphorus potassium
- P:
-
Phosphorus
- SPV:
-
Sulfo-phospho-vanillin
- STP:
-
Sewage treatment plant
- TCA:
-
Trichloroacetic acid
- TN:
-
Total nitrogen
- TP:
-
Total phosphorus
- UWW:
-
University wastewater
- WW:
-
Wastewater
References
Aketo T, Hoshikawa Y, Nojima D et al (2020) Selection and characterization of microalgae with potential for nutrient removal from municipal wastewater and simultaneous lipid production. J Biosci Bioeng 129:565–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2019.12.004
Alazaiza MYD, Albahnasawi A, Maskari T Al, et al (2023) Economics , and its environmental impacts
Ambika HD (2023) Positive and negative environmental impacts on algae. Elsevier Inc.
Begum H, Yusoff FMD, Banerjee S et al (2015) Availability and utilization of pigments from microalgae. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 56:2209–2222. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2013.764841
Bhatia SK, Mehariya S, Bhatia RK et al (2021) Wastewater based microalgal biorefinery for bioenergy production: Progress and challenges. Sci Total Environ 751:141599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141599
Bustos SA, Golden SS (1991) Expression of the psbDII gene in Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942 requires sequences downstream of the transcription start site. J Bacteriol 173:7525–7533. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.173.23.7525-7533.1991
Central Pollution Control Board (2020) Status of sewage generation and treatment capacity in metropolitan cities. In: ENVIS Cent. Hyg. Sanit. Sew. Treat. Syst. Technol. http://www.sulabhenvis.nic.in/Database/STST_wastewater_2090.aspx
Chen Y, Vaidyanathan S (2013) Simultaneous assay of pigments, carbohydrates, proteins and lipids in microalgae. Anal Chim Acta 776:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2013.03.005
Chokshi K, Pancha I, Ghosh A, Mishra S (2016) Microalgal biomass generation by phycoremediation of dairy industry wastewater: an integrated approach towards sustainable biofuel production. Bioresour Technol 221:455–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.09.070
Dammak I, Fersi M, Hachicha R, Abdelkafi S (2023) Current insights into growing microalgae for municipal wastewater treatment and biomass generation. Resources 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources12100119
downtoearth.org (2022) Indian agriculture: The route post-CoP 26. https://www.downtoearth.org.in/blog/climate-change/indian-agriculture-the-route-post-cop-26-81154#:~:text=As per the Third Biennial,per cent%3B and waste 2.7. Accessed 4 May 2023
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK et al (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356. https://doi.org/10.1021/AC60111A017/ASSET/AC60111A017.FP.PNG_V03
Fasaei F, Bitter JH, Slegers PM, Van BAJB (2018) Techno-economic evaluation of microalgae harvesting and dewatering systems. Algal Res 31:347–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2017.11.038
Gowd SC, Kumar D, Lin R, Rajendran K (2022a) Nutrient recovery from wastewater in India: a perspective from mass and energy balance for a sustainable circular economy. Bioresour Technol Reports 18:101079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2022.101079
Gowd SC, Ramakrishna S, Rajendran K (2022b) Wastewater in India: an untapped and under-tapped resource for nutrient recovery towards attaining a sustainable circular economy. Chemosphere 291:132753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132753
Gowd SC, Ramesh P, Vigneswaran VS et al (2023) Life cycle assessment of comparing different nutrient recovery systems from municipal wastewater: a path towards self-reliance and sustainability. J Clean Prod 410:137331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.137331
HACH (2014) Nitrite Method 8153. In: Nitrite, Ferr. sulfate method (Method 8153). https://www.hach.com/asset-get.download.jsa?id=7639983744. Accessed 25 Sep 2022
HACH (2019) Phosphorus, Reactive (Orthophosphate) Molybdovanadate Method. https://in.hach.com/phosphate-standard-solution-500-mg-l-as-po4-nist-pk-16-10-ml-voluette-ampules/product-downloads?id=15500211949. Accessed 22 Sep 2022
Hemalatha M, Sravan JS, Min B, Venkata Mohan S (2019) Microalgae-biorefinery with cascading resource recovery design associated to dairy wastewater treatment. Bioresour Technol 284:424–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.03.106
Katiyar R, Gurjar BR, Kumar A, Bharti RK (2021) An integrated approach for phycoremediation of municipal wastewater and production of sustainable transportation fuel using oleaginous Chlorella sp. J Water Process Eng 42:102183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102183
Klein RL, Gibbs C (2019) Nitrate method 8039. In: Water Anal. Handb. https://in.hach.com/quick.search-quick.search.jsa?keywords=DOC316.53.01066. Accessed 22 Sep 2022
Lee CS, Lee SA, Ko SR et al (2015) Effects of photoperiod on nutrient removal, biomass production, and algal-bacterial population dynamics in lab-scale photobioreactors treating municipal wastewater. Water Res 68:680–691. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2014.10.029
Li K, Liu Q, Fang F et al (2019) Microalgae-based wastewater treatment for nutrients recovery: a review. Bioresour Technol 291:121934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.121934
López-Sánchez A, Silva-Gálvez AL, Aguilar-Juárez Ó, et al (2022) Microalgae-based livestock wastewater treatment (MbWT) as a circular bioeconomy approach: Enhancement of biomass productivity, pollutant removal and high-value compound production. J Environ Manage 308:. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114612
Masojídek J, Torzillo G (2014) Mass cultivation of freshwater microalgae. Ref Modul Earth Syst Environ Sci, pp 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-409548-9.09373-8
Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change (2022) National status of waste water generation and treatment. http://www.sulabhenvis.nic.in/Database/STST_wastewater_2090.aspx. Accessed 16 May 2023
Ministry of Jal Shakti (2022) Per capita water availability. https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1882796. Accessed 22 Oct 2022
Mishra SK, Suh WI, Farooq W et al (2014) Rapid quantification of microalgal lipids in aqueous medium by a simple colorimetric method. Bioresour Technol 155:330–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.12.077
Mohsenpour SF, Hennige S, Willoughby N et al (2021) Integrating micro-algae into wastewater treatment: a review. Sci Total Environ 752:142168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142168
Nishshanka GKSH, Liyanaarachchi VC, Premaratne M et al (2021) Wastewater-based microalgal biorefineries for the production of astaxanthin and co-products: current status, challenges and future perspectives. Bioresour Technol 342:126018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126018
Nzayisenga JC, Farge X, Groll SL, Sellstedt A (2020) Effects of light intensity on growth and lipid production in microalgae grown in wastewater. Biotechnol Biofuels 13:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-019-1646-x
Pancha I, Chokshi K, Maurya R et al (2015) Salinity induced oxidative stress enhanced biofuel production potential of microalgae Scenedesmus sp. CCNM 1077. Bioresour Technol 189:341–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.04.017
Silambarasan S, Logeswari P, Sivaramakrishnan R, et al (2023) Scenedesmus sp. strain SD07 cultivation in municipal wastewater for pollutant removal and production of lipid and exopolysaccharides. Environ Res 218:115051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.115051
Slocombe SP, Ross M, Thomas N et al (2013) A rapid and general method for measurement of protein in micro-algal biomass. Bioresour Technol 129:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.10.163
Stanier RY, Kunisawa R, Mandel M, Cohen-Bazire G (1971) Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (order Chroococcales). Bacteriol Rev 35:171–205. https://doi.org/10.1128/mmbr.35.2.171-205.1971
Statista.com (2023) Value of fertilizers imported into India from financial year 2011 to 2022. https://www.statista.com/statistics/625203/import-value-of-fertilizer-india/. Accessed 10 May 2023
The World Bank (2021) Renewable internal freshwater resources per capita. https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/ER.H2O.INTR.PC?end=2020&start=1961&view=chart. Accessed 10 Jun 2023
Trivedi J, Atray N, Agrawal D (2021) Enhanced biomass production of Scenedesmus obliquus in a flat-panel photobioreactor, grown in photoautotrophic mode. Biofuels 12:53–59. https://doi.org/10.1080/17597269.2018.1448634
United Nations (2022) World population forecast. https://www.un.org/en/global-issues/population#:~:text=The world’s population is expected,billion in the mid-2080s. Accessed 15 May 2023
USEPA (1980) HACH 8000: Oxygen demand, chemical using reactor digestion method. https://in.hach.com/quick.search-quick.search.jsa?keywords=DOC316.53.01099. Accessed 15 Oct 2022
Van Wychen S, Laurens LML (2013) Determination of total carbohydrates in algal biomass. Tech Rep NREL/TP-5100–60957 Natl Renew Energy Lab 17
Zheng H, Liu M, Lu Q et al (2018) Balancing carbon/nitrogen ratio to improve nutrients removal and algal biomass production in piggery and brewery wastewaters. Bioresour Technol 249:479–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.10.057
Ziganshina EE, Bulynina SS, Ziganshin AM (2022) Growth characteristics of chlorella sorokiniana in a photobioreactor during the utilization of different forms of nitrogen at various temperatures. Plants 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11081086
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Vijayawada Municipal Corporation and Sangam Milk Producers Company Limited, Guntur, for providing wastewater to carry out the experiment.
Funding
This work was carried out with the financial support received from SRM University—AP through the SRM University—AP Research Grant under Grant No. SRMAP/URG/E&EP/2022–23/004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SCG: Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation, Writing and Editing. KM: Methodology and Data curation. PG: Data curation. JM: Review and Editing. IP: Review and Editing. KR: Writing—Review and Editing, Supervision, Project Administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Ethical approval
The authors declare that no animal and human studies are presented in this manuscript and no potentially identifiable human images or data are given in this research. Ethical approval does not apply since it is considered that there are no ethical conflicts.
Consent to participate
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent for publication
I, Karthik Rajendran, grant Springer Nature the exclusive right to publish and distribute my original manuscript titled " Microalgae as a single-pot system for nutrient removal and wastewater treatment: Comparison of effluents and species performance" in Clean Technologies and Environmental Policy and any related publications, both in print and electronic formats. I confirm that the manuscript has not been published elsewhere and is not under consideration by any other publisher. All co-authors have been appropriately credited and have consented to the submission and publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gowd, S.C., Mehta, K., Ganeshan, P. et al. Microalgae as a single-pot system for nutrient removal and wastewater treatment: comparison of effluents and species performance. Clean Techn Environ Policy (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-024-02808-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-024-02808-z