Abstract
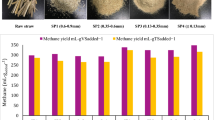
Lignocellulosic agro-residues can be used as a low-cost raw material for the production of biomethane, which in turn can be used as a sustainable alternative for conventional fossil fuels. In the present study, the effect of mild-thermal pretreatment on the biomethanation potential of two different lignocellulosic substrates, rice straw and napier grass, was evaluated. The substrates were thermally pretreated at 80 °C and 120 °C for 1 h and further subjected to anaerobic digestion at 30 °C for 40 days. The thermally pretreated napier grass showed a methane yield enhancement of 14% (25.66 ml CH4/gsub) with respect to the control, whereas the thermally pretreated rice straw showed an enhancement of 56% (15.12 ml CH4/gsub) with respect to the control. The enhancement in the biomethane yield of the pretreated substrates may be attributed to the partial biodegradation of carbon present in the biomass, which can be validated by the COD reduction observed (up to 67%) after the anaerobic digestion process. FTIR analysis of the substrates indicated the degradation and/or transformation of the organic compounds after thermal pretreatment. In conclusion, the study revealed that mild-thermal pretreatment can be employed as an effective strategy to enhance the biomethanation potential of lignocellulosic substrates.
Graphic abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abbas Y, Jamil F, Rafiq S, Ghauri M, Khurram MS, Aslam M, Bokhari A, Faisal A, Rashid U, Yun S, Mubeen M (2020) Valorization of solid waste biomass by inoculation for the enhanced yield of biogas. Clean Technol Environ Policy 22(2):513–522. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-019-01799-6
Abraham A, Mathew AK, Park H, Choi O, Sindhu R, Parameswaran B, Pandey A, Park JH, Sang BI (2020) Pretreatment strategies for enhanced biogas production from lignocellulosic biomass. Biores Technol 301:122725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122725
Agricultural statistics at a glance 2018, http://agricoop.gov.in/ Accessed on 10 Sep 2020
APHA, 2005. Standard methods for the examination of Water and Wastewater, 21th ed. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environmental Federation, Washington, DC, New York, USA
Angelidaki I, Alves M, Bolzonella D, Borzacconi L, Campos JL, Guwy AJ, Van Lier JB (2009) Defining the biomethane potential (BMP) of solid organic wastes and energy crops: a proposed protocol for batch assays. Water Sci TeChnol 59(5):927–934. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2009.040
Ariunbaatar J, Panico A, Esposito G, Pirozzi F, Lens PN (2014) Pretreatment methods to enhance anaerobic digestion of organic solid waste. Appl Energy 123:143–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.02.035
Bauer A, Lizasoain J, Theuretzbacher F, Agger JW, Rincón M, Menardo S, Saylor MK, Enguídanos R, Nielsen PJ, Potthast A, Zweckmair T (2014) Steam explosion pretreatment for enhancing biogas production of late harvested hay. Biores Technol 166:403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(19)62573-6
Bhuvaneshwari S, Hettiarachchi H, Meegoda JN (2019) Crop residue burning in India: policy challenges and potential solutions. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16(5):832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16050832
Bolado-Rodríguez S, Toquero C, Martín-Juárez J, Travaini R, García-Encina PA (2016) Effect of thermal, acid, alkaline and alkaline-peroxide pretreatments on the biochemical methane potential and kinetics of the anaerobic digestion of wheat straw and sugarcane bagasse. Biores Technol 201:182–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.11.047
Chandra R, Takeuchi H, Hasegawa T (2012) Methane production from lignocellulosic agricultural crop wastes: a review in context to second generation of biofuel production. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16(3):1462–1476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2011.11.035
Chen X, Yu J, Zhang Z, Lu C (2011) Study on structure and thermal stability properties of cellulose fibers from rice straw. Carbohydr polym 85(1):245–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.02.022
Dai X, Hua Y, Dai L, Cai C (2019) Particle size reduction of rice straw enhances methane production under anaerobic digestion. Biores Technol 293:122043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122043
Du J, Qian Y, Xi Y, Lü X (2019) Hydrothermal and alkaline thermal pretreatment at mild temperature in solid state for physicochemical properties and biogas production from anaerobic digestion of rice straw. Renew Energy 139:261–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.01.097
Esposito G, Frunzo L, Liotta F, Panico A, Pirozzi F (2012) Bio-methane potential tests to measure the biogas production from the digestion and co-digestion of complex organic substrates. Open Environ Eng J. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874829501205010001
Holm-Nielsen JB, Al Seadi T, Oleskowicz-Popiel P (2009) The future of anaerobic digestion and biogas utilization. Biores Technol 100(22):5478–5484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.12.046
Kim M, Kim BC, Nam K, Choi Y (2018) Effect of pretreatment solutions and conditions on decomposition and anaerobic digestion of lignocellulosic biomass in rice straw. Biochem Eng J 140:108–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2018.09.012
Kumar B, Subrahmanyam B, Akhil P and Prashanth B, (2017) Biogas: a renewable energy for future. Int J Mech Eng Res Dev (IJMERD), 6(1). https://ssrn.com/abstract=3516504
Kumar B, Bhardwaj N, Agrawal K, Chaturvedi V, Verma P (2020) Current perspective on pretreatment technologies using lignocellulosic biomass: an emerging biorefinery concept. Fuel Process Technol 199:106244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2019.106244
Li L, Kong X, Yang F, Li D, Yuan Z, Sun Y (2012) Biogas production potential and kinetics of microwave and conventional thermal pretreatment of grass. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166(5):1183–1191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-011-9503-9
Li D, Zhou Y, Tan Y, Pathak S, bin Abdul Majid M, Ng WJ (2016) Alkali-solubilized organic matter from sludge and its degradability in the anaerobic process. Bioresour Technol 200:579–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.10.083
Luo T, Huang H, Mei Z, Shen F, Ge Y, Hu G, Meng X (2019) Hydrothermal pretreatment of rice straw at relatively lower temperature to improve biogas production via anaerobic digestion. Chin Chem Lett 30(6):1219–1223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2019.03.018
Maheswari CU, Reddy KO, Muzenda E, Guduri BR, Rajulu AV (2012) Extraction and characterization of cellulose microfibrils from agricultural residue–Cocos nucifera L. Biomass Bioenerg 46:555–563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.06.039
Mohapatra S, Mishra C, Behera SS, Thatoi H (2017) Application of pretreatment, fermentation and molecular techniques for enhancing bioethanol production from grass biomass–a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 78:1007–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.05.026
Momayez F, Karimi K, Horváth IS (2018) Enhancing ethanol and methane production from rice straw by pretreatment with liquid waste from biogas plant. Energy Convers Manage 178:290–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.10.023
National Policy for Management of Crop Residues (NPMCR) (2018). https://agricoop.nic.in/sites/default/files/NPMCR_1.pdf Accessed 20 Jan 2021
Patipong T, Lotrakul P, Padungros P, Punnapayak H, Bankeeree W, Prasongsuk S (2019) Enzymatic hydrolysis of tropical weed xylans using xylanase from Aureobasidium melanogenum PBUAP46 for xylooligosaccharide production. 3 Biotech 9(2):56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1586-y
Paudel SR, Banjara SP, Choi OK, Park KY, Kim YM, Lee JW (2017) Pretreatment of agricultural biomass for anaerobic digestion: current state and challenges. Biores Technol 245:1194–1205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.182
Rajput AA, Visvanathan C (2018) Effect of thermal pretreatment on chemical composition, physical structure and biogas production kinetics of wheat straw. J Environ Manage 221:45–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.05.011
Reddy JP, Rhim JW (2018) Extraction and characterization of cellulose microfibers from agricultural wastes of onion and garlic. J Nat Fibers 15(4):465–473. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2014.945227
Sawanon S, Sangsri P, Leungprasert S, Sinbuathong N (2017) Methane production from Napier grass by co-digestion with cow dung. In: Zhang X, Dincer I (eds) Energy solutions to combat global warming. Springer, Cham, pp 169–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-26950-4_7
Sawasdee V, Pisutpaisal N (2014) Feasibility of biogas production from napier grass. Energy Procedia 61:1229–1233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2014.11.1064
Shahabazuddin Md, Sheikh AY, Sandeep NM (2019) Sustainable low-thermal pretreatment enhances substrate solubilization and biogas production: a case study with potato peel waste. Int J Innov Eng Technol 12(2):31–38. https://doi.org/10.21172/ijiet.122.05
Sharma SK, Mishra IM, Sharma MP, Saini JS (1988) Effect of particle size on biogas generation from biomass residues. Biomass 17(4):251–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.08.182
Sluiter A, Hames B, Ruiz R, Scarlata C, Sluiter J, Templeton D, Crocker DLAP (2008) Determination of structural carbohydrates and lignin in biomass. Lab Anal Proced 1617(1):1–16
Surendra KC, Ogoshi R, Zaleski HM, Hashimoto AG, Khanal SK (2018) High yielding tropical energy crops for bioenergy production: effects of plant components, harvest years and locations on biomass composition. Biores Technol 251:218–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.12.044
Takara D, Khanal SK (2015) Characterizing compositional changes of Napier grass at different stages of growth for biofuel and biobased products potential. Biores Technol 188:103–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-1164-y
Tripathi L, Mishra AK, Dubey AK, Tripathi CB, Baredar P (2016) Renewable energy: an overview on its contribution in current energy scenario of India. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 60:226–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.01.047
Tsai MH, Lee WC, Kuan WC, Sirisansaneeyakul S, Savarajara A (2018) Evaluation of different pretreatments of Napier grass for enzymatic saccharification and ethanol production. Energy Sci Eng 6(6):683–692. https://doi.org/10.1002/ese3.243
Wang D, Shen F, Yang G, Zhang Y, Deng S, Zhang J, Zeng Y, Luo T, Mei Z (2018) Can hydrothermal pretreatment improve anaerobic digestion for biogas from lignocellulosic biomass? Biores Technol 249:117–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.09.197
Weiland P (2010) Biogas production: current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85(4):849–860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2246-7
Yan Y, Chen H, Xu W, He Q, Zhou Q (2013) Enhancement of biochemical methane potential from excess sludge with low organic content by mild thermal pretreatment. Biochem Eng J 70:127–134. https://doi.org/10.18517/ijaseit.7.2.2094
Zheng Y, Zhao J, Xu F, Li Y (2014) Pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for enhanced biogas production. Prog Energy Combust Sci 42:35–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecs.2014.01.001
Zhu S, Wu Y, Yu Z, Liao J, Zhang Y (2005) Pretreatment by microwave/alkali of rice straw and its enzymic hydrolysis. Process Biochem 40(9):3082–3086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2005.03.016
Acknowledgements
Inchara Crasta is grateful to Ms. Asha M for assistance with the analytical techniques.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the work done in the present study is original. The authors also declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crasta, I., Sivakumar, S., Banuvalli, B. et al. Mild-thermal pretreatment of agro-residues enhances biomethanation potential: a comparative study of napier grass and rice straw. Clean Techn Environ Policy 25, 737–745 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-021-02148-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-021-02148-2