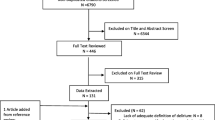
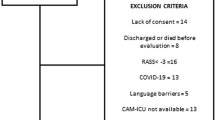
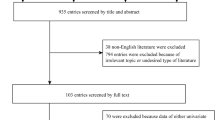
Abstract
Delirium is a common complication in acute stroke patients. A 2011 meta-analysis showed an increased risk of in-hospital mortality and mortality within 12 months post-stroke, longer hospitalization durations, and increased likelihood of being discharged to a nursing home for patients experiencing post-stroke delirium. There is a need for an updated meta-analysis with several new studies having been since published. The PubMed and Scopus databases were screened for relevant studies. Inclusion criteria were as follows: retrospective or prospective studies reporting on the effects of delirium accompanying acute stroke on mortality, functional outcomes, length of hospital stay and need for re-admission. Strength of association was presented as pooled adjusted relative risk (RR) for categorical outcomes and weighted mean difference (WMD) for continuous outcomes. Statistical analysis was done using STATA version 16.0. The meta-analysis included 22 eligible articles. Eighteen of the 22 studies were prospective follow ups. Included studies were of good quality. Post-stroke delirium was associated with increased risk of in-hospital mortality, as well as mortality within 12 months post-stroke. Patients with delirium experienced increased hospital stay durations, were at greater risk for hospital readmission, and showed elevated risk for poor functional outcome. Compared to those who did not have delirium, stroke patients with delirium were 42% less likely to be discharged to home. Acute stroke patients with delirium are at an increased risk for poor short- and long-term outcomes. More research is needed to identify the best set of interventions to manage such patients and improve outcomes.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Marcantonio ER (2017) Delirium in Hospitalized Older Adults. N Engl J Med 377(15):1456–1466
Wilson JE, Mart MF, Cunningham C, Shehabi Y, Girard TD, MacLullich AMJ (2020) Delirium. Nat Rev Dis Prim 6(1):90
Fuchs S, Bode L, Ernst J, Marquetand J, von Känel R, Böttger S (2020) Delirium in elderly patients: Prospective prevalence across hospital services. Gen Hosp Psychiatr 67:19–25
Ospina JP, King F IV, Madva E, Celano CM (2018) Epidemiology, mechanisms, diagnosis, and treatment of delirium: a narrative review. Clin Med Ther 1(1):3
Al Farsi RS, Al Alawi AM, Al Huraizi AR, Al-Saadi T, Al-Hamadani N, Al Zeedy K et al (2023) Delirium in Medically Hospitalized Patients: Prevalence, Recognition and Risk Factors: A Prospective Cohort Study. J Clin Med 12(12):3897
Shaw RC, Walker G, Elliott E, Quinn TJ (2019) Occurrence Rate of Delirium in Acute Stroke Settings: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Stroke 50(11):3028–3036
Hshieh TT, Inouye SK, Oh ES (2020) Delirium in the elderly. Clin Geriatr Med 36(2):183–199
Maldonado JR (2018) Delirium pathophysiology: An updated hypothesis of the etiology of acute brain failure. Int J Geriatr Psychiatr 33(11):1428–1457
Kowalska K, Klimiec E, Weglarczyk K, Pera J, Slowik A, Siedlar M et al (2018) Reduced ex vivo release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and elevated plasma interleukin-6 are inflammatory signatures of post-stroke delirium. J Neuroinflammation. 15(1):111. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1156-y. [cited 2021 Nov 8]
Ahmed S, Leurent B, Sampson EL (2014) Risk factors for incident delirium among older people in acute hospital medical units: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Age Ageing 43(3):326–333
Inouye SK, Charpentier PA (1996) Precipitating factors for delirium in hospitalized elderly persons. Predictive model and interrelationship with baseline vulnerability. JAMA. 275(11):852–7
Ormseth CH, LaHue SC, Oldham MA, Josephson SA, Whitaker E, Douglas VC (2023) Predisposing and Precipitating Factors Associated With Delirium: A Systematic Review. JAMA Netw Open 6(1):e2249950
Franco JG, Valencia C, Bernal C, Ocampo MV, Trzepacz PT, de Pablo J et al (2010) Relationship between cognitive status at admission and incident delirium in older medical inpatients. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 22(3):329–337
Gravante F, Giannarelli D, Pucci A, Gagliardi AM, Mitello L, Montagna A, Latina R (2021) Prevalence and risk factors of delirium in the intensive care unit: An observational study. Nurs Crit Care 26(3):156–165
Wakefield BJ (2002) Risk for acute confusion on hospital admission. Clin Nurs Res 11(2):153–172
Sandberg O, Franklin KA, Bucht G, Gustafson Y (2001) Sleep apnea, delirium, depressed mood, cognition, and ADL ability after stroke. J Am Geriatr Soc 49(4):391–397
Oldenbeuving AW, de Kort PLM, Jansen BPW, Algra A, Kappelle LJ, Roks G (2011) Delirium in the acute phase after stroke: incidence, risk factors, and outcome. Neurology 76(11):993–999
Markus R, Reutens DC, Kazui S, Read S, Wright P, Pearce DC et al (2004) Hypoxic tissue in ischaemic stroke: persistence and clinical consequences of spontaneous survival. Brain J Neurol 127(Pt 6):1427–1436
Hoffman WE, Wheeler P, Edelman G, Charbel FT, Torres NJ, Ausman JI (2000) Hypoxic brain tissue following subarachnoid hemorrhage. Anesthesiology 92(2):442–446
Oldenbeuving AW, de Kort PLM, Jansen BPW, Roks G, Kappelle LJ (2007) Delirium in acute stroke: a review. Int J Stroke Off J Int Stroke Soc 2(4):270–275
Dahl MH, Rønning OM, Thommessen B (2010) Delirium in acute stroke–prevalence and risk factors. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 190:39–43
Alvarez-Perez FJ, Paiva F (2017) Prevalence and Risk Factors for Delirium in Acute Stroke Patients. A Retrospective 5-Years Clinical Series. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis Off J Natl Stroke Assoc. 26(3):567–73
Shi Q, Presutti R, Selchen D, Saposnik G (2012) Delirium in acute stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stroke 43(3):645–649
Wells G, Shea B, O’Connell D, Robertson J, Peterson J, Welch V et al (2014) The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analysis. Available from: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp. Accessed 8 Nov 2021
Higgins J, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page M, et al. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions [Internet]. [cited 2021 Jul 31]. Available from: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current. Accessed 31 July 2021
Miu DKY, Yeung JCY (2013) Incidence of post-stroke delirium and 1-year outcome. Geriatr Gerontol Int 13(1):123–129
Kotfis K, Bott-Olejnik M, Szylińska A, Listewnik M, Rotter I. Characteristics, Risk Factors And Outcome Of Early-Onset Delirium In Elderly Patients With First Ever Acute Ischemic Stroke - A Prospective Observational Cohort Study. Clin Interv Aging [Internet]. 2019 Oct 21 [cited 2021 Nov 8];14:1771–82. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6814355/. Accessed 8 Nov 2021
Qu J, Chen Y, Luo G, Zhong H, Xiao W, Yin H (2018) Delirium in the Acute Phase of Ischemic Stroke: Incidence, Risk Factors, and Effects on Functional Outcome. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis Off J Natl Stroke Assoc 27(10):2641–2647
Pasińska P, Wilk A, Kowalska K, Szyper-Maciejowska A, Klimkowicz-Mrowiec A (2019) The long-term prognosis of patients with delirium in the acute phase of stroke: PRospective Observational POLIsh Study (PROPOLIS). J Neurol 266(11):2710–2717
Vahidy FS, Bambhroliya AB, Meeks JR, Rahman O, Ely EW, Slooter AJC et al (2019) In-hospital outcomes and 30-day readmission rates among ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke patients with delirium. PLoS ONE 14(11):e0225204
Klimiec-Moskal E, Lis A, Pera J, Slowik A, Dziedzic T. Subsyndromal delirium is associated with poor functional outcome after ischaemic stroke. 2019 [cited 2021 Nov 8]; Available from: https://dl.uswr.ac.ir/handle/Hannan/54384. Accessed 8 Nov 2021
Dostović Z, Smajlović D, Sinanović O, Vidović M (2009) Duration of delirium in the acute stage of stroke. Acta Clin Croat 48(1):13–17
Mc Manus JT, Pathansali R, Ouldred E, Stewart R, Jackson SHD (2011) Association of delirium post-stroke with early and late mortality. Age Ageing 40(2):271–274
Sheng AZ, Shen Q, Cordato D, Zhang YY, Yin Chan DK (2006) Delirium within three days of stroke in a cohort of elderly patients. J Am Geriatr Soc 54(8):1192–1198
Melkas S, Laurila JV, Vataja R, Oksala N, Jokinen H, Pohjasvaara T et al (2012) Post-stroke delirium in relation to dementia and long-term mortality. Int J Geriatr Psychiatr 27(4):401–408
Hénon H, Lebert F, Durieu I, Godefroy O, Lucas C, Pasquier F et al (1999) Confusional state in stroke: relation to preexisting dementia, patient characteristics, and outcome. Stroke 30(4):773–779
Gustafson Y, Olsson T, Eriksson S, Asplund K, Bucht G. Acute Confusional States (Delirium) in Stroke Patients. Cerebrovasc Dis [Internet]. 1991 [cited 2021 Nov 8];1(5):257–64. Available from: https://www.karger.com/Article/FullText/108852. Accessed 8 Nov 2021
Ojagbemi A, Bello T, Elugbadebo O, Owolabi M, Baiyewu O (2020) Different Cognitive and Functional Outcomes in Attenuated and Full Delirium Syndromes Among Recent Stroke Survivors. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis Off J Natl Stroke Assoc 29(11):105251
Caeiro L, Ferro JM, Albuquerque R, Figueira ML (2004) Delirium in the first days of acute stroke. J Neurol 251(2):171–178
Nydahl P, Bartoszek G, Binder A, Paschen L, Margraf NG, Witt K, et al. Prevalence for delirium in stroke patients: A prospective controlled study. Brain Behav [Internet]. 2017 Jun 23 [cited 2021 Nov 8];7(8):e00748. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5561309/. Accessed 8 Nov 2021
Kozak HH, Uğuz F, Kılınç İ, Uca AU, SerhatTokgöz O, Akpınar Z et al (2017) Delirium in patients with acute ischemic stroke admitted to the non-intensive stroke unit: Incidence and association between clinical features and inflammatory markers. Neurol Neurochir Pol 51(1):38–44
Turco R, Bellelli G, Morandi A, Gentile S, Trabucchi M (2013) The effect of poststroke delirium on short-term outcomes of elderly patients undergoing rehabilitation. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol 26(2):63–68
Zaitoun AM, Elsayed DAF, Ramadan BM, Gaffar HAA. Assessment of the risk factors and functional outcome of delirium in acute stroke. Egypt J Neurol Psychiatry Neurosurg [Internet]. 2019 Feb 20 [cited 2021 Nov 8];55(1):17. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41983-019-0059-x
Fialho Silva IT, Assis Lopes P, Timotio Almeida T, Ramos SC, CalimanFontes AT, Guimarães Silva D et al (2021) Impact of Delirium and Its Motor Subtypes on Stroke Outcomes. Stroke 52(4):1322–1329
McManus J, Pathansali R, Hassan H, Ouldred E, Cooper D, Stewart R, Macdonald A, Jackson S (2009) The course of delirium in acute stroke. Age Ageing 38(4):385–389
Ali S, Patel M, Jabeen S, Bailey RK, Patel T, Shahid M, et al. Insight into Delirium. Innov Clin Neurosci [Internet]. 2011 Oct [cited 2021 Nov 8];8(10):25–34. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3225129/. Accessed 8 Nov 2021
Mansutti I, Saiani L, Palese A. Detecting delirium in patients with acute stroke: a systematic review of test accuracy. BMC Neurol [Internet]. 2019 Dec 2 [cited 2021 Nov 8];19(1):310. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1547-4
Makin SDJ, Wardlaw J (2014) Predicting delirium after a stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 85(4):357
Carin-Levy G, Mead GE, Nicol K, Rush R, van Wijck F (2012) Delirium in acute stroke: screening tools, incidence rates and predictors: a systematic review. J Neurol 259(8):1590–1599
Funding
Zhejiang Province Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Plan Project (No.: 2020ZB183).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XG, SJ conceived and designed the study; YZ, LH were involved in literature search and data collection; LH and WY analyzed the data; XG, SJ wrote the paper; and WY reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary file 1
(DOC 79.5 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, X., Jin, S., Zhou, Y. et al. Impact of delirium on acute stroke outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurol Sci 45, 1897–1911 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-023-07287-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-023-07287-6