Abstract
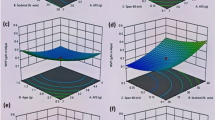
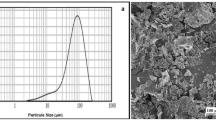
In this study, the influence of glycerol and sonicated soybean expeller (SSE) on composite edible films supporting natamycin and nisin was investigated using Response Surface Methodology. Assessments were conducted on mechanical properties, moisture content, water solubility (SW), and color. Optimal results were achieved with 0.46% SSE and 1.4% glycerol, yielding a maximum tensile strength (TS) of 1.0 ± 0.1 MPa and a minimum SW of 19.0 ± 0.3%. SSE had no impact on Tg values (82–89 °C), while antimicrobials reduced Tg (70–73 °C) due to increased water retention. Water vapor permeability was (2.5 ± 0.2) × 10–9 −1 s−1 Pa−1. FTIR analysis revealed strong component interactions. The composite films demonstrated biodegradability in compost after seven days and effective action against Listeria innocua and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. These findings suggest that these materials hold promise as active films for food preservation.




Similar content being viewed by others

References
Alirezalu, K., Pirouzi, S., Yaghoubi, M., Karimi-Dehkordi, M., Jafarzadeh, S., & Khaneghah, A.M. (2021). Packaging of beef fillet with active chitosan film incorporated with ɛ-polylysine: An assessment of quality indices and shelf life. Meat Science, 176, 108475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2021.108475
Arismendi, C., Chillo, S., Conte, A., Del Nobile, M.A., Flores, S., & Gerschenson, L.N. (2013). Optimization of physical properties of xanthan gum/tapioca starch edible matrices containing potassium sorbate and evaluation of its antimicrobial effectiveness. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 53(1), 290-296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2013.01.022
ASTM D1925 (1988). Standard Test Method for Yellowness Index of Plastics. American Society for Testing and Materials. Philadelphia, USA.
ASTM E96-00 (2000). Standard test method for water vapor transmission of materials. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, USA.
Berti, S., Jagus, R.J., & Flores, S.K. (2021). Effect of Rice Bran Addition on Physical Properties of Antimicrobial Biocomposite Films Based on Starch. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 1–12.
Berti, S., Flores, S.K., & Jagus, R.J. (2020) Improvement of the microbiological quality of Argentinian Port Salut cheese by applying starch‐based films and coatings reinforced with rice bran and containing natural antimicrobials. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, e14827.
Bodirlau, R., Teaca, C.A., & Spiridon, I. (2013). Influence of natural fillers on the properties of starch-based biocomposite films. Composites Part B: Engineering, 44(1), 575-583. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.14827
Castellanos-Fuentes, A.P., Genevois, C.E., Flores, S.K., & de Escalada Pla, M.F. (2020). Valorisation of soy by-products as substrate for food ingredients containing L. casei through solid state fermentation. LWT, 132, 109779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2020.109779
Civelek, I., & Cagri-mehmetoglu, A. (2019). Determination of Antifungal Effect of Edible Coatings Containing Williopsis saturnus var. saturnus Against Yeast and Mold Growth on Kashar Cheese. Journal of Food Science, 84(2), 311–318. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.14431
Chen, J., Wang, X., Long, Z., Wang, S., Zhang, J., & Wang, L. (2020). Preparation and performance of thermoplastic starch and microcrystalline cellulose for packaging composites: Extrusion and hot pressing. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 165, 2295-2302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.117
Costa, M.J., Maciel, L.C., Teixeira, J.A., Vicente, A.A., & Cerqueira, M.A. (2018). Use of edible films and coatings in cheese preservation: Opportunities and challenges. Food Research International, 107, 84–92.
Durango, A.M., Soares, N.D.F., & Arteaga, M.R., (2011). Filmes y revestimientos comestibles como empaques activos biodegradables en la conservación de alimentos. Biotecnología en el Sector Agropecuario y Agroindustrial, 9(1), 112-118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2018.02.013
Edhirej, A., Sapuan, S., Jawaid, M., & Zahari, N. (2017). Cassava/sugar palm fiber reinforced cassava starch hybrid composites: Physical, thermal and structural properties. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 101, 75–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.03.045
Fang, J.M., Fowler, P.A., Tomkinson, J., & Hill C.A.S. (2002). The preparation and characterization of a series of chemically modified potato starches. Carbohydrate Polymers, 47(3):245–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(01)00187-4
Freitas, P.A., Arias, C.I.L.F., Torres-Giner, S., González-Martínez, C., & Chiralt, A. (2021). Valorization of rice straw into cellulose microfibers for the reinforcement of thermoplastic corn starch films. Applied Sciences, 11(18), 8433. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11188433
Galicia-García, T., Martínez‐Bustos, F., Jiménez‐Arévalo, O.A., Arencón, D., Gámez-Pérez, J., & Martínez, A.B. (2012). Films of native and modified starch reinforced with fiber: Influence of some extrusion variables using response surface methodology. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 126(S1), E327-E336. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.36982
Jafarzadeh, S., Nafchi, A.M., Salehabadi, A., Oladzad-Abbasabadi, N., & Jafari, S.M. (2021). Application of bio-nanocomposite films and edible coatings for extending the shelf life of fresh fruits and vegetables. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 102405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2021.102405
Juan N.A., Massigoge J.I., Errasquin L., Mendez J.M, Ochandio D.C., Alejandro Eduardo Saavedra A.E., Paolilli M.C., Alladio R.M., Accoroni C., Behr E.F. (2016). Quality of the processed soybeans and expeller produced by the extrusion-pressing industry in Argentina. INTI report.
https://inta.gob.ar/documentos/calidad-de-la-soja-procesada-y-del-expeller-producido-por-la-industria-de-extrusado-prensado-en-argentina Last accessed: june 2023
Kacurakova, M., Capek, P., Sasinkova, V., Wellner, N., & Ebringerova, A. (2000). FT-IR study of plant cell wall model compounds: pectic polysaccharides and hemicelluloses. Carbohydrate polymers, 43(2), 195-203. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(00)00151-X
Kargarzadeh, H., Johar, N., & Ahmad, I. (2017). Starch biocomposite film reinforced by multiscale rice husk fiber. Composites Science and Technology, 151, 147–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.08.018
Kocabaş, D.S., Akçelik, M.E., Bahçegül, E., & Özbek, H.N. (2021). Bulgur bran as a biopolymer source: Production and characterization of nanocellulose-reinforced hemicellulose-based biodegradable films with decreased water solubility. Industrial Crops and Products, 171, 113847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113847
Manley, M., Van Zyl, L., & Osborne, B. G. (2002). Using Fourier transform near infrared spectroscopy in determining kernel hardness, protein and moisture content of whole wheat flour. Journal of Near Infrared Spectroscopy, 10(1), 71-76. https://doi.org/10.1255/jnirs.323
Nandane, A.S., & Jain, R.K. (2018). Optimization of formulation and process parameters for soy protein-based edible film using response surface methodology. Journal of Packaging Technology and Research, 2(3), 203-210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41783-018-0045-2
Ollé Resa, C., Jagus, R., & Gerschenson, L. (2014). Effect of natamycin, nisin and glycerol on the physicochemical properties, roughness and hydrophobicity of tapioca starch edible films. Materials Science and Engineering C, 40, 281–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2014.04.005
Pagella, C., Spigno, G., & De Faveri, D.M. (2002). Characterization of starch based edible coatings. Food and Bioproducts Processing, 80(3), 193–198. https://doi.org/10.1205/096030802760309214
Paolilli, M.C., Cabrini, S.M., Pagliaricci, L.O., Fillat, F.A., & Bitar, M.V. (2019). Importancia de la cadena de soja en Argentina. Revista de Tecnología Agropecuaria, 10(39), 42-46.
Silva, V.D.M., Macedo, M.C.C., Rodrigues, C.G., dos Santos, A.N., e Loyola, A.C.D.F., & Fante, C.A. (2020). Biodegradable edible films of ripe banana peel and starch enriched with extract of Eriobotrya japonica leaves. Food Bioscience, 38, 100750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2020.100750
Stoll, L., Silva, A.M.D., Iahnke, A.O.E.S., Costa, T.M.H., Flores, S.H., & Rios, A.D.O. (2017). Active biodegradable film with encapsulated anthocyanins: Effect on the quality attributes of extra‐virgin olive oil during storage. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 41(6), e13218. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.13218
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the University of Buenos Aires (UBACYT 2018-2023 20020170100063BA and UBACYT 2018-2023 20020170100092BA), and the National Agency for Scientific and Technical Research (PICT-2019-01551 and PICT-2019-1842). The authors also wish to thank R-Mix S.R.L. (Urdinarrain, Argentina).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sofía, B., Juana, J.R. & Karina, F.S. Development of antimicrobial starch-based composite films reinforced with soybean expeller for sustainable active packaging applications. Food Sci Biotechnol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-023-01516-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-023-01516-6