Abstract
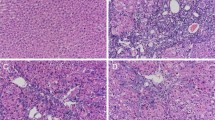
Hepatic stellate cell (HSC) activation is a key event in extracellular matrix accumulation, causing hepatic fibrosis. Therefore, identifying chemicals that inhibit HSC activation is an important therapeutic strategy for hepatic fibrosis. The aim of this study was to investigate the therapeutic effects of paeonol on HSC activation. In LX-2 cells, paeonol inhibited the expression of collagen and decreased the expression of HSC activation markers. In mice with thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis, paeonol treatment decreased the serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine transaminase and mRNA expression of α-smooth muscle actin, platelet-derived growth factor-β, and connective-tissue growth factor. Investigation of the underlying molecular mechanism of paeonol showed that paeonol inhibits the SMAD2/3 and STAT3 signaling pathways that are important for HSC activation. On the basis of these results, paeonol should be investigated and developed further for hepatic fibrosis treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bataller R, Brenner DA. Liver fibrosis. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 115: 209-218 (2005)
Carpino G, Morini S, Ginanni Corradini S, Franchitto A, Merli M, Siciliano M, Gentili F, Onetti Muda A, Berloco P, Rossi M, Attili AF, Gaudio E. Alpha-SMA expression in hepatic stellate cells and quantitative analysis of hepatic fibrosis in cirrhosis and in recurrent chronic hepatitis after liver transplantation.Digestive and Liver Disease. 37: 349-356 (2005)
Chakraborty D, Šumová B, Mallano T, Chen C-W, Distler A, Bergmann C, Ludolph I, Horch RE, Gelse K, Ramming A, Distler O, Schett G, Šenolt L, Distler JHW. Activation of STAT3 integrates common profibrotic pathways to promote fibroblast activation and tissue fibrosis. Nature Communications. 8: 1130 (2017)
Cheng CS, Chen JX, Tang J, Geng YW, Zheng L, Lv LL, Chen LY, Chen Z. Paeonol inhibits pancreatic cancer cell migration and invasion through the inhibition of TGF-β1/Smad signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal-transition. Cancer Management and Research. 12: 641-651 (2020)
Chou TC. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of paeonol in carrageenan-evoked thermal hyperalgesia. British Journal of Pharmacology. 139: 1146-1152 (2003)
Chun SC, Jee SY, Lee SG, Park SJ, Lee JR, Kim SC. Anti-inflammatory activity of the methanol extract of moutan cortex in LPS-activated Raw264.7 cells. Evid. Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 4: 327–333 (2007)
Chung JY, Chan MK, Li JS, Chan AS, Tang PC, Leung KT, To KF, Lan HY, Tang PM. TGF-β signaling: from tissue fibrosis to tumor microenvironment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 22: 7575 (2021)
Dai M, Zhi X, Peng D, Liu Q. Inhibitory effect of paeonol on experimental atherosclerosis in quails. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 24: 488–490, 512 (1999)
Dewidar B, Soukupova J, Fabregat I, Dooley S. TGF-β in hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrogenesis: updated. Current Pathobiology Reports. 3: 291-305 (2015)
Fabregat I, Caballero-Díaz D. Transforming growth factor-β-induced cell plasticity in liver fibrosis and hepatocarcinogenesis. Frontiers in Oncology. 8: 357 (2018)
Ginès P, Castera L, Lammert F, Graupera I, Serra‐Burriel M, Allen AM, Wong VWS, Hartmann P, Thiele M, Caballeria L, De Knegt RJ, Grgurevic I, Augustin S, Tsochatzis EA, Schattenberg JM, Guha IN, Martini A, Morillas RM, Garcia‐Retortillo M, De Koning HJ, Fabrellas N, Pich J, Ma AT, Diaz MA, Roulot D, Newsome PN, Manns M, Kamath PS, Krag A. Population screening for liver fibrosis: toward early diagnosis and intervention for chronic liver diseases. Hepatology. 75: 219-228 (2022)
Han CV, Bhat R. In vitro control of food-borne pathogenic bacteria by essential oils and solvent extracts of underutilized flower buds of Paeonia suffruticosa (Andr.). Industrial Crops and Products. 54: 203–208 (2014)
Hata A, Chen YG. TGF-β signaling from receptors to Smads. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology. 8: a022061 (2016)
Hsieh CL, Cheng CY, Tsai TH, Lin IH, Liu CH, Chiang SY, Lin JG, Lao CJ, Tang NY. Paeonol reduced cerebral infarction involving the superoxide anion and microglia activation in ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 106: 208-215 (2006)
Hu HH, Chen DQ, Wang YN, Feng YL, Cao G, Vaziri ND, Zhao YY. New insights into TGF-β/Smad signaling in tissue fibrosis. Chemico-Biological Interactions. 292: 76-83 (2018)
Hu S, Shen G, Zhao W, Wang F, Jiang X, Huang D. Paeonol, the main active principles of Paeonia moutan, ameliorates alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 128: 100-106 (2010)
Kasembeli MM, Bharadwaj U, Robinson P, Tweardy DJ. Contribution of STAT3 to inflammatory and fibrotic diseases and prospects for its targeting for treatment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 19: 2299 (2018)
Lee SJ, Lee IS, Mar W. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 activity by 1,2,3,4,6-penta-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucose in murine macrophage cells. Archives of Pharmacal Research. 26: 832-839 (2003)
Liu F, Chen L, Rao H-Y, Teng X, Ren Y-Y, Lu Y-Q, Zhang W, Wu N, Liu F-F, Wei L. Automated evaluation of liver fibrosis in thioacetamide, carbon tetrachloride, and bile duct ligation rodent models using second-harmonic generation/two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy. Laboratory Investigation. 97: 84-92 (2017)
Nagasawa H, Iwabuchi T, Inatomi H. Protection by tree-peony (Paeonia suffruticosa Andr) of obesity in (SLN x C3H/He) F1 obese mice. In Vivo. 5: 115-118 (1991)
Pan Y, Gao Z, Huang X-Y, Chen J-J, Geng C-A. Chemical and biological comparison of different parts of Paeonia suffruticosa (Mudan) based on LCMS-IT-TOF and multi-evaluation in vitro. Industrial Crops and Products. 144: 112028 (2020)
Park YJ, An H-T, Park J-S, Park O, Duh AJ, Kim K, Chung KH, Lee KC, Oh Y, Lee S. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor neratinib attenuates liver fibrosis by targeting activated hepatic stellate cells. Scientific Reports 10: 14756 (2020)
Park YJ, Jeon MS, Lee S, Kim JK, Jang TS, Chung KH, Kim KH. Anti-fibrotic effects of brevilin A in hepatic fibrosis via inhibiting the STAT3 signaling pathway. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 41: 127989 (2021)
Park YJ, Kim DM, Jeong MH, Yu JS, So HM, Bang IJ, Kim HR, Kwon SH, Kim KH, Chung KH. (-)-Catechin-7-O-β-d-apiofuranoside inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation by suppressing the STAT3 signaling pathway. Cells. 9: 30 (2019)
Peng D, Fu M, Wang M, Wei Y, Wei X. Targeting TGF-β signal transduction for fibrosis and cancer therapy. Molecular Cancer. 21: 104 (2022)
Pisani P, Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J. Estimates of the worldwide mortality from 25 cancers in 1990. International Journal of Cancer. 83: 18-29 (1999)
Senoo H, Yoshikawa K, Morii M, Miura M, Imai K, Mezaki Y. Hepatic stellate cell (vitamin A-storing cell) and its relative—past, present and future. Cell Biology International. 34: 1247-1272 (2010)
Sun SW, Du J, Hwang E, Yi TH. Paernol extracted from Paeonia suffruticosa Andr. amealiorated UVB-induced skin photoaging via DLD/Nrf2/ARE and MAPK/AP-1 pathway. Phytotherapy Research. 32(9): 1741-1749 (2018)
Tang LY, Heller M, Meng Z, Yu LR, Tang Y, Zhou M, Zhang YE. Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) directly activates the JAK1-STAT3 axis to induce hepatic fibrosis in coordination with the SMAD pathway. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 292: 4302-4312 (2017)
Tsuchida T, Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology. 14: 397-411 (2017)
Wang H, Lafdil F, Kong X, Gao B. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in liver diseases: a novel therapeutic target. International Journal of Biological Sciences. 7: 536-550 (2011)
Zhang J, Liu Q, He J, Li Y. Novel therapeutic targets in liver fibrosis. Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences. 8: 766855 (2021)
Zhang YE. Non-Smad pathways in TGF-β signaling. Cell Research. 19: 128-139 (2009)
Zhao J, Qi YF, Yu YR. STAT3: a key regulator in liver fibrosis. Annals of Hepatology. 21: 100224 (2021)
Zhu S, Shirakawa A, Shi Y, Yu X, Tamura T, Shibahara N, Yoshimatsu K, Komatsu K. Impact of different post-harvest processing methods on the chemical compositions of peony root. Journal of Natural Medicines. 72: 757-767 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Kyungsung University Research Grants in 2021.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, HJ., Koo, S., Kang, YH. et al. Hepatoprotective effects of paeonol by suppressing hepatic stellate cell activation via inhibition of SMAD2/3 and STAT3 pathways. Food Sci Biotechnol (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-023-01440-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-023-01440-9