Abstract
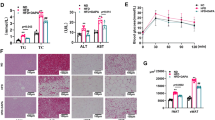
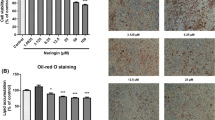
In this study, we investigated the effect of cycloastragenol (CAG), a triterpenoid isolated from Astragalus membranaceus roots, on regulating the adipogenesis and fat accumulation in vitro and in vivo. During the adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells, CAG inhibited lipid accumulation and the expression of key adipogenic factors, proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) and CCAAT enhancer binding protein α (C/EBPα) and increased the expression of Gli1, a key mediator in Hedgehog (Hh) signaling. In HFD-induced animal experiment, CAG significantly reduced body weight gain without affecting brown fat weight. In addition, CAG regulated the expression of PPARγ, C/EBPα, and Gli1 in visceral white adipose tissue (vWAT). We also confirmed the inhibitory effect of CAG on specifically targeting white adipose tissue (WAT) formation in stromal vascular fraction (SVF) cell differentiation. Taken together, these results suggest that CAG may be a potent phytochemical preventing adipogenesis and obesity via Hh signaling.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altaba ARI. Gli proteins and Hedgehog signaling—development and cancer. Trends Genet. 15: 418-425 (1999)
Andersen C, Rayalam S, Della-Fera MA, Baile CA. Phytochemicals and adipogenesis. Biofactors. 36: 415-422 (2010)
Aune UL, Ruiz L, Kajimura S. Isolation and differentiation of stromal vascular cells to beige/brite cells. J. Vis. Exp. 28: 50191 (2013)
Chen J, Bao C, Kim JT, Cho JS, Qiu S, Lee HJ. Sulforaphene inhibition of adipogenesis via Hedgehog signaling in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 66: 11926-11934 (2018)
Chen Q, Shou P, Zheng C, Jiang M, Cao G, Yang Q, Cao J, Xie N, Velletri T, Zhang X, Xu C, Zhang L, Yang H, Hou J, Wang Y, Shi Y. Fate decision of mesenchymal stem cells: adipocytes or osteoblasts? Cell Death Differ. 23: 1128-1139 (2016)
Cousin W, Fontaine C, Dani C, Peraldi P. Hedgehog and adipogenesis: fat and fiction. Biochimie. 89: 1447-1453 (2007)
Cypess AM, Kahn CR. Brown fat as a therapy for obesity and diabetes. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 17: 143-149 (2010)
Feldmann HM, Golozoubova V, Cannon B, Nedergaard J. UCP1 ablation induces obesity and abolishes diet-induced thermogenesis in mice exempt from thermal stress by living at thermoneutrality. Cell Metab. 9: 203-209 (2009)
Fontaine C, Cousin W, Plaisant M, Dani C, Peraldi P. Hedgehog signaling alters adipocyte maturation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 26: 1037-1046 (2008)
Forbes AJ, Nakano Y, Taylor AM, Ingham PW. Genetic-analysis of Hedgehog signaling in the Drosophila embryo. Development. 119: 115–124 (1993)
Fuccillo M, Joyner AL, Fishell G. Morphogen to mitogen: the multiple roles of Hedgehog signalling in vertebrate neural development (vol 7, pg 772, 2006). Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 7: 902-902 (2006)
Ghaben AL, Scherer PE. Adipogenesis and metabolic health. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 20: 242-258 (2019)
Gu M, Zhang S, Zhao Y, Huang J, Wang Y, Li Y, Fan S, Yang L, Ji G, Tong Q, Huang C. Cycloastragenol improves hepatic steatosis by activating farnesoid X receptor signalling. Pharmacol. Res. 121: 22-32 (2017)
Hwang JT, Park IJ, Shin JI, Lee YK, Lee SK, Baik HW, Ha J, Park OJ. Genistein, EGCG, and capsaicin inhibit adipocyte differentiation process via activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 338: 694-699 (2005)
Kopinke D, Roberson EC, Reiter JF. Ciliary Hedgehog signaling restricts injury-induced adipogenesis. Cell. 170: 340-351 e312 (2017)
Laforest S, Labrecque J, Michaud A, Cianflone K, Tchernof A. Adipocyte size as a determinant of metabolic disease and adipose tissue dysfunction. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 52: 301-313 (2015)
Lai K, Kaspar BK, Gage FH, Schaffer DV. Sonic Hedgehog regulates adult neural progenitor proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Nat. Neurosci. 6: 645-645 (2003)
Lai LP, Mitchell J. Indian Hedgehog: its roles and regulation in endochondral bone development. J. Cell. Biochem. 96: 1163-1173 (2005)
Li Z, Zhang H, Denhard LA, Liu LH, Zhou H, Lan ZJ. Reduced white fat mass in adult mice bearing a truncated Patched 1. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 4: 29-36 (2008)
Longo M, Zatterale F, Naderi J, Parrillo L, Formisano P, Raciti GA, Beguinot F, Miele C. Adipose tissue dysfunction as determinant of obesity-associated metabolic complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20: 2358 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092358
Maeda Y, Nakamura E, Nguyen MT, Suva LJ, Swain FL, Razzaque MS, Mackem S, Lanske B. Indian Hedgehog produced by postnatal chondrocytes is essential for maintaining a growth plate and trablecular bone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104: 6382-6387 (2007)
McMahon AP, Ingham PW, Tabin CJ. Developmental roles and clinical significance of Hedgehog signaling. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 53: 1-114 (2003)
Picard F, Kurtev M, Chung N, Topark-Ngarm A, Senawong T, Machado De Oliveira R, Leid M, McBurney MW, Guarente L. Sirt1 promotes fat mobilization in white adipocytes by repressing PPAR-gamma. Nature. 429: 771-776 (2004)
Pospisilik JA, Schramek D, Schnidar H, Cronin SJF, Nehme NT, Zhang XY, Knauf C, Cani PD, Aumayr K, Todoric J, Bayer M, Haschemi A, Puviindran V, Tar K, Orthofer M, Neely GG, Dietzl G, Manoukian A, Funovics M, Prager G, Wagner O, Ferrandon D, Aberger F, Hui CC, Esterbauer H, Penninger JM. Drosophila genome-wide obesity screen reveals Hedgehog as a determinant of brown versus white adipose cell fate. Cell. 140: 148-160 (2010)
Qiu S, Chen J, Kim JT, Zhou Y, Moon JH, Lee SB, Park HJ, Lee HJ. Suppression of adipogenesis and fat accumulation by vitexin through activation of Hedgehog signaling in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J. Med. Food. 25: 313-323 (2022)
Qiu S, Cho JS, Kim JT, Moon JH, Zhou Y, Lee SB, Park HJ, Lee HJ. Caudatin suppresses adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and reduces body weight gain in high-fat diet-fed mice through activation of Hedgehog signaling. Phytomedicine. 92: 153715 (2021)
Rios JL, Waterman PG. A review of the pharmacology and toxicology of Astragalus. Phytother. Res. 11: 411-418 (1997)
Rosen ED, MacDougald OA. Adipocyte differentiation from the inside out. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7: 885-896 (2006)
Ruiz i Altaba A, Mas C, Stecca B. The Gli code: an information nexus regulating cell fate, stemness and cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 17: 438-447 (2007)
Shi Y, Long F. Hedgehog signaling via Gli2 prevents obesity induced by high-fat diet in adult mice. eLife. 6: e31649 (2017)
Suh JM, Gao X, McKay J, McKay R, Salo Z, Graff JM. Hedgehog signaling plays a conserved role in inhibiting fat formation. Cell Metab. 3: 25-34 (2006)
Thyagarajan B, Foster MT. Beiging of white adipose tissue as a therapeutic strategy for weight loss in humans. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 31: 20170016 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1515/hmbci-2017-0016
Wajchenberg BL. Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: their relation to the metabolic syndrome. Endocr. Rev. 21: 697-738 (2000)
Wang S, Zhai C, Liu Q, Wang X, Ren Z, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Wu Q, Sun S, Li S, Qiao Y. Cycloastragenol, a triterpene aglycone derived from Radix astragali, suppresses the accumulation of cytoplasmic lipid droplet in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Research Commun. 450: 306-311 (2014)
Wehrli NE, Bural G, Houseni M, Alkhawaldeh K, Alavi A, Torigian DA. Determination of age-related changes in structure and function of skin, adipose tissue, and skeletal muscle with computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and positron emission tomography. Semin. Nucl. Med. 37: 195-205 (2007)
Wu C, Zhu X, Liu W, Ruan T, Tao K. Hedgehog signaling pathway in colorectal cancer: function, mechanism, and therapy. OncoTargets Ther. 10: 3249-3259 (2017)
Zhou Y, Kim JT, Qiu S, Lee SB, Park HJ, Soon MJ, Lee HJ. 1,3,5,8-Tetrahydroxyxanthone suppressed adipogenesis via activating Hedgehog signaling in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 31: 1473-1480 (2022)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2022R1A2C1092959) and a Grant (21153MFDS605) from the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety in 2023 and the Chung-Ang University Graduate Research Scholarship in 2023.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.T., Chen, J., Zhou, Y. et al. Cycloastragenol inhibits adipogenesis and fat accumulation in vitro and in vivo through activating Hedgehog signaling. Food Sci Biotechnol 33, 711–720 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-023-01403-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-023-01403-0