Abstract
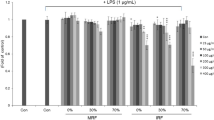
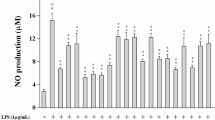
This study examined the anti-inflammatory effects of 70% ethanol crude extract of immature Citrus unshiu fruits (ICE) and its solvent fractions in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. In addition, we analyzed the active compounds related to suppression of inflammation. It was found that the ethyl acetate (EtOAc) fraction showed the highest level of inhibition of NO production, and this inhibitory activity was concentration-dependent. Moreover, the EtOAc fraction not only inhibited TNF-α and IL-6 production but also inhibited iNOS and COX-2 protein expression. Furthermore, inhibition of NF-κB activity and MAPK phosphorylation was also observed. In addition, β-sitosterol, campesterol and isoferulic acid were identified as major anti-inflammatory components in the EtOAc fraction. These results suggested that the EtOAc fraction of immature C. unshiu fruit extract exerts anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways, and that this fruit could be used as a natural anti-inflammatory material.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker S, Mundandhara S, Devlin RB, Madden M. Regulation of cytokine production in human alveolar macrophages and airway epithelial cells in response to ambient air pollution particles: further mechanistic studies. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 207: 269-275 (2005)
Choi YH, Kim GY, Lee HH. Anti-inflammatory effects of cordycepin in lipopolysaccharide-stiumulated RAW 264.7 macrophages through Toll-like receptor 4-mediated suppression of mitogen-activated protein kinases and NF-κB signaling pathways. Drug Design, Development and Therapy. 8: 1941-1953 (2014)
Chovatiya R, Medzhitov R. Stress, inflammation, and defense of homeostais. Molecular Cell. 54: 281-288 (2014)
Chun JM, Nho KJ, Kim HS, Lee AY, Moon BC, Kim HK. An ethyl acetate fraction derived from Houttuynia cordata extract inhibits the production of inflammatory markers by suppressing NF-κB and MAPK activation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 14: 1-11 (2014).
Gao Z, Gae W, Zeng SL, Li P, Liu EH. Chemical structures, bioactivities and molecular mechanisms of citrus polymethoxyflavones. Journal of Functional Foods. 40: 498-509 (2018).
Ham YM, Cho SH, Song SM, Yoon SA, Lee YB, Kim CS, Kwon SH, Jeong MS, Yoon WJ, Kim KN. Litsenolide A2: the major anti-inflammatory activity compound in Litsea japonica fruit. Journal of Functional Foods. 39: 168-174 (2017)
Hwang KA, Heo W, Hwang HJ, Han BK, Song MC, Kim YJ. Anti-inflammatory effect of immature sword bean pod (Canavalia gladiata) in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 Cells. Journal of Medicinal Food. 23: 1183-1191 (2020)
Hyun JM, JO YJ, Kim JE, An HJ, Choi YH, Hyun CG, Lee NH. Tetramethyl-O-scutellarin isolated from peels of immature Shiranuhi fruit exhibits anti-inflammatory effects on LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 16: 2197-2205 (2017)
Jung HW, Son HY, Minh CV, Kim YH, Park YK. Methanol extract of Ficus leaf inhibits the production of nitric oxide and proinflammatory cytokines in LPS-stimulated microglial via the MAPK pathway. Phytotherapy Research. 22: 1064-1069 (2008)
Jung KH, Ha E, Kim MJ, Won HJ, Zheng LT, Kim HK, Hong SJ, Chung JH, Yim SV. Suppressive effects of nitric oxide (NO) production and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression by Citrus reticulata extract in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 45: 1545-1550 (2007)
Kaplanski G, Marin V, Montero-Juliaan F, Mantovani A, Farnarier C. IL-6: a regulator of the transition from neutrophil to monocyte recruitment during inflammation. Trends in Immunology. 24: 25-29 (2003)
Kim DS, Lim SB. Extraction of flavanones from immature Citrus unshiu pomace: process optimization and antioxidant evaluation. Scientific Reports. 10: 1-13 (2020)
Lai CS, Li S, Chai CY, Lo CY, Ho CT, Wang YJ, Pan MH. Inhibitory effect of citrus 5-hydroxy-3,6,7,8,3’,4’-hexamethoxyflavone on 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate-induced skin inflammation and tumor promotion in mice. Carcinogenesis. 28: 2581-2588 (2007)
Laskin DL, Laskin JD. Role of macrophage and inflammatory mediators in chemically induced toxicity. Toxicology. 160: 111-118 (2001)
Lee J, Lee J, Kim M, Kim JH. Fermented extraction of Citrus unshiu peel inhibits viability and migration of human pancreatic cancers. Journal of Medicinal Food. 21: 5-12 (2018)
Lisso J, Altmann T, Müssig C. Metabolic changes in fruits of the tomato dx mutant. Phytochemistry. 67: 2232–2238 (2006)
McNelis JC, Olefsky JM. Macrophages, immunity, and metabolic disease. Immunity. 41: 36-48 (2014).
Medzhitov R. Inflammation 2010: new adventures of an old flame. Cell. 140: 771-776 (2010).
Mu MM, Chakravortty D, Sugiyama T, Koide N, Takahashi K, Mori I, Yoshida T, Yokochi T. The inhibitory action of quercetin on lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Journal of Endotoxin Research. 7: 431-438 (2001)
Nam NH. Naturally occurring NF-κB inhibitors. Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry. 6:945-951 (2006)
Noma T, Takahashi-Yanaga F, Arioka M, Mori Y, Sasaguri T. Inhibition of GSK-3 reduces prostaglandin E2 production by decreasing the expression levels of COX-2 and mPGES-1 in monocyte/macrophage lineage cells. Biochemical Pharmacology. 116: 120-129 (2016).
Odegaard JI, Chawla A. Alternative macrophage activation and metabolism. Annual Review Pathology. 6: 275-297 (2011).
Ren J, Chung SH. Anti-inflammatory effect of α-linolenic acid and its mode of action through the inhibition of nitric oxide production and inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression via NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry. 55: 5073-5080 (2007)
Roberts PJ, Der CJ: Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 26: 3291-3310 (2007)
Roessner U, Wagner C, Kopka J, Trethewey RN, Willmitzer L. Simultaneous analysis of metabolites in potato tuber by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. The plant journal. 23:131-142 (2000)
Ryu JH, Ahn H, Kim JY, Kim YK. Inhibitory activity of plant extracts on nitric oxide synthesis in LPS-activiated macrophages. Phytotherapy Research. 17: 485-489 (2003)
Saleem M, Afaq F, Adhami VM, Mukhtar H. Lupeol modulates NF-kB and PI3K/Akt pathways and inhibits skin cancer in CD-1 mice. Oncogene. 23: 5203-5214 (2004)
Shin HS, Kang SI, Ko HC, Kim HM, Hong YS, Yoon SA, Kim SJ. Anti-inflammatory effect of the immature peel extract of Jinkyool (Cirtus sunki Hort. ex Tanaka). Food Science and Biotechnology. 20: 1235-1241 (2011)
Song HY, Jeong DE, Lee M. Bioactivity-guided extracts optimization of Osmanthus fragrans var. aurantiacus leaves and anti-inflammatory activities of phillyrin. Plants. 10: 1545 (2021)
Surh YJ, Chun KS, Cha HH, Han SS, Keum YS, Park KK, Lee SS. Molecular mechanisms underlying chemopreventive activities of anti-inflammatory phytochemicals: down-regulation of COX-2 and iNOS through suppression of NF-κB activation. Mutation Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis. 480: 243-268 (2001)
Tian Y, Zhou S, Takeda R, Okazaki K, Sekita M, Sakamoto k. Anti-inflammatory activities of amber extract in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy. 141: 111854 (2021)
Yi L, Ma S, Ren D. Phytochemistry and bioactivity of citrus flavonoides: a focus on antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer and cardiovascular protection activities. Phytochemistry Reviews. 16: 479-511 (2017)
Yuan L, Zhang F, Shen M, Jia S, Xie J. Phytosterols suppress phagocytosis and inhibit inflammatory mediators via ERK pathway on LPS-triggered inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 macrophages and the correlation with their structure. Foods. 8: 582 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), funded by the Ministry of Education (Grant No. 2016R1A6A1A03012862) and a Grant (715003-07) from the Research Center for Production Management and Technical Development for High Quality Livestock Products through Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs Convergence Technologies Program for Educating Creative Global Leader, Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, M.G., Kim, S., Boo, KH. et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of immature Citrus unshiu fruit extracts via suppression of NF-κB and MAPK signal pathways in LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophage cells. Food Sci Biotechnol 33, 903–911 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-023-01390-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-023-01390-2