Abstract
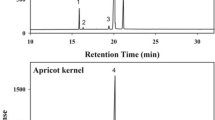
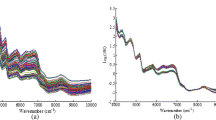
Amygdalin content in apricot kernels is an essential factor in the rapid and nondestructive identification of sweet or bitter apricot kernels through spectroscopy. Now, amygdalin content has been determined by high-performance liquid chromatography and near-infrared spectral database to construct a model so that the sweet or bitter apricot kernels could be identified and classified. Principal component analysis–K-nearest neighbor classification algorithm combined with multivariate scattering correction pretreatment method could distinguish sweet and bitter apricot kernels in the wavelength range of 1650–1740 nm with 98.3% accuracy and apricot kernel species with 96.3% recognition rate in the full wavelength spectrum. Furthermore, prediction of amygdalin content in bitter and sweet apricot kernels by partial least squares model was superior to that by back-propagation neural network model. This study provides a theoretical basis for quality identification of apricot kernel quality, as well as a method for nondestructive and rapid detection of sweet and bitter apricot kernels.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aman S, Babita P. An efficient diagnosis system for detection of liver disease using a novel integrated method based on principal component analysis and K-nearest neighbor PCA-KNN. International Journal of Healthcare Information Systems and Informatics. 11: 56-69 (2016). https://doi.org/10.4018/IJHISI.2016100103.
Arslan M, Zou X, Shi J, Tahir HE, Bilal M. In situ prediction of phenolic compounds in puff dried Ziziphus Jujuba Mill. using hand-held spectral analytical system. Food Chemistry. 331: 127361 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127361.
Camps C, Christen D. Non-destructive assessment of apricot fruit quality by portable visible- near infrared spectroscopy. LWT—Food Science and Technology. 42: 1125-1131 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2009.01.015.
Christoph K, Claudia C, Christian P, Bernd S, Jürgen P. Distribution of amygdalin in apricot (Prunus armeniaca) seeds studied by Raman microscopic imaging. Applied Spectroscopy. 66: 644-649 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1366/11-06521.
Deng P, Cui B, Zhu HL, Phommakoun B, Zhang D, Li YM, Zhao F, Zhao Z. Accumulation pattern of amygdalin and prunasin and its correlation with fruit and kernel agronomic characteristics during apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) kernel development. Foods (Basel, Switzerland). 10: 397 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10020397.
Eman ZG. In vitro antioxidant, antimicrobial, and antitumor activities of bitter almond and sweet apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) kernels. Food Science and Biotechnology. 22: 455-463 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-013-0101-1.
Eva B, José MA, Frans van den B, Ricard B, Olga B. Fast and robust discrimination of almonds (Prunus amygdalus) with respect to their bitterness by using near infrared and partial least squares-discriminant analysis. Food Chemistry. 153: 15-19 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.12.032.
Ferrara G, Maggio P, Pizzigallo R. Cyanogenic D-amygdalin contents of the kernels of cultivated almonds and wild Amygdalus webbii Spach. The Journal of Horticultural Science and Biotechnology. 85: 410-414 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2010.11512689.
Gómez-Martínez H, Bermejo A, Zuriaga E, Badenes ML. Polyphenol content in apricot fruits. Scientia Horticulturae. 277: 109828 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109828.
Huang XY, Qian M, Xu FB. Nondestructive detection of dried apricots quality based on machine vision and near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectroscopy technology. Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering. 28: 260-265 (2012). https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2012.07.043.
Huang Y, Cao JL, Ye SF, Duan J, Wu LJ, Li QQ, Min SG, Xiong YM. Near-infrared spectral imaging for quantitative analysis of active component in counterfeit imidacloprid using PLS regression. Optik-International Journal for Light and Electron Optics. 124: 1644-1649 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2012.05.051.
Huang X, Tuersunguli WLYM, Guo L. Phenotypic traits and amygdalin content of apricot seed kernels in southern Xinjiang. Nonwood Forest Research, 38: 143-151+160 (2020). https://doi.org/10.14067/j.cnki.1003-8981.2020.04.017.
Huang X, Han AZ, Tuersunguli WLYM, Guo L. Identification of mineral elements of apricot seed kernels used in combination with fruit kernels in southern Xinjiang. Northern Horticulture. 3: 19-26 (2021a). https://doi.org/10.11937/bfyy.20202155.
Huang X, Han AZ, Tuersunguli WLYM, Guo L. Comparison and analysis of amino acids in kernel of apricot core germplasm in southern Xinjiang. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University. 40: 133-140 (2021b). https://doi.org/10.13300/j.cnki.hnlkxb.2021.04.016.
Islamiyat FB, Caroline O, Michael RAM. Amygdalin content of seeds, kernels and food products commercially-available in the UK. Food Chemistry. 152: 133-139 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.11.002.
Karsavuran N, Charehsaz M, Celik H, Asma BM, Yakinci C, Aydin A. Amygdalin in bitter and sweet seeds of apricots. Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry. 96: 1564-1570 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2015.1030667.
Kung YL, Lu CY, Badrealam KF, Kuo WW, Shibu MA, Day CH, Chen R, Lu SY, Padma VV, Huang CY. Cardioprotective potential of amygdalin against angiotensin II induced cardiac hypertrophy, oxidative stress and inflammatory responses through modulation of Nrf2 and NF-κB activation. Environmental Toxicology. 36: 926-934 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/tox.23094.
Liang PS, Slaughter DC, Ortega-Beltran A, Michailides TJ. Detection of fungal infection in almond kernels using near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Biosystems Engineering. 137: 64-72 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2015.07.010.
Lúcia PS, Menno S, Rob V, Young HC. Quantitative analysis of amygdalin and prunasin in Prunus serotina Ehrh. using 1H-NMR spectroscopy. Phytochemical Analysis Pca. 25: 122-126 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/pca.2476.
Lv WF, Ding MY, Zheng R. Isolation and quantitation of amygdalin in apricot-kernel and Prunus tomentosa Thunb. by HPLC with solid-phase extraction. Journal of Chromatographic Science. 43: 383-387 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/43.7.383.
Ma YX, Wang SX, Liu XJ, Yu HY, Yu D, Li GT, Wang LB. Oil content, fatty acid composition and biodiesel properties among natural provenances of Siberian apricot (Prunus sibirica L.) from China. GCB Bioenergy. 13: 112-132 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1111/gcbb.12759.
Maria-Cristina P, Razvan C, Sergiu SP. 2DIR correlation spectroscopy and chemometric methods in gastric cancer diagnosis. Journal of Molecular Structure. 1214: 128211 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128211.
Salas-Salvadó J, Casas-Agustench P, Salas-Huetos A. Cultural and historical aspects of Mediterranean nuts with emphasis on their attributed healthy and nutritional properties. Nutrition, Metabolism & Cardiovascular Diseases. 21: S1-S6 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2010.10.013.
Su CY, Zheng XC, Zhang DD, Chen Y, Xiao J, He Y, He JR, Wang B, Shi XW. Investigation of sugars, organic acids, phenolic compounds, antioxidant activity and the aroma fingerprint of small white apricots grown in Xinjiang. Journal of Food Science. 85: 4300-4311 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.15523.
Takuya Y, Kazunori Y, Yasuhisa A. Identification and characterization of CYP79D16 and CYP71AN24 catalyzing the first and second steps in l-phenylalanine-derived cyanogenic glycoside biosynthesis in the Japanese apricot, Prunus mume Sieb. et Zucc. Plant Mol Biol. 86: 215-223 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-014-0225-6.
Tiecher T, Moura-Bueno JM, Caner L, Minella JPG, Evrard O, Ramon R, Naibo G, Barros Cláudia AP, Silva Yuri JAB, Amorim Fábio F, Rheinheimer Danilo S. Improving the quantification of sediment source contributions using different mathematical models and spectral preprocessing techniques for individual or combined spectra of ultraviolet–visible, near-and middle-infrared spectroscopy. Geoderma. 384: 114815 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114815.
Vicker A. Alternative cancer cures: “unproven”or “dis-proven”?. CA A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 54: 110-118 (2004). https://doi.org/10.3322/canjclin.54.2.110.
Victoria C, Pau T, José MB, María JL-G. Potential of NIR spectroscopy to predict amygdalin content established by HPLC in intact almonds and classification based on almond bitterness. Food Control. 91: 68-75 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.03.040.
Victoria C, Pau T, José MB, María JLG. Discrimination of intact almonds according to their bitterness and prediction of amygdalin concentration by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Postharvest Biology and Technology. 148: 236-241 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.05.006.
Yiğit D, Yiğit N, Mavi A. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of bitter and sweet apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) kernels. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research. 42: 346-352 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-879X2009000400006.
Zdrojewicz Z, Otlewska A, Hackemer P, Otlewska A. Amigdalina—budowai znaczenie kliniczne [Amygdalin—structure and clinical significance]. Polski Merkuriusz Lekarski Polish Medical Journal. 38: 300-303 (2015)
Zhou WQ, Niu YY, Ding X, Zhao SR, Li YL, Fan GQ, Zhang SK, Liao K. Analysis of carotenoid content and diversity in apricots (Prunus armeniaca L.) grown in China. Food Chemistry. 330: 127223 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127223.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program (Grant No. 2019YFD1000600), the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31760560 and 32160694) and the Graduate Research Innovation Project of Tarim University (Grant No. TDGRI202013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10068_2022_1095_MOESM4_ESM.pdf
Supplementary file4 (PDF 5651 KB) Fig. S4 Summary of raw spectra of three bitter apricot kernels and three sweet apricot kernels
10068_2022_1095_MOESM7_ESM.pdf
Supplementary file7 (PDF 734 KB) Fig. S7 PCA dimensionality reduction results of original spectra of eight apricot kernels
10068_2022_1095_MOESM9_ESM.pdf
Supplementary file9 (PDF 532 KB) Fig. S9 PCA dimensionality reduction results after MSC preconditioning of eight apricot kernels
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, X., Xu, J., Gao, F. et al. Rapid quantitative typing spectra model for distinguishing sweet and bitter apricot kernels. Food Sci Biotechnol 31, 1123–1131 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-022-01095-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-022-01095-y