Abstract
Objectives
Interleukin (IL)-24 has been considered as an inflammatory cytokine in autoimmune diseases. However, conflicting data exist and its biological function remains controversial. Additionally, little is known about its functional impact on natural killer (NK) cells. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of IL-24 in NK cell activation and its clinical implication in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Methods
Serum cohort consisting of 299 SLE patients, 214 RA patients, and 159 healthy controls (HCs) and plasma cohort consisting of 70 SLE patients, 82 RA patients, and 123 HCs were included in evaluating IL-24 concentrations. Impact of IL-24 on NK cell activation was assessed in two NK cell subsets, i.e., CD56dimCD16+ and CD56brightCD16− NK cells. Human NK-92 cell line was applied to evaluate functional potential of IL-24 on NK cell migration and invasion.
Results
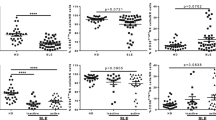
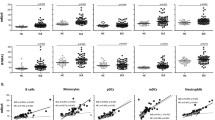
Serum and plasma levels of IL-24 were comparable between patients with SLE or RA and HCs. While recombinant human (rh) IL-2 consistently induced an increased expression of CD69 on both CD56dimCD16+ and CD56brightCD16− cells derived from both healthy subjects and patients with SLE, IL-24 alone was insufficient to activate the CD56dim and CD56bright NK cells. Similarly, while the migratory NK-92 cell numbers were significantly increased with rhIL-2 stimulation, IL-24 alone was unable to enhance NK-92 cell migratory and invasive capacity.
Conclusion
Our data indicate that there were no significant differences in serum and plasma concentrations of IL-24 between SLE patients and healthy controls. Recombinant IL-24 has no effect on NK cell activation and migration.
Key points • This is the first study to investigate functional potential of IL-24 on NK cell activation. • Recombinant IL-24 lacks functional capacity on NK cell activation in either CD56dimCD16+ or CD56brightCD16- NK cell subsets derived from both healthy subjects and patients with SLE. • No significant differences in serum and plasma levels of IL-24 between SLE patients and healthy controls. |




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Spada R, Rojas JM, Barber DF (2015) Recent findings on the role of natural killer cells in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Leukoc Biol 98(4):479–487. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.4RU0315-081RR
Hervier B, Beziat V, Haroche J, Mathian A, Lebon P, Ghillani-Dalbin P, Musset L, Debré P, Amoura Z, Vieillard V (2011) Phenotype and function of natural killer cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: excess interferon-γ production in patients with active disease. Arthritis Rheum 63(6):1698–1706. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.30313
Cooper MA, Fehniger TA, Caligiuri MA (2001) The biology of human natural killer-cell subsets. Trends Immunol 22(11):633–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1471-4906(01)02060-9
Caligiuri MA (2008) Human natural killer cells. Blood 112(3):461–469. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2007-09-077438
Nagler A, Lanier LL, Cwirla S, Phillips JH (1989) Comparative studies of human FcRIII-positive and negative natural killer cells. J Immunol 143(10):3183–3191
Erkeller-Yuksel FM, Lydyard PM, Isenberg DA (1997) Lack of NK cells in lupus patients with renal involvement. Lupus 6(9):708–712. https://doi.org/10.1177/096120339700600905
Park YW, Kee SJ, Cho YN, Lee EH, Lee HY, Kim EM, Shin MH, Park JJ, Kim TJ, Lee SS, Yoo DH, Kang HS (2009) Impaired differentiation and cytotoxicity of natural killer cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 60(6):1753–1763. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.24556
Schepis D, Gunnarsson I, Eloranta ML, Lampa J, Jacobson SH, Kärre K, Berg L (2009) Increased proportion of CD56bright natural killer cells in active and inactive systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology 126(1):140–146. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.02887.x
Wang M, Liang P (2005) Interleukin-24 and its receptors. Immunology 114(2):166–170. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02094.x
Kunz S, Wolk K, Witte E, Witte K, Doecke WD, Volk HD, Sterry W, Asadullah K, Sabat R (2006) Interleukin (IL)-19, IL-20 and IL-24 are produced by and act on keratinocytes and are distinct from classical ILs. Exp Dermatol 15(12):991–1004. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0625.2006.00516.x
Wolk K, Kunz S, Asadullah K, Sabat R (2002) Cutting edge: immune cells as sources and targets of the IL-10 family members? J Immunol 168(11):5397–5402. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.168.11.5397
Poindexter NJ, Walch ET, Chada S, Grimm EA (2005) Cytokine induction of interleukin-24 in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Leukoc Biol 78(3):745–752. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.0205116
Wang M, Tan Z, Zhang R, Kotenko SV, Liang P (2002) Interleukin 24 (MDA-7/MOB-5) signals through two heterodimeric receptors, IL-22R1/IL-20R2 and IL-20R1/IL-20R2. J Biol Chem 277(9):7341–7347. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M106043200
Scrivo R, Conigliaro P, Riccieri V, Di Franco M, Alessandri C, Spadaro A, Perricone R, Valesini G (2015) Distribution of interleukin-10 family cytokines in serum and synovial fluid of patients with inflammatory arthritis reveals different contribution to systemic and joint inflammation. Clin Exp Immunol 179(2):300–308. https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.12449
Li RC, Guo J, Su LC, Huang AF (2019) Elevated levels of IL-24 in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Lupus 28(6):748–754. https://doi.org/10.1177/0961203319845476
Zhang M, Xu WD, Zhu Y, Wen PF, Leng RX, Pan HF, Ye DQ (2014) Serum levels of cytokines in systemic lupus erythematosus : association study in a Chinese population. Z Rheumatol 73(3):277–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00393-013-1274-y
Lebedeva IV, Su ZZ, Chang Y, Kitada S, Reed JC, Fisher PB (2002) The cancer growth suppressing gene mda-7 induces apoptosis selectively in human melanoma cells. Oncogene 21(5):708–718. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205116
Yacoub A, Mitchell C, Hong Y, Gopalkrishnan RV, Su ZZ, Gupta P, Sauane M, Lebedeva IV, Curiel DT, Mahasreshti PJ, Rosenfeld MR, Broaddus WC, James CD, Grant S, Fisher PB, Dent P (2004) MDA-7 regulates cell growth and radiosensitivity in vitro of primary (non-established) human glioma cells. Cancer Biol Ther 3(8):739–751. https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.3.8.968
Sarkar D, Su ZZ, Lebedeva IV, Sauane M, Gopalkrishnan RV, Valerie K, Dent P, Fisher PB (2002) mda-7 (IL-24) Mediates selective apoptosis in human melanoma cells by inducing the coordinated overexpression of the GADD family of genes by means of p38 MAPK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(15):10054–10059. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.152327199
Sarkar D, Su ZZ, Vozhilla N, Park ES, Gupta P, Fisher PB (2005) Dual cancer-specific targeting strategy cures primary and distant breast carcinomas in nude mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(39):14034–14039. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0506837102
Jiang H, Su ZZ, Lin JJ, Goldstein NI, Young CS, Fisher PB (1996) The melanoma differentiation associated gene mda-7 suppresses cancer cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93(17):9160–9165. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.17.9160
Su Z, Emdad L, Sauane M, Lebedeva IV, Sarkar D, Gupta P, James CD, Randolph A, Valerie K, Walter MR, Dent P, Fisher PB (2005) Unique aspects of mda-7/IL-24 antitumor bystander activity: establishing a role for secretion of MDA-7/IL-24 protein by normal cells. Oncogene 24(51):7552–7566. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208911
Chada S, Mhashilkar AM, Ramesh R, Mumm JB, Sutton RB, Bocangel D, Zheng M, Grimm EA, Ekmekcioglu S (2004) Bystander activity of Ad-mda7: human MDA-7 protein kills melanoma cells via an IL-20 receptor-dependent but STAT3-independent mechanism. Mol Ther 10(6):1085–1095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2004.08.020
Sauane M, Gopalkrishnan RV, Choo HT, Gupta P, Lebedeva IV, Yacoub A, Dent P, Fisher PB (2004) Mechanistic aspects of mda-7/IL-24 cancer cell selectivity analysed via a bacterial fusion protein. Oncogene 23(46):7679–7690. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1207958
Sauane M, Lebedeva IV, Su ZZ, Choo HT, Randolph A, Valerie K, Dent P, Gopalkrishnan RV, Fisher PB (2004) Melanoma differentiation associated gene-7/interleukin-24 promotes tumor cell-specific apoptosis through both secretory and nonsecretory pathways. Cancer Res 64(9):2988–2993. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-04-0200
Ramesh R, Mhashilkar AM, Tanaka F, Saito Y, Branch CD, Sieger K, Mumm JB, Stewart AL, Boquoi A, Dumoutier L, Grimm EA, Renauld JC, Kotenko S, Chada S (2003) Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 7/interleukin (IL)-24 is a novel ligand that regulates angiogenesis via the IL-22 receptor. Cancer Res 63(16):5105–5113
Sieger KA, Mhashilkar AM, Stewart A, Sutton RB, Strube RW, Chen SY, Pataer A, Swisher SG, Grimm EA, Ramesh R, Chada S (2004) The tumor suppressor activity of MDA-7/IL-24 is mediated by intracellular protein expression in NSCLC cells. Mol Ther 9(3):355–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2003.11.014
Kreis S, Philippidou D, Margue C, Rolvering C, Haan C, Dumoutier L, Renauld JC, Behrmann I (2007) Recombinant interleukin-24 lacks apoptosis-inducing properties in melanoma cells. PLoS One 2(12):e1300. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001300
Caudell EG, Mumm JB, Poindexter N, Ekmekcioglu S, Mhashilkar AM, Yang XH, Retter MW, Hill P, Chada S, Grimm EA (2002) The protein product of the tumor suppressor gene, melanoma differentiation-associated gene 7, exhibits immunostimulatory activity and is designated IL-24. J Immunol 168(12):6041–6046. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.168.12.6041
Buzas K, Oppenheim JJ, Zack Howard OM (2011) Myeloid cells migrate in response to IL-24. Cytokine 55(3):429–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2011.05.018
Maarof G, Bouchet-Delbos L, Gary-Gouy H, Durand-Gasselin I, Krzysiek R, Dalloul A (2010) Interleukin-24 inhibits the plasma cell differentiation program in human germinal center B cells. Blood 115(9):1718–1726. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-05-220251
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF, Schaller JG, Talal N, Winchester RJ (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25(11):1271–1277. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780251101
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31(3):315–324. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780310302
Guo GH, Dong J, Yuan XH, Dong ZN, Tian YP (2013) Clinical evaluation of the levels of 12 cytokines in serum/plasma under various storage conditions using evidence biochip arrays. Mol Med Rep 7(3):775–780. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2013.1263
Henney CS, Kuribayashi K, Kern DE, Gillis S (1981) Interleukin-2 augments natural killer cell activity. Nature 291(5813):335–338. https://doi.org/10.1038/291335a0
Castriconi R, Carrega P, Dondero A, Bellora F, Casu B, Regis S, Ferlazzo G, Bottino C (2018) Molecular mechanisms directing migration and retention of natural killer cells in human tissues. Front Immunol 9:2324. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02324
Edsparr K, Johansson BR, Goldfarb RH, Basse PH, Nannmark U, Speetjens FM, Kuppen PJ, Lennernäs B, Albertsson P (2009) Human NK cell lines migrate differentially in vitro related to matrix interaction and MMP expression. Immunol Cell Biol 87(6):489–495. https://doi.org/10.1038/icb.2009.35
Olofsson PE, Forslund E, Vanherberghen B, Chechet K, Mickelin O, Ahlin AR, Everhorn T, Onfelt B (2014) Distinct migration and contact dynamics of resting and IL-2-activated human natural killer cells. Front Immunol 5:80. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2014.00080
Vanherberghen B, Olofsson PE, Forslund E, Sternberg-Simon M, Khorshidi MA, Pacouret S, Guldevall K, Enqvist M, Malmberg KJ, Mehr R, Önfelt B (2013) Classification of human natural killer cells based on migration behavior and cytotoxic response. Blood 121(8):1326–1334. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-06-439851
Kragstrup TW, Otkjaer K, Holm C, Jørgensen A, Hokland M, Iversen L, Deleuran B (2008) The expression of IL-20 and IL-24 and their shared receptors are increased in rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthropathy. Cytokine 41(1):16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2007.10.004
Fonseca-Camarillo G, Furuzawa-Carballeda J, Granados J, Yamamoto-Furusho JK (2014) Expression of interleukin (IL)-19 and IL-24 in inflammatory bowel disease patients: a cross-sectional study. Clin Exp Immunol 177(1):64–75. https://doi.org/10.1111/cei.12285
Wang M, Tan Z, Thomas EK, Liang P (2004) Conservation of the genomic structure and receptor-mediated signaling between human and rat IL-24. Genes Immun 5(5):363–370. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gene.6364101
Sauane M, Gopalkrishnan RV, Lebedeva I, Mei MX, Sarkar D, Su ZZ, Kang DC, Dent P, Pestka S, Fisher PB (2003) Mda-7/IL-24 induces apoptosis of diverse cancer cell lines through JAK/STAT-independent pathways. J Cell Physiol 196(2):334–345. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.10309
Parrish-Novak J, Xu W, Brender T, Yao L, Jones C, West J, Brandt C, Jelinek L, Madden K, McKernan PA, Foster DC, Jaspers S, Chandrasekher YA (2002) Interleukins 19, 20, and 24 signal through two distinct receptor complexes. Differences in receptor-ligand interactions mediate unique biological functions. J Biol Chem 277(49):47517–47523. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M205114200
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31870913, No. 31670915, No. 31470875, and No. 82071814), Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. 7162192), and the University of Michigan Medical School (UMMS) and Peking University Health Science Center (PUHSC) Joint Institute (JI) Projects (No. BMU2020JI003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Jianping Guo: conceptualization, supervision, formal analysis, funding acquisition, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. Xia Li: conceptualization, investigation. Yundi Tang: investigation, methodology, data curation, formal analysis, validation, writing—original draft. Xiaotong Sun: investigation, methodology, resources, data curation, validation. Yuxuan Wang and Huijie Luan: investigation, methodology. Ruijun Zhang: methodology, resources. Fanlei Hu and Xiaoling Sun: supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The study obtained ethical approval from the Ethics committee of Peking University People’s Hospital. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Y., Sun, X., Wang, Y. et al. Role of IL-24 in NK cell activation and its clinical implication in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol 40, 2707–2715 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-021-05618-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-021-05618-6