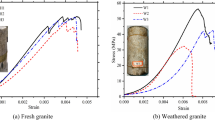
Abstract
The lignite would undergo dehydration cracking at normal temperature, which has an important impact on the stability of coal-rock slope in open-pit mine. In this paper, the uniaxial compression test of lignite with different dehydration times under normal temperature and humidity control conditions was carried out, and the mechanical parameters, deformation, AE characteristics, and macro–micro crack evolution law of dehydrated lignite were obtained. After that, the correlation between the porosity and mechanical parameters of rock samples based on dehydration deformation was discussed; meanwhile, according to the macro- and microcrack evolution characteristics of dehydrated lignite, the gradual change law of crack fractal dimension was elaborated. Finally, the initial damage of dehydrated lignite was defined by the relative porosity as a variable, and the damage constitutive model of lignite subjected to the dehydration and axial load was established. The results show the dehydration of lignite at normal temperature exactly causing the deterioration of mechanical properties, which also accompanied by the shrinkage deformation, the change of fractal dimension of macro–micro cracks, and the obvious AE activity in the compression test. In addition, the established damage constitutive model, considering the characteristics of compaction stage, is in good agreement with the experimental results. The research results are of great significance to reveal the instability and failure mechanism of lignite under the action of dehydration and stress.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data used in the study are included in the published article.
Abbreviations
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
- XRF:
-
X-ray fluorescence
- AE:
-
Acoustic emission
- h:
-
Hour
- AF:
-
Average frequency
- \(N_{t}\) :
-
Porosity of lignite after \(t\) h dehydration
- \(\Delta V_{tw}\) :
-
Water decreased volume of lignite
- \(\Delta m\) :
-
Water decrease mass
- \(\rho_{w}\) :
-
Density of water under 25 °C
- \(V_{tr}\) :
-
Volume of lignite after \(t\) h dehydration
- \(\Delta V_{tr}\) :
-
Decrease volume relative to initial state
- \(A_{{{\text{dB}}}}\) :
-
Maximum amplitude of AE event
- \(N\) :
-
Number of times exceeding the set threshold
- \(b\) :
-
AE b value
- \(F(s)\) :
-
Fractal dimension
- \(N(\varepsilon )\) :
-
Number of boxes with \(\varepsilon\) side length in the coverage area
- \(\varepsilon\) :
-
Side length of the box
- \(D_{t}\) :
-
Initial damage value calculated based on relative porosity
- \(\rho_{t}\) :
-
Relative porosity of lignite after \(t\) h dehydration
- \(\rho_{\max }\) :
-
Maximum porosity of the dehydrated lignite
- \(\sigma\), \(E\) :
-
Nominal stress and nominal elastic modulus, respectively
- \(\sigma^{*}\), \(E^{*}\) :
-
Effective stress and effective elastic modulus, respectively
- \(\sigma_{t}\), \(\varepsilon_{t}\) :
-
Stress and strain, respectively, of lignite with \(t\) h dehydration
- \(E_{0}\) :
-
Elastic modulus without dehydration
- \(E_{t}\) :
-
Elastic modulus of lignite with \(t\) h dehydration
- \(D_{l}\) :
-
Damage value caused by axial load
- \(D_{w}\) :
-
Damage variable considering the lignite dehydration and axial load
- \(\eta\), \(\beta\) :
-
Size parameter and shape parameter, respectively
- \(\sigma_{c,t}\) :
-
The stress at the end of compaction stage
- \(\varepsilon_{c,t}\) :
-
The strain at the end of compaction stage
- \(\sigma_{p,t}\), \(\varepsilon_{p,t}\) :
-
Peak stress and peak strain
References
Bian K, Liu J, Zhang W et al (2019) Mechanical behavior and damage constitutive model of rock subjected to water-weakening effect and uniaxial loading. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:97–106. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1580-4
Dai ZJ, Chen SX, Li J (2020) Physical model test of seepage and deformation characteristics of shallow expansive soil slope. B Eng Geol Environ 79:4063–4078. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01811-0
Deng J, Cu DS (2011) On a statistical damage constitutive model for rock materials. Comput Geosci-UK 37:122–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2010.05.018
Dong ML, Kulatilake PHSW, Zhang FM et al (2018) Deformation and stability investigations in 3-D of an excavated rock slope in a hydroelectric power station in China. Comput Geotech 96:132–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2017.10.019
Dong ML, Zhang FM, Lv JQ et al (2020) Study on deformation and failure law of soft-hard rock interbedding toppling slope base on similar test. B Eng Geol Environ 79:4625–4637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01845-4
Eeckhout EMV, Peng SS (1975) The effect of humidity on the compliances of coal mine shales. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 13:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(76)90705-1
Ferrand TP, Hilairet N, Incel S et al (2017) Dehydration-driven stress transfer triggers intermediate-depth earthquakes. Nat Commun 8:15247. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15247
Feng G, Wang XC, Wang M et al (2020a) Experimental investigation of thermal cycling on fracture characteristics of granite in a geothermal-energy reservoir. Eng Fract Mech 235:107180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2020.107180
Feng G, Wang XC, Kang Y et al (2020b). Effect of thermal cycling-dependent cracks on physical and mechanical properties of granite for enhanced geothermal system. Int J Rock Mech Min 134: 104476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104476
Grosse CU, Finck F, Kurz JH et al (2004) Improvements of AE technique using wavelet algorithms, coherence functions and automatic data analysis. Constr Build Mate 18:203–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2003.10.010
Gutenberg B, Richter CF (1994) Frequency of earthquakes in California. B Seismol Soc Am 34:185–188. https://doi.org/10.1038/156371a0
Han J, Zhang L, Kim HJ et al (2018) Fast pyrolysis and combustion characteristic of three different brown coals. Fuel Process Technol 176:15–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2018.03.010
He MC, Zhao F, Cai M et al (2015) A novel experimental technique to simulate pillar burst in laboratory. Rock Mech Rock Eng 48:1833–1848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-014-0687-5
Henri L, Daniel F, Sergio LF et al (2018) Reaction fronts, permeability and fluid pressure development during dehydration reactions. Earth Planet Sc Lett 496:227–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2018.05.005
Hou JF, Guo ZP, Liu WZ et al (2020) Study on damage model and damage evolution characteristics of backfill with prefabricated fracture under seepage-stress coupling. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2020:3642356. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3642356
Jung H, Green HW, Dobrzhinetskaya LF (2004) Intermediate-depth earthquake faulting by dehydration embrittlement with negative volume change. Nature 428:545–549. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02412
Lemaitre J (1984) How to use damage mechanics. Nucl Eng Des 80:233–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-5493(84)90169-9
Li XZ, Shan ZS, Fan LF (2016) A micro-macro method for predicting the shear strength of brittle rock under compressive loading. Mech Res Commun 75:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechrescom.2016.05.008
Li Z, Reddish D (2004) The effect of groundwater recharge on broken rocks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41:409–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.03.054
Liu G, Li YM, Xiao FK et al (2019) Study on failure mechanics behavior and damage evolution law of yellow sandstone under uniaxial triaxial and pore water action. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 38(S2):3532–3544. https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2019.0625
Liu WZ, Niu SW, Tang HB et al (2021) Pore structure evolution during lignite pyrolysis based on nuclear magnetic resonance. Case Stud Therm Eng 26:101125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2021.101125
Liu YX, Xu J, Zhou G (2018) Relation between crack propagation and internal damage in sandstone during shear failure. J Geophys and Eng 15:2104–2109. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-2140/aac85e
Ma HF, Chen SJ, Song YQ et al (2021a) Experimental investigation into the effects of composition and microstructure on the tensile properties and failure characteristics of different gypsum rocks. Sci Rep-UK 11:14517. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-93947-6
Ma HF, Song YQ, Chen SJ et al (2021b) Experimental investigation on the mechanical behavior and damage evolution mechanism of water-immersed gypsum rock. Rock Mech Rock Eng 59:4929–4948. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02548-2
Ma Q, Tan YL, Liu XS et al (2020) Effect of coal thicknesses on energy evolution characteristics of roof rock-coal-floor rock sandwich composite structure and its damage constitutive model. Compos Part B-Eng 198:108086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2020.108086
Meng T, You YC, Chen J et al (2017) Investigation on the permeability evolution of gypsum interlayer under high temperature and triaxial pressure. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50:2059–2069. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1222-2
Milsch HH, Scholz CH (2005) Dehydration-induced weakening and fault slip in gypsum: implications for the faulting process at intermediate depth in subduction zones. J Geophys Res-Sol Ea 110:B04202. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JB003324
Mirauda D, Russo MG (2020) Modeling bed shear stress distribution in rectangular channels using the entropic parameter. Entropy-Switz 22:87. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22010087
Qiu SL, Feng XT, Zhang CQ et al (2012) Experimental research on mechanical properties of deep marble under different initial damage levels and unloading paths. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 31:1686–1697. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.08.024
Roshan H, Oeser M (2012) A non-isothermal constitutive model for chemically active elastoplastic rocks. Rock Mech Rock Eng 45:361–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-011-0204-z
Rutter EH, Llana-Funez S, Brodie KH (2009) Dehydration and deformation of intact cylinders of serpentinite. J Struct Geol 31:29–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2008.09.008
Shao TB, Song MS, Li JF et al (2016) Brittle and semi-brittle fractures of antigorite serpentinite in triaxial compression. Acta Petrol Sin 32:1675–1687. CNKI:SUN:YSXB.0.2016-06-008
Shkuratnik VL, Filimonov YL, Kuchurin SV (2005) Regularities of acoustic emission in coal samples under triaxial compression. J Min Sci+ 41:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10913-005-0062-8
Si CD, Wu JJ, Wang Y et al (2015) Experimental study on three-stage microwave-assisted fluidized bed drying of Shengli lump lignite. Dry Technol 34:685–691. https://doi.org/10.1080/07373937.2015.1070359
Sun WQ, Dai LD, Li HP et al (2017) Effect of dehydration on the electrical conductivity of phyllite at high temperatures and pressures. Miner Petrol 111:853–863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00710-017-0494-2
Song YQ, Ma HF, Yang JK et al (2022) Dynamic mechanical behaviors and failure mechanism of lignite under SHPB compression test. Sustainability-Basel 14:10528. https://doi.org/10.3390/su141710528
Tang LS, Zhang PC, Wang SJ (2002) Testing study on effects of chemical action of aqueous solution on crack propagation in rock. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 21:822–827. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2002.06.012
Tang ZQ, Yang SQ, Zhai C et al (2018) Coal pores and fracture development during CBM drainage: their promoting effects on the propensity for coal and gas outbursts. J Nat Gas Sci Eng 51:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jngse.2018.01.003
Tao ZG, Zhu C, He MC et al (2020) Research on the safe mining depth of anti-dip bedding slope in Changshanhao Mine. Geomech Geophys Geo 6:36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-020-00159-9
Tao ZG, Zhu C, He MC et al (2021) A physical modeling-based study on the control mechanisms of negative Poisson’s ratio anchor cable on the stratified toppling deformation of anti-inclined slopes. Int J Rock Mech Min 138: 104632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2021.104632
Thompson AB (2001) Partial melting of metavolcanics in amphibolite facies regional metamorphism. J Earth Syst Sci 110:287–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02702895
Ulusay R (2015) The ISRM suggested methods for rock characterization, testing and monitoring: 2007–2014[M]. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-07713-0
Vásárhelyi B (2005) Statistical analysis of the influence of water content on the strength of the Miocene limestone. Rock Mech Rock Eng 38:69–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-004-0034-3
Wang CL, He BB, Hou XL et al (2019) Stress–energy mechanism for rock failure evolution based on damage mechanics in hard rock. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53:1021–1037. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01953-y
Wang CL, Hou XL, Liu YB (2020a) Three-dimensional crack recognition by unsupervised machine learning. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54:893–903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02287-w
Wang DY, Song YC, Liu Y et al (2012) The influence of igneous intrusions on the peak temperatures of host rocks: finite-time emplacement, evaporation, dehydration, and decarbonation. Comput Geosci-UK 38:99–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2011.05.011
Wang L, Rybacki E, Bonnelye A et al (2021a) Experimental investigation on static and dynamic bulk moduli of dry and fluid-saturated porous sandstones. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54:129–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02248-3
Wang LL, Bornert M, Heripre E et al (2015) The mechanisms of deformation and damage of mudstones: a micro-scale study combining ESEM and DIC. Rock Mech Rock Eng 48:1913–1926. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-014-0670-1
Wang XG, Lian BQ, Feng WK (2020b) A nonlinear creep damage model considering the effect of dry-wet cycles of rocks on reservoir bank slopes. Water-Sui 12:2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12092396
Wang Y, Meng HJ, Long DY (2021b) Experimental investigation of fatigue crack propagation in interbedded marble under multilevel cyclic uniaxial compressive loads. Fatigue Fract Eng M 44(4):933–951. https://doi.org/10.1111/ffe.13404
Weibull W (1951) A statistical distribution function of wide applicability. Int J Appl Mech 18:293–297. https://doi.org/10.1093/qjmam/6.4.453
Xie HP (1989) The fractal effect of irregularity of crack branching on the fracture toughness of brittle materials. Int J Fracture 41:267–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018858
Xin FD, Xu H, Tang DZ et al (2020) Experimental study on the change of reservoir characteristics of different lithotypes of lignite after dehydration and improvement of seepage capacity. Fuel 277:118196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118196
Yang RS, Xu P (2017) Fractal study of media damage under blasting loading. Chin J Coal Soci 42:3065–3071. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2017.0107
Yin Q, Liu RC, Jing HW et al (2019) Experimental study of nonlinear flow behaviors through fractured rock samples after high-temperature exposure. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:2963–2983. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-1741-0
Yin Q, Jing HW, Liu RC et al (2020) Pore characteristics and nonlinear flow behaviors of granite exposed to high temperature. B Eng Geol Environ 79:1239–1257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01628-6
Yin Q, Wu JY, Zhu C et al (2021a) Shear mechanical responses of sandstone exposed to high temperature under constant normal stiffness boundary conditions. Geomech Geophys Geo 7:35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-021-00234-9
Yin Q, Wu JY, Zhu C et al (2021b) The role of multiple heating and water cooling cycles on physical and mechanical responses of granite rocks. Geomech Geophys Geo 7:69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-021-00267-0
Yin DH, Xu QJ (2021) Investigating the damage evolution of sandstone using electrical impedance spectroscopy. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 144:104817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2021.104817
Yin Q, Wu JY, Jiang Z et al (2022) Investigating the effect of water quenching cycles on mechanical behaviors for granites after conventional triaxial compression. Geomech Geophys Geo 8:77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-022-00388-0
Zhang CH, He XW, Zhu SQ et al (2011) Distribution, character and utilization of lignite in China. Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference, Wuhan, Peoples R China. https://doi.org/10.1109/appeec.2011.5748423
Zhang JH, Chen HK, Wang H et al (2019a) Experimental study on damage evolution characteristics of rock-like material. Arab J Sci Eng 44:8503–8513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-03864-0
Zhang HM, Meng XZ, Peng C, et al (2019b) Rock damage constitutive model based on residual intensity characteristics under freeze-thaw and load. Chin J Coal Soci 44:3404–3411. https://doi.org/10.13225/j.cnki.jccs.2018.1681
Zhao YC, Yang TH, Xu T et al (2017) Mechanical and energy release characteristics of different water-bearing sandstones under uniaxial compression. Int J Damage Mech 27:640–656. https://doi.org/10.1177/1056789517697472
Zhu C, He MC, Karakus M et al (2020) Investigating toppling failure mechanism of anti-dip layered slope due to excavation by physical modelling. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53:5029–5050. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02207-y
Zhu C, He MC, Karakus M et al (2021) Numerical simulations of the failure process of anaclinal slope physical model and control mechanism of negative Poisson’s ratio cable. B Eng Geol Environ 80:3365–3380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02148-y
Acknowledgements
We are very grateful to the editors and reviewers for their valuable suggestions on the revising process of this paper.
Funding
We gratefully acknowledge the financial supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFC2904100), the State Key Laboratory of Coal Resources and Safe Mining, China University of Mining and Technology, Beijing (SKLCRSM20KFA11), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2022YJSLJ09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, H., Song, Y., Yang, J. et al. Experimental investigation on acoustic emission and damage characteristics of dehydrated lignite in uniaxial compression test. Bull Eng Geol Environ 82, 292 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03315-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-023-03315-z