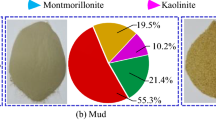
Abstract
Rock masses generally contain many fissures filled with weak materials. At present, the interaction mechanisms of crack coalescence and seepage in rock with filled fissures are still poorly understood. Therefore, this study conducts systematic laboratory tests on sandstone samples with two filled fissures under hydromechanical coupling conditions. The influences of the fissures, filling, ligament length, and bridge angle on the strength, fracture pattern, and permeability are explored. The results show that the strength properties of the sandstone are weakened more significantly by fissures than by water pressure. The increase of strength properties induced by the fillings is more remarkable in the samples with either a longer ligament length or a lower bridge angle. Unlike for mud filling, for sand filling, most of the sand particles in the fissures are crushed after loading, reflecting that the bearing capacity of the sand filling is fully utilized. Thus, sand filling generally has a greater effect on the strength properties than mud filling does. Furthermore, the failure of double-fissure sandstone can be divided into five modes. With the exception of the samples with a high bridge angle, the samples undergo failure modes that change with the existence of fillings, and for samples with a long ligament length or a low bridge angle, the change is more sensitive to the filling type. The weakening effect of fillings on permeability is associated with the failure mode, and it is more remarkable in samples with the “wing cracks + indirect crack coalescence” or “wing cracks + direct crack coalescence” failure modes than in other samples.













Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
25 May 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02296-1
References
Alneasan M, Behnia M, Bagherpour R (2018) Frictional crack initiation and propagation in rocks under compressive loading. Theor Appl Fract Mech 97:189–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2018.08.011
Asadizadeh M, Hossaini MF, Moosavi M, Masoumi H, Ranjith PG (2019) Mechanical characterisation of jointed rock-like material with non-persistent rough joints subjected to uniaxial compression. Eng Geol 260:105224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105224
Bahaaddini M, Sharrock G, Hebblewhite BK (2013) Numerical investigation of the effect of joint geometrical parameters on the mechanical properties of a non-persistent jointed rock mass under uniaxial compression. Comput Geotech 49:206–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2012.10.012
Bastola S, Cai M (2019) Investigation of mechanical properties and crack propagation in pre-cracked marbles using lattice-spring-based synthetic rock mass (LS-SRM) modeling approach. Comput Geotech 110:28–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2019.02.009
Brace WF, Walsh JB, Frangos WT (1968) Permeability of granite under high pressure. J Geophys Res 73(6):2225–2236. https://doi.org/10.1029/JB073i006p02225
Cheng H, Zhou XP, Zhu J, Qian QH (2016) The effects of crack openings on crack initiation, propagation and coalescence behavior in rock-like materials under uniaxial compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(9):3481–3494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-0998-9
Chang X, Deng Y, Li Z, Wang S, Tang CA (2018) Crack propagation from a filled flaw in rocks considering the infill influences. J Appl Geophysics 152:137–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2018.03.018
Chen X, Yu J, Tang CA, Li H, Wang SY (2017a) Experimental and numerical investigation of permeability evolution with damage of sandstone under triaxial compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50(6):1529–1549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1169-3
Chen SW, Yang CH, Wang GB (2017b) Evolution of thermal damage and permeability of Beishan granite. Appl Therm Eng 110:1533–1542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.09.075
Chona R, Irwin GR, Shukla A (1982) Two and three parameter representations of crack-tip stress fields. J Strain Anal Eng 17(2):79–86. https://doi.org/10.1243/03093247V172079
Clarke PL, Abedi R (2018) Modeling the connectivity and intersection of hydraulically loaded cracks with in situ fractures in rock. Int J Numer Anal Met 42(14):1592–1623. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.2800
Davy CA, Skoczylas F, Barnichon JD, Lebon P (2007) Permeability of macro-cracked argillite under confinement: gas and water testing. Phys Chem Earth 32(8–14):667–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2006.02.055
Das R, Singh TN (2021) Effect of closely spaced, non-persistent ubiquitous joint on tunnel boundary deformation: a case study from Himachal Himalaya. Geotech Geol Eng 39:2447–2459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-020-01637-3
Du K, Su R, Tao M, Yang CZ, Momeni A, Wang SF (2019) Specimen shape and cross-section effects on the mechanical properties of rocks under uniaxial compressive stress. B Eng Geol Environ 78(8):6061–6047. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01518-x
Du YT, Li TC, Li WT, Ren YD, Wang G, He P (2020) Experimental study of mechanical and permeability behaviors during the failure of sandstone containing two preexisting fissures under triaxial compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(8):3673–3697. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02119-x
Duriez J, Scholtes L, Donze FV (2016) Micromechanics of wing crack propagation for different flaw properties. Eng Fract Mech 153:378–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2015.12.034
Esterhuizen GS, Dolinar DR, Ellenberger JL (2011) Pillar strength in underground stone mines in the United States. Int J Rock Mech Min 48:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.06.003
Haeri H, Shahriar K, Marji MF, Moarefvand P (2014) Cracks coalescence mechanism and cracks propagation paths in rock-like specimens containing pre-existing random cracks under compression. J Cent South Univ 6:2404–2414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-014-2194-y
Han W, Jiang YJ, Luan HJ, Du YT, Zhu YG, Liu JK (2020) Numerical investigation on the shear behavior of rock-like materials containing fissure-holes with FEM-CZM method. Comput Geotech 125:103670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103670
Heiland J (2003) Permeability of triaxially compressed sandstone: influence of deformation and strain-rate on permeability. Pure Appl Geophys 160(5–6):889–908. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00012571
Hoek E, Martin CD (2014) Fracture initiation and propagation in intact rock-a review. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 6(4):287–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2014.06.001
Huang D, Cen DF, Ma GW, Huang RQ (2015) Step-path failure of rock slopes with intermittent joints. Landslides 12(5):911–926. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-014-0517-6
Huang D, Gu DM, Yang C, Huang RQ, Fu GY (2016) Investigation on mechanical behaviors of sandstone with two preexisting flaws under triaxial compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49:375–399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0757-3
Huang YH, Yang SQ (2019) Mechanical and cracking behavior of granite containing two coplanar flaws under conventional triaxial compression. Int J Damage Mech 28(4):590–610. https://doi.org/10.1177/1056789518780214
Janeiro RP, Einstein HH (2010) Experimental study of the cracking behavior of specimens containing inclusions (under uniaxial compression). Int J Fract 164(1):83–102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-010-9457-x
Lee J, Hong JW, Jung JW (2017) The mechanism of fracture coalescence in pre-cracked rock-type material with three flaws. Eng Geol 223:31–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.04.014
Lei RD, Zhang ZY, Berto F, Ranjith PG, Liu L (2020) Cracking process and acoustic emission characteristics of sandstone with two parallel filled-flaws under biaxial compression. Eng Fract Mech 237:103257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2020.107253
Li ZH, Xiong ZM, Chen HX, Lu H, Huang M, Ma C, Liu YM (2020) Analysis of stress-strain relationship of brittle rock containing microcracks under water pressure. B Eng Geol Environ 79(4):1909–1918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-019-01660-6
Liu LW, Li HB, Li XF, Wu RJ (2020) Full-field strain evolution and characteristic stress levels of rocks containing a single pre-existing flaw under uniaxial compression. B Eng Geol Environ 79(6):3145–3161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01764-4
Liu TY, Cao P, Lin H (2014) Damage and fracture evolution of hydraulic fracturing in compression-shear rock cracks. Theor Appl Fract Mech 74:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2014.06.013
Martin CD, Chandler NA (1994) The progressive fracture of Lac du Bonnet granite. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 31(6):643–659. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(94)90005-1
Mejía Camones LA, Amaral Vargas ED, Pelucí de Figueiredo R, Quadros Velloso R (2013) Application of the discrete element method for modeling of rock crack propagation and coalescence in the step-path failure mechanism. Eng Geol 153(2):80–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.11.013
Miao ST, Pan PZ, Wu ZH, Li SJ, Zhao SK (2018) Fracture analysis of sandstone with a single filled flaw under uniaxial compression. Eng Fract Mech 204:319–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2018.10.009
Mondal S, Olsen-Kettle L, Gross L (2019) Simulating damage evolution and fracture propagation in sandstone containing a preexisting 3-D surface flaw under uniaxial compression. Int J Numer Anal Met 43(7):1448–1466. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.2908
Morgan SP, Johnson C, Einstein HH (2013) Cracking processes in Barre granite: fracture process zones and crack coalescence. Int J Fract 180(2):177–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10704-013-9810-y
Naderloo M, Moosavi M, Ahmadi M (2019) Using acoustic emission technique to monitor damage progress around joints in brittle materials. Theor Appl Fract Mec 104:102368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2019.102368
Niu Y, Zhou XP, Zhou LS (2020) Fracture damage prediction in fissured red sandstone under uniaxial compression: acoustic emission b-value analysis. Fatigue Fract Eng M 43(1):175–190. https://doi.org/10.1111/ffe.13113
Park CH, Bobet A (2009) Crack coalescence in specimens with open and closed flaws: a comparison. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 46(5):819–829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2009.02.006
Pan PZ, Miao ST, Jiang Q, Wu ZH, Shao CY (2020) The influence of infilling conditions on flaw surface relative displacement induced cracking behavior in hard rock. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(10):4449–4470. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-02033-x
Pepe G, Mineo S, Pappalardo G, Cevasco A (2018) Relation between crack initiation-damage stress thresholds and failure strength of intact rock. B Eng Geol Environ 77(2):709–724. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1172-7
Prudencio M, Van Sint JM (2007) Strength and failure modes of rock mass models with non-persistent joints. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 44(6):890–902. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2007.01.005
Saadat M, Taheri A (2019) A numerical approach to investigate the effects of rock texture on the damage and crack propagation of a pre-cracked granite. Comput Geotech 111:89–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2019.03.009
Sharafisafa M, Shen L, Zheng Y, Xiao J (2019) The effect of flaw filling material on the compressive behaviour of 3D printed rock-like discs. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 117:105–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.03.031
Tanikawa W, Shimamoto T (2009) Comparison of Klinkenberg-corrected gas permeability and water permeability in sedimentary rocks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 46(2):229–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2008.03.004
Wang HL, Xu WY, Jia CJ, Cai M, Meng QX (2016) Experimental research on permeability evolution with microcrack development in sandstone under different fluid pressures. J Geotech Geoenviron 142(6):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0001462
Wang XT, Li SC, Xu ZH, Li XZ, Lin P, Lin CJ (2019a) An interval risk assessment method and management of water inflow and inrush in course of karst tunnel excavation. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 92:103033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2019.103033
Wang WC, Sun SR, Le HL, Shu Y, Zhu F, Fan HT, Liu Y (2019b) Experimental and numerical study on failure modes and shear strength parameters of rock-like specimens containing two infilled flaws. Int J Civ Eng 17(12):1895–1908. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40999-019-00449-8
Wang M, Wan W, Zhao YL (2020a) Experimental study on crack propagation and the coalescence of rock-like materials with two preexisting fissures under biaxial compression. B Eng Geol Environ 79(6):3121–3144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01759-1
Wang YX, Zhang H, Lin H, Zhao YL, Li X, Liu Y (2020b) Mechanical behavior and failure analysis of fracture-filled gneissic granite. Theor Appl Fract Mech 108:102674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tafmec.2020.102674
Wang HL, Zhao K, Qu X, Xu JR, Cai M (2020c) Hydro-mechanical properties of rock-like specimens with pre-existing intermittent joints. Eur J Environ Civ En. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2020.1763853
Wong LNY, Einstein H H (2009) Crack coalescence in molded gypsum and carrara marble: Part 1. macroscopic observations and interpretation. Rock Mech Rock Eng 42(3): 475–511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-008-0002-4.
Wong LNY, Li HQ (2013) Numerical study on coalescence of two pre-existing coplanar flaws in rock. Int J Solids Struct 50(22–23):3685–3706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2013.07.010
Wu JY, Chen ZQ, Feng MM, Wang YM, Han GS (2019) The length of pre-existing fissure effects on the dilatancy behavior, acoustic emission, and strength characteristics of cracked sandstone under different confining pressures. Environ Earth Sci 77(12):430. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7608-y
Xiao WJ, Zhang DM, Wang XJ (2020) Experimental study on progressive failure process and permeability characteristics of red sandstone under seepage pressure. Eng Geol 265:105–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.105406
Xu J, Li ZX (2019) Crack propagation and coalescence of step-path failure in rocks. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52(4):965–979. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1661-4
Xu J, Xiao XC, Lv XF, Guo PF, Peng YY (2020) Simulation of compression-induced shear-mode cracks in rocks based on experimental investigations performed on gypsum specimens. B Eng Geol Environ 79(8):4309–4319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-020-01832-9
Yang HQ, Liu JF, Wong LNY (2018) Influence of petroleum on the failure pattern of saturated pre-cracked and intact sandstone. B Eng Geol Environ 77(2):767–774. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1075-7
Yang SQ (2011) Crack coalescence behavior of brittle sandstone samples containing two coplanar fissures in the process of deformation failure. Eng Fract Mech 78(17):3059–3081. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2011.09.002
Yang S, Zhou HW, Zhang SQ, Ren WG (2019) A fractional derivative perspective on transient pulse test for determining the permeability of rocks. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 113:92–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2018.11.013
Yin P, Wong RHC, Chau KT (2014) Coalescence of two parallel pre-existing surface cracks in granite. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 68:66–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2014.02.011
Yu J, Chen SJ, Chen X, Zhang YZ, Cai YY (2015) Experimental investigation on mechanical properties and permeability evolution of red sandstone after heat treatments. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci A 16(9):749–759. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A1400362
Zhao YL, Zhang LY, Wang WJ, Pu CZ, Wan W, Tang JZ (2016) Cracking and stress-strain behavior of rock-like material containing two flaws under uniaxial compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(7):2665–2687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-0932-1
Zhao C, Zhou YM, Zhao CF, Bao C (2018) Cracking processes and coalescence modes in rock-like specimens with two parallel pre-existing cracks. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51(11):3377–3393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-018-1525-y
Zhou XP, Li GQ, Ma HC (2020) Real-time experiment investigations on the coupled thermomechanical and cracking behaviors in granite containing three pre-existing fissures. Eng Fract Mech 224:106797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfracmech.2019.106797
Zhu QQ, Li DY, Han ZY, Li XB, Zhou ZL (2019) Mechanical properties and fracture evolution of sandstone specimens containing different inclusions under uniaxial compression. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 115:33–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.01.010
Zhuang XY, Zhou SW (2020) An experimental and numerical study on the influence of filling materials on double-crack propagation. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(12):5571–5591. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02220-1
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41772299, 51279096, and 51808041) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (No. ZR2019PEE005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
The original online version of this article was revised: The authors would like to update Figures 11 and 13. The ordinate titles of some stress-volumetric strain curves in Fig. 11 are confusing and the positions of (c) (d) and (e) (f) in Fig. 13 need to be swapped.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Du, Y., Zhu, Q. et al. Experimental study on strength properties, fracture patterns, and permeability behaviors of sandstone containing two filled fissures under triaxial compression. Bull Eng Geol Environ 80, 5921–5938 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02286-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-021-02286-3