Abstract
In order to evaluate the effect of established gob coal pillars on the stress in lower rock strata, in the context of of mining in
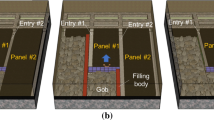
Jurassic coal mine in the Datong mine field, this study theoretically analysed a collapsed roof structure in gobs of Jurassic coal strata and the physics of concentrated loads on coal pillars. The collapse state of roofing in the gobs inclined with the working face and the effect of established coal pillars on the lower rock strata were obtained. Results indicated: a stabilised natural arch structure is formed in Jurassic coal strata by squeezing of collapsed upper roof blocks inclined with the working face, and the arch springing applies a highly concentrated load on the established coal pillars; affected by the established coal pillars, the upper roof of multi-gob coal pillars appears to be a pier-type structure, used as a supporting point for the upper roof load; we propose a method of calculating the stress in the lower rock strata imparted by the coal pillars. In the context of mining Jurassic coal strata at the Tongxin coal mine in the Datong mine field, the depth of the strata affected by the concentrated stress imparted by established gob coal pillars was calculated. The effective range of energy density concentration was also calculated.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Du XL, Song HW, Chen J (2011) Numerical simulation of the evolution of the pressure arch during coal mining. J China Univ Min Technol 6:863–867
Gao MS, Dou LM, Zhang N, Zheng BS, Kan JG (2005) Cusp catastrophic model for instability of coal pillar burst damage and analysis of its application. J China Univ Min Technol 4:433–437
Liu BC, Shen HQ (1988) The mathematical model and solution for optimization of coal pillar for preventing building. J China Coal Soc 3:18–25
Liu CY, Huang BX, Meng XJ (2007) Research on abutment pressure distribution law of over length isolated fully-mechanized top coal caving face. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 1:2671–2676
Miao XX (1990) Natural balance arch and the surrounding rock stability. Ground Press Strat Control 2:55–57
Qian MG, Miao XX, He FL (1994) Analysis of key blocks in the structure of voussoir in longwall mining. J China Coal Soc 6:557–563
Wang B, He KQ (2006) Study on limit equilibrium height expression of critical soil cave of karst collapse. Rock Soil Mech 3:458–462
Wang WJ, Hou CJ (2003) Stability analysis of coal pillar and immediate bottom of extraction opening. Rock Soil Mech 1:75–78
Wang JA, Zhao ZH, Hou ZY (2007) Study on the catastrophic collapse of surface land induced by mining under a shallow and hard strata. J China Coal Soc 10:1051–1056
Xie GX, Yang K, Liu QM (2006) Study on distribution laws of stress in inclined coal pillar for fully-mechanized top-coal caving face. Chin J Rock Mech Eng 3:545–549
Xu ZL (2006) Elastic mechanics. Higher Education Press, Beijing
Yang W, Liu CY, Huang BX, Yang Y (2012) Determination on reasonable malposition of combined mining in close-distance coal seams. J Min Saf Eng 1:101–105
Yang JX, Liu CY, Yang Y, Li JW (2013) Study of the bearing mechanism of the coal roof and the dimension selection of the room and pillar in the shallow and close distance coal seam. J China Univ Min Technol 2:161–168
Yang JX, Liu CY, Yu B (2014) Mechanism of intense strata behaviors at working face influenced by gob pillars of overlying coal seam. Disaster Adv 4:27–35
Yu B, Liu CY, Yang JX, Liu JR (2014) Mechanism of strong pressure reveal under the influence of mining dual system of coal pillar in Datong mining area. J China Coal Soc 1:40–46
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this work was provided by the NSFC program (No. 51174192), the Innovation Project of Graduate Students Training of Jiangsu Province (No. CXLX12_0964), and the “333” Training Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BRA2010024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J.X., Liu, C.Y., Yu, B. et al. The effect of a multi-gob, pier-type roof structure on coal pillar load-bearing capacity and stress distribution. Bull Eng Geol Environ 74, 1267–1273 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-014-0685-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-014-0685-6