Abstract
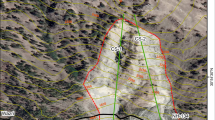
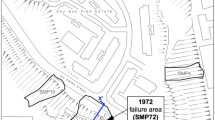
There are very complicated engineering geological conditions in the left abutment slope of the Jinping I hydropower station with the stress-release opening of fractures along existing faults and where lamprophyre veins are present. Prior to the excavation for the dam, the slope generally consisted of a thick marble mass between fault f5 and the free face. As a consequence of the removal of some of the marble to create the abutment, the stability of the slope would be reduced. The paper reports the stability assessments undertaken, based on engineering geological analysis and block theory and the results of the analysis of key rock masses under four conditions: natural, heavy-rain, earthquake and heavy-rain plus earthquake.
Résumé
Des conditions très compliquées, relevant de la géologie de l’ingénieur, se présentent au niveau de l’appui en rive gauche de la station hydroélectrique de Jinping I avec, en conséquence du relâchement des contraintes, l’ouverture de fractures le long des failles présentes et au niveau de veines de lamprophyres. Avant les travaux d’excavation pour le barrage, la pente se présentait comme une masse rocheuse constituée de marbre, la faille f5 se présentant à ce niveau. En conséquence de l’excavation pour la création de l’appui, la stabilité de la pente pourrait être diminuée. L’article présente les analyses de stabilité réalisées, basées sur une étude de géologie de l’ingénieur et la théorie des blocs, et les conclusions sur la stabilité de masses rocheuses clés sous quatre conditions: conditions naturelles, sous fortes pluies, sous séisme et sous fortes pluies et séisme.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang Run-qiu (2000) Time dependent deformation of a high rock slope and its engineering-geological significance. J Eng Geol 8(2):148–153 (In Chinese)
Huang R, Yan M, Lin F (2005) Study on stability and supporting countermeasure of main engineering slopes of Jinping I Hydropower Station. Chengdu: State Key Laboratory of Geohazard Prevention and Geoenvironment Protection, Chengdu University of Technology (in Chinese)
Institute of Chengdu Investigation and Design of National Electrical Power (2003) Feasibility study report of Jinping I Hydropower Station (3) Engineering geology (in Chinese)
Lin F, Huang R, Shi X (2007) Development and application of BAS3D-Block stability analysis software. J Chengdu Univ Technol(Sci Technol Ed) 34(1):82–85 (in Chinese)
Qi S, Wu F, Yan F, Lan H (2004) Mechanism of deep cracks in the left bank slope of Jinping first stage hydropower station. Eng Geol 73(1–2):129–144
Wang S, Huang R, Li Y (1998) Significant engineering geologic research of Jinping hydropower station. Publishing Company of University of Electronic Science and Technology, Chengdu (in Chinese)
Zong R (1996) Numerical modeling on formation mechanism of deep fissures in the Pusiluogou dam site of Jinping I Hydropower Station. Des Hydroelectr Power Stn 12(1):73–79 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the assistance and cooperation of the Chengdu Hydroelectric Investigation and Design Institute of China Hydropower Consulting Group.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, R., Lin, F. & Yan, M. Deformation mechanism and stability evaluation for the left abutment slope of Jinping I hydropower station. Bull Eng Geol Environ 69, 365–372 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-010-0283-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-010-0283-1
Keywords
- Jinping I Hydropower Station
- Deep fractures
- Deformed and cracked rock masses
- Key rock masses
- Stability evaluation
- Monitoring