Abstract
Purpose
The incidence of complex hernias with loss of domain (CHLD) has been increasing and the treatment of these cases may require auxiliary techniques in addition to surgery. This study aims to refine the progressive preoperative pneumoperitonium (PPP) in patients with CHLD, to achieve an increased in wall dimensions.
Methods
Patients presented with a CHLD undergoing PPP protocol were analyzed between May 2017 and May 2019. Our PPP protocol was to use two daily insufflations of 1000 ml of ambient air during a period of 14 days. We compared the abdominal cavity volume (ACV), the hernial sac volume (HSV) and the volume ratio (VR), before and after our refined PPP.
Results
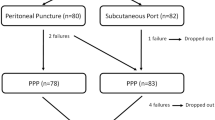
During our evaluation period, the protocol was performed on 16 patients. The mean age was 55.73 (± 12.87), and the mean BMI was 31.35 (± 7.33). The median of HSV was 2104.53 ml; Mean ACV was 6722.36 ml, and median of VR was 29.97% (27.46–34.38 IIQ). The averages were: daily volume of gas ± 1526.66 ml, total volume ± 17,350 ml, and the PPP period of ± 10.7 days. The increase in post-PPP ACV was 52.13% (p < 0.0001), and the VR decreased to 26.9% (p < 0.609). All patients’ symptoms and complications were mild (according Clavien–Dindo grades I and II), and there were no loop injuries, no catheter complications, or any surgical re-interventions.
Conclusion
The study suggests that the use of this method results in a significant increase in ACV, and reduction of the herniated content in a safe and efficient manner, with mild complications.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Poulose BK, Shelton J, Phillips S, Moore D, Nealon W, Penson D et al (2012) Epidemiology and cost of ventral hernia repair: making the case for hernia research. Hernia 16(2):179–183
Dabbas N, Adams K, Pearson K, Royle G (2011) Frequency of abdominal wall hernias: is classical teaching out of date? JRSM Short Rep 2(1):1–6
Schumpelick V, Willis S (2000) Use of progressive pneumoperitoneum in the repair of giant hernias. Hernia 4(2):105–111
Parker SG, Halligan S, Blackburn S, Plumb AAO, Archer L, Mallett S et al (2019) What exactly is meant by “loss of domain” for ventral hernia? Systematic review of definitions. World J Surg. 43(2):396–404. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-018-4783-7
Koontz AR, Graves JW (1954) Preoperative pneumoperitoneum as an aid in the handling of gigantic hernias. Ann Surg 140(5):759–762
Bueno-Lledó J, Torregrosa A, Jiménez R, Pastor PG (2018) Preoperative combination of progressive pneumoperitoneum and botulinum toxin type A in patients with loss of domain hernia. Surg Endosc 32(8):3599–3608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-018-6089-0
Oprea V, Matei O, Gheorghescu D, Leuca D, Buia F, Rosianu M et al (2014) Progressive preoperative pneumoperitoneum (PPP) as an adjunct for surgery of hernias with loss of domain. Chir 109(5):664–669
Rives J, Lardennois B, Pire J, Hibon J (1973) Large incisional hernias the importance of flail abdomen and of subsequent respiratory disorders. Chirurgie. 88:547–563
Mayagoitia JC, Suárez D, Arenas JC, Díaz-de-León V (2006) Preoperative progressive pneumoperitoneum in patients with abdominal-wall hernias. Hernia 10(3):213–217
McAdory S, Cobb W, Carbonell A (2009) Progressive pneumoperitoneum for hernias with loss of domain. Am Surg 75:504–509
Valezi AC, de Melo BGF, Marson AC, Liberatti M, Lopes AG (2018) Preoperative progressive pneumoperitoneum in obese patients with loss of domain hernias. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 14(2):138–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soard.2017.10.009
Sabbagh C, Dumont F, Robert B, Badaoui R, Verhaeghe P, Regimbeau JM (2011) Peritoneal volume is predictive of tension-free fascia closure of large incisional hernias with loss of domain: a prospective study. Hernia 15(5):559–565
Tanaka EY, Yoo JH, Rodrigues AJ, Utiyama EM, Birolini D, Rasslan S (2010) A computerized tomography scan method for calculating the hernia sac and abdominal cavity volume in complex large incisional hernia with loss of domain. Hernia 14(1):63–69
Kingsnorth AN, Sivarajasingham N, Wong S, Butler M (2004) Open mesh repair of incisional hernias with significant loss of domain. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 86(5):363–366
Moreno GI (1947) Chronic eventrations and large hernias; preoperative treatment by progressive pneumoperitoneum: original procedure. Surgery. 22:945–953
Agnew SP, Small W, Wang E, Smith LJ, Hadad I, Dumanian GA (2010) Prospective measurements of intra-abdominal volume and pulmonary function after repair of massive ventral hernias with the components separation technique. Ann Surg 251(5):981–988
Bueno-Lledó J, Torregrosa A, Ballester N, Carreño O, Carbonell F, Pastor PG et al (2017) Preoperative progressive pneumoperitoneum and botulinum toxin type A in patients with large incisional hernia. Hernia 21(2):233–243
Rives J, Pire J, Flament J, Palot J (1985) Treatment of large eventrations. New therapeutic indications apropos of 322 cases. Chirurgie. 111:215–225
Sabbagh C, Dumont F, Fuks D, Yzet T, Verhaeghe P, Regimbeau JM (2012) Progressive preoperative pneumoperitoneum preparation (the Goni Moreno protocol) prior to large incisional hernia surgery: Volumetric, respiratory and clinical impacts. A prospective study. Hernia 16(1):33–40
Muysoms F, Campanelli G, Champault GG, DeBeaux AC, Dietz UA, Jeekel J et al (2012) EuraHS: the development of an international online platform for registration and outcome measurement of ventral abdominal wall Hernia repair. Hernia 16(3):239–250
Muysoms FE, Miserez M, Berrevoet F, Campanelli G, Champault GG, Chelala E et al (2009) Classification of primary and incisional abdominal wall hernias. Hernia 13(4):407–414
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien P (2004) Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 240(2):205–213
Kingsnorth AN, Shahid MK, Valliattu AJ, Hadden RA, Porter CS (2008) Open onlay mesh repair for major abdominal wall hernias with selective use of components separation and fibrin sealant. World J Surg 32(1):26–30
Martre P, Sarsam M, Tuech JJ, Coget J, Schwarz L, Khalil H (2019) New, simple and reliable volumetric calculation technique in incisional hernias with loss of domain. Hernia. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-019-01990-0
Mason E (1995) Pneumoperitoneum in giant hernia. Hernia 4:515–552
Martinez M, Quijano O, Padilha L, Hesiquio S (2002) Cateter de doble luz para pneumoperineo en hernias gigantes. Cir Gen 24:313–318
Steichen F (1965) A simple method for establishing, maintaining and regulating surgically induced pneumoperitoneum in preparation for large hernia repairs. Surge 58:1031–1032
Alyami M, Passot G, Voiglio E, Lundberg PW, Valette PJ, Muller A et al (2015) Feasibility of catheter placement under ultrasound guidance for progressive preoperative pneumoperitoneum for large incisional hernia with loss of domain. World J Surg 39(12):2878–2884
Caldironi MW, Romano M, Bozza F, Pluchinotta AM, Pelizzo MR, Toniato A et al (2010) Progressive pneumoperitoneum in the management of giant incisional hernias: a study of 41 patients. Br J Surg 251(3):981–988
Alam NN, Narang SK, Pathak S, Daniels IR, Smart NJ (2016) Methods of abdominal wall expansion for repair of incisional herniae: a systematic review. Hernia 20(2):191–199
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The protocol was approved by the ethics committee of the institution.
Statement of human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cunha, L.A.C., Cançado, A.R.S., Silveira, C.A.B. et al. Management of complex hernias with loss of domain using daily and fractioned preoperative progressive pneumoperitoneum: a retrospective single-center cohort study. Hernia 25, 1499–1505 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-020-02298-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10029-020-02298-0