Abstract
Purpose
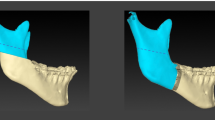
One of the operative complications of the sagittal split osteotomy of the mandible is a bad split, which describes an unfavorable or irregular fracture of the mandible in the course of the osteotomy. The purpose of this study is to identify previous studies which reported incidences of bad split occurrence during sagittal split osteotomy and to discuss its mechanisms and risk factors, based on a literature review, in order to minimize their occurrence. A few illustrative cases are also presented.
Methods
An electronic search was undertaken in January 2011. The titles and abstracts from these results (n = 363) were read for identifying studies which reported incidences of bad split occurrence during sagittal split osteotomy procedures.
Results
Twenty-one studies were identified and assessed. The incidence of bad splits from these studies varied between 0.21% and 22.72%. The buccal plate of the proximal segment and the posterior aspect of the distal segment were the most affected areas.
Discussion
The surgical patient should be evaluated according to age and the presence of unerupted/impacted third molars. Prevention is focused on adequate osteotomy design, eliminating sharp angle where abnormal stress occurs on bony segments, completion of adequate cuts into the retrolingular depression and through the inferior border, and careful separation of the segments. The SSO is an extremely technical and sensitive procedure, and careful attention will probably prevent most unfavorable splits. If a fracture occurs, the fractured segments should be incorporated into the fixation scheme if possible. The occurrence of bad splits cannot always be avoided. When adequately treated the chances of functional success are good.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schuchart K (1942) Ein Beitrag zur chirurgischen Kieferorthopadie unter Berucksichtigung ihrer Bedeutung fur die Behandlung angeborener under worbener Kieferdeformitaten die Soldaten. Dtsch Zahn- Mund-Kieferhk 9:73–89
Trauner R, Obwegeser H (1955) Zur Operationstechnik bei der Progenie und anderen Unterkieferanomalien. Dtsch Zahn Mund Kieferheilk 23:11–26
Mathis H (1956) Über die Möglichkeit der rein enoralen Durchführung der beiderseitigen Osteotomie zur Behandlung der Progenie. Österr Z Stomat 53:362
Dal Pont G (1961) Retromolar osteotomy for the correction of prognathism. J Oral Surg Anesth Hosp Dent Serv 19:42–47
Hunsuck EE (1968) A modified intraoral sagittal splitting technique for correction of mandibular prognathism. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 26:250–253
Epker BN (1977) Modifications in the sagittal osteotomy of the mandible. J Oral Surg 35:157–159
Wolford LM, Bennett MA, Rafferty CG (1987) Modification of the mandibular ramus sagittal split osteotomy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 64:146–155
Loh FC (1992) Technical modification the sagittal split mandibular ramus osteotomy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 74:723–726
Marquez IM, Stella JP (1998) Modification of sagittal split ramus osteotomy to avoid unfavorable fracture around impacted third molars. Int J Adult Orthod Orthognath Surg 13:183–187
Teltzrow T, Kramer FJ, Schulze A, Baethge C, Brachvogel P (2005) Perioperative complications following sagittal split osteotomy of the mandible. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 33:307–313
Guernsey LH, DeChamplain RW (1971) Sequelae and complications of the intra oral sagittal osteotomy in the mandibular rami. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 32:176–192
Behrman SJ (1972) Complications of sagittal osteotomy of the mandibular ramus. J Oral Surg 30:554–561
Veras RB, Kriwalsky MS, Hoffmann S, Maurer P, Schubert J (2008) Functional and radiographic long-term results after bad split in orthognathic surgery. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 37:606–611
Turvey TA (1985) Intraoperative complications of sagittal osteotomy of the mandibular ramus: incidence and management. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 43:504–509
O’Ryan F (1990) Complications of orthognathic surgery. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am 2:593–601
Panula K, Finne K, Oikarinen K (2001) Incidence of complications and problems related to orthognathic surgery: a review of 655 patients. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 59:1128–1137
Martis CS (1984) Complications of mandibular sagittal split osteotomy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 42:101–107
Akhtar S, Tuinzing DB (1999) Unfavorable splits in sagittal split osteotomy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 87:267–268
Simpson W (1981) Problems encountered in the sagittal split operation. Int J Oral Surg 10:81–86
Epker BN, Fish LC (1986) Dentofacial Deformities: integrated Orthodontic and Surgical Correction. Vol. 1 St. Louis, CV Mosby, pp 232–234
Mehra P, Castro V, Freitas RZ, Wolford LM (2001) Complications of the mandibular sagittal split ramus osteotomy associated with the presence or absence of third molars. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 59:854–859
van Merkesteyn JP, Groot RH, van Leeuwaarden R, Kroon FH (1987) Intraoperative complications in sagittal and vertical ramus osteotomies. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 16:665–670
el Deeb M, Wolford L, Bevis R (1989) Complications of orthognathic surgery. Clin Plast Surg 16:825–840
Jönsson E, Svatrz K, Welander V (1979) Sagittal split technique. Part I. Immediate postoperative conditions: a radiographic follow-up study. Int J Oral Surg 8:75–81
MacIntosh RB (1981) Experience with the sagittal osteotomy of the mandibular ramus: a 13-year review. J Maxillofac Surg 9:151–165
Tucker MR (1995) Sagittal ramus osteotomy with and without third molars. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 53(suppl 4):80
Van de Perre JP, Stoelinga PJ, Blijdorp PA, Brouns JJ, Hoppenreijs TJ (1996) Perioperative morbidity in maxillofacial orthopaedic surgery: a retrospective study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 24:263–270
Precious DS, Lung KE, Pynn BR, Goodday RH (1998) Presence of impacted teeth as a determining factor of unfavorable splits in 1256 sagittal split osteotomies. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 85:362–365
Acebal-Bianco F, Vuylsteke PL, Mommaerts MY, De Clercq CA (2000) Perioperative complications in corrective facial orthopedic surgery: a 5-year retrospective study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 58:754–760
Maurer P, Otto C, Eckert AW, Schubert J (2001) Komplikationen bei der chirurgischen Behandlung von Dysgnathien-ein 50 jähriger Behandlungsbericht. Mund Kiefer Gesichtschir 5:357–361
Reyneke JP, Tsakiris P, Becker P (2002) Age as a factor in the complication rate after removal of unerupted/impacted third molars at the time of mandibular sagittal split osteotomy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:654–659
Kim SG, Park SS (2007) Incidence of complications and problems related to orthognathic surgery. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65:2438–2444
Kriwalsky MS, Maurer P, Veras RB, Eckert AW, Schubert J (2008) Risk factors for a bad split during sagittal split osteotomy. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 46:177–179
Falter B, Schepers S, Vrielinck L, Lambrichts I, Thijs H, Politis C (2010) Occurrence of bad splits during sagittal split osteotomy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 110:430–435
Schubert W, Kobienia BJ, Pollock RA (1997) Cross-sectional area of the mandible. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 55:689–692, discussion 693
Schwartz H (2002) The timing of third molar removal in patients undergoing a bilateral sagittal split osteotomy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:132–133
Jones TA, Garg T, Monaghan A (2004) Removal of a deeply impacted mandibular third molar through a sagittal split ramus osteotomy approach. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 42:365–368
Precious DS (2004) Removal of third molars with sagittal split osteotomies: the case for. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 62:1144–1146
Gil JN, Marin C, Claus JD, Lima SM Jr (2007) Modified osteotome for inferior border sagittal split osteotomy. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 65:1840–1842
Nagakawa K, Ueki K, Matsumoto N, Takatsuka S, Yamamoto E, Ooe H (1997) The assessment of trigeminal nerve paresthesia after bilateral sagittal split osteotomy: modified somatosensory evoked potentials recording methods. J Cranio Maxillofac Surg 25:97–101
Joss CU, Vassalli IM (2009) Stability after bilateral sagittal split osteotomy advancement surgery with rigid internal fixation: a systematic review. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:301–313
Tucker MR (2004) Prevention and management of bad splits in sagittal split osteotomies. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 62(suppl 1):14
Mommaerts MY (1992) Two similar ‘bad splits’ and how they were treated. Report of two cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 21:331–332
Patterson AL, Bagby SK (1999) Posterior vertical body osteotomy (PVBO): a predictable rescue procedure for proximal segment fracture during sagittal split ramus osteotomy of the mandible. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 57:475–477
O’Ryan F, Poor DB (2004) Completing sagittal split osteotomy of the mandible after fracture of the buccal plate. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 62:1175–1176
Duguet V, Precious DS, Clinton R (1987) Clivage sagittal des branches montantes mandibulaires: prevention des tranmatismes du pedicule dentaire inferieur. Rev Stomatol Chir Maxillofac 88:71–76
Simpson W (1972) The short lingual cut in the sagittal osteotomy. J Oral Surg 30:811–812
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chrcanovic, B.R., Freire-Maia, B. Risk factors and prevention of bad splits during sagittal split osteotomy. Oral Maxillofac Surg 16, 19–27 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-011-0287-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10006-011-0287-4