Abstract
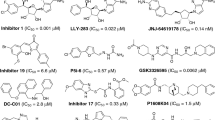
Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5), an important member in PRMT family, has been validated as a promising anticancer target. In this study, through the combination of virtual screening and biological experiments, we have identified two PRMT5 inhibitors with novel scaffold structures. Among them, compound Y2431 showed moderate activity with IC50 value of 10.09 μM and displayed good selectivity against other methyltransferases. The molecular docking analysis and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations suggested that the compound occupied the substrate-arginine binding site. Furthermore, Y2431 exhibited anti-proliferative activity to leukemia cells by inducing cell cycle arrest. Overall, the hit compound could provide a novel scaffold for further optimization of small-molecule PRMT5 inhibitors.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bedford MT, Clarke SG (2009) Protein arginine methylation in mammals: who, what, and why. Mol Cell 33:1–13
Di Lorenzo A, Bedford MT (2011) Histone arginine methylation. FEBS Lett 585:2024–2031
Feng Y, Maity R, Whitelegge JP, Hadjikyriacou A, Li Z, Zurita-Lopez C et al (2013) Mammalian protein arginine methyltransferase 7 (PRMT7) specifically targets RXR sites in lysine- and arginine-rich regions. J Biol Chem 288:37010–37025
Hu H, Qian K, Ho MC, Zheng YG (2016) Small molecule inhibitors of protein arginine methyltransferases. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 25:335–358
Pal S, Vishwanath SN, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Sif S (2004) Human SWI/SNF-associated PRMT5 methylates histone H3 arginine 8 and negatively regulates expression of ST7 and NM23 tumor suppressor genes. Mol Cell Biol 24:9630–9645
Deng X, Gu L, Liu C, Lu T, Lu F, Lu Z et al (2010) Arginine methylation mediated by the Arabidopsis homolog of PRMT5 is essential for proper pre-mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:19114–19119
Andreu-Perez P, Esteve-Puig R, de Torre-Minguela C, Lopez-Fauqued M, Bech-Serra JJ, Tenbaum S et al (2011) Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 regulates ERK1/2 signal transduction amplitude and cell fate through CRAF. Sci Signal 4:ra58-ra
Nishida KM, Okada TN, Kawamura T, Mituyama T, Kawamura Y, Inagaki S et al (2009) Functional involvement of Tudor and dPRMT5 in the piRNA processing pathway in Drosophila germlines. EMBO J 28:3820–3831
Kanda M, Shimizu D, Fujii T, Tanaka H, Shibata M, Iwata N et al (2016) Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 is associated with malignant phenotype and peritoneal metastasis in gastric cancer. Int J Oncol 49:1195–1202
Zhang B, Dong S, Zhu R, Hu C, Hou J, Li Y et al (2015) Targeting protein arginine methyltransferase 5 inhibits colorectal cancer growth by decreasing arginine methylation of eIF4E and FGFR3. Oncotarget 6:22799–22811
Tarighat S, Santhanam R, Frankhouser D, Radomska HS, Lai H, Anghelina M et al (2016) The dual epigenetic role of PRMT5 in acute myeloid leukemia: gene activation and repression via histone arginine methylation. Leukemia 30:789–799
Antonysamy S, Bonday Z, Campbell RM, Doyle B, Druzina Z, Gheyi T et al (2012) Crystal structure of the human PRMT5:MEP50 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:17960–17965
Smil D, Eram MS, Li F, Kennedy S, Szewczyk MM, Brown PJ et al (2015) Discovery of a dual PRMT5-PRMT7 inhibitor. ACS Med Chem Lett 6:408–412
Bonday ZQ, Cortez GS, Grogan MJ, Antonysamy S, Weichert K, Bocchinfuso WP et al (2018) LLY-283, a potent and selective inhibitor of arginine methyltransferase 5, PRMT5, with antitumor activity. ACS Med Chem Lett 9:612–617
Ye F, Zhang W, Ye X, Jin J, Lv Z, Luo C (2018) Identification of selective, cell active inhibitors of protein arginine methyltransferase 5 through structure-based virtual screening and biological assays. J Chem Inf Model 58:1066–1073
Gerhart SV, Kellner WA, Thompson C, Pappalardi MB, Zhang XP, Montes de Oca R et al (2018) Activation of the p53-MDM4 regulatory axis defines the anti-tumour response to PRMT5 inhibition through its role in regulating cellular splicing. Sci Rep 8:9711
Ye Y, Zhang B, Mao R, Zhang C, Wang Y, Xing J et al (2017) Discovery and optimization of selective inhibitors of protein arginine methyltransferase 5 by docking-based virtual screening. Org Biomol Chem 15:3648–3661
Alinari L, Mahasenan KV, Yan F, Karkhanis V, Chung JH, Smith EM et al (2015) Selective inhibition of protein arginine methyltransferase 5 blocks initiation and maintenance of B-cell transformation. Blood 125:2530–2543
Cavasotto CN, Orry AJW (2007) Ligand docking and structure-based virtual screening in drug discovery. Curr Top Med Chem 7:1006–1014
Lipinski CA, Lombardo F, Dominy BW, Feeney PJ (2001) Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 46:3–26
Whitty A (2011) Growing PAINS in academic drug discovery. Future Med Chem 3:797–801
Jin WY, Ma Y, Li WY, Li HL, Wang RL (2018) Scaffold-based novel SHP2 allosteric inhibitors design using receptor-Ligand pharmacophore model, virtual screening and molecular dynamics. Comput Biol Chem 73:179–188
Shelley JC, Cholleti A, Frye LL, Greenwood JR, Timlin MR, Uchimaya M (2007) Epik: a software program for pK( a ) prediction and protonation state generation for drug-like molecules. J Comput Aided Mol Des 21:681–691
Friesner RA, Banks JL, Murphy RB, Halgren TA, Klicic JJ, Mainz DT et al (2004) Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J Med Chem 47:1739–49
Zhang WY, Lu WC, Jiang H, Lv ZB, Xie YQ, Lian FL et al (2017) Discovery of alkyl bis(oxy)dibenzimidamide derivatives as novel protein arginine methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1) inhibitors. Chem Biol Drug Des 90:1260–1270
Mao R, Shao J, Zhu K, Zhang Y, Ding H, Zhang C et al (2017) Potent, Selective, and cell active protein arginine methyltransferase 5 (PRMT5) inhibitor developed by structure-based virtual screening and hit optimization. J Med Chem 60:6289–6304
Salomon-Ferrer R, Case DA, Walker RC (2013) An overview of the Amber biomolecular simulation package. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Comput Mol Sci 3:198–210
Case DA, Cheatham TE 3rd, Darden T, Gohlke H, Luo R, Merz KM Jr et al (2005) The Amber biomolecular simulation programs. J Comput Chem 26:1668–1688
Wang J, Wolf RM, Caldwell JW, Kollman PA, Case DA (2004) Development and testing of a general amber force field. J Comput Chem 25:1157–1174
Jakalian A, Jack DB, Bayly CI (2002) Fast, efficient generation of high-quality atomic charges. AM1-BCC model: II. Parameterization and validation. J Comput Chem 23:1623–41
Wang J, Wang W, Kollman PA, Case DA (2006) Automatic atom type and bond type perception in molecular mechanical calculations. J Mol Graph Model 25:247–260
Nayar D, Agarwal M, Chakravarty C (2011) Comparison of tetrahedral order, liquid state anomalies, and hydration behavior of mTIP3P and TIP4P water models. J Chem Theory Comput 7:3354–3367
Roe DR, Cheatham TE 3rd (2013) PTRAJ and CPPTRAJ: software for processing and analysis of molecular dynamics trajectory data. J Chem Theory Comput 9:3084–3095
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K (1996) VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J Mol Graph 14(33–8):27–28
Miller BR 3rd, McGee TD Jr, Swails JM, Homeyer N, Gohlke H, Roitberg AE (2012) MMPBSA.py: an efficient program for end-state free energy calculations. J Chem Theory Computation 8:3314–21
Gohlke H, Kiel C, Case DA (2003) Insights into protein-protein binding by binding free energy calculation and free energy decomposition for the Ras-Raf and Ras-RalGDS complexes. J Mol Biol 330:891–913
Zhu K, Jiang CS, Hu J, Liu X, Yan X, Tao H et al (2018) Interaction assessments of the first S-adenosylmethionine competitive inhibitor and the essential interacting partner methylosome protein 50 with protein arginine methyltransferase 5 by combined computational methods. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 495:721–727
Funding
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81803339 to J.J.) and Jiaxing Science and Technology Project (2018AY32002 to C.C.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Project design, manuscript editing were performed by Fei Ye. Material preparation, data collections, and results analysis were performed by Qian Zhang, Lun Zhang, Jia Jin, Chenxi Cao, Yaohua Fan, Xiaoguang Wang, Haofeng Hu and Xiaoqing Ye.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Q., Zhang, L., Jin, J. et al. Identification of PRMT5 inhibitors with novel scaffold structures through virtual screening and biological evaluations. J Mol Model 28, 184 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-022-05125-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-022-05125-8