Abstract
Objectives
Analysis of the effects of titanium surface properties on the biological behavior of human gingival fibroblasts (HGFs).
Materials and methods
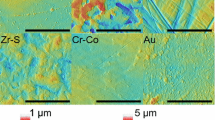
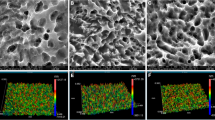
HGFs were in vitro cultured on a titanium surface modified by a dual acid-etched procedure and on a control machined surface. Cell adhesion, proliferation, apoptosis, production of certain extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins, and expression of granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor receptor (GM-CSFR) were investigated using in each experiment a total of 18 samples for each titanium surface.
Results
Cell attachment at 3 h of culture was statistically significantly higher on the etched surface. HGF growth increased on both surfaces during the entire experimental period and at day 14 of culture cell proliferation was statistically significantly higher on the treated surface than on the control. No statistically significant differences in percentage of apoptosis events were observed between the surfaces. ECM protein production increased progressively over time on both surfaces. A statistically significant deposition was observed at day 7 and 14 for collagen I and only at day 14 for fibronectin and tenascin, when compared to the baseline. GM-CSFR registered a positive expression on both surfaces, statistically significant at day 14 on the etched surface in comparison with the machined one.
Conclusions
Data showed that titanium surface microtopography modulates in vitro cell response and phenotypical expression of HGFs. The etched surface promoted a higher cell proliferation and differentiation improving the biological behavior of HGFs.
Clinical relevance
Results suggest a possible beneficial effect of surface etching modification on peri-implant biological integration and soft tissue healing which is critical for the formation of a biological seal around the neck of dental implants.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cochran DL (1999) A comparison of endosseous dental implant surfaces. J Periodontol 70:1523–1539
Shalabi MM, Gortemaker A, Van’t Hof MA, Jansen JA et al (2006) Implant surface roughness and bone healing: a systematic review. J Dent Res 85:496–500
Chappuis V, Buser R, Brägger U, Bornstein MM et al (2013) Long-term outcomes of dental implants with a titanium plasma-sprayed surface: a 20-year prospective case series study in partially edentulous patients. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 15:780–790
Esposito M, Maghaireh H, Grusovin MG, Ziounas I et al (2012) Soft tissue management for dental implants: what are the most effective techniques? A Cochrane systematic review. Eur J Oral Implantol 5:221–238
Lavelle CL (1981) Mucosal seal around endosseous dental implants. J Oral Implantol 9:357–371
Tomasi C, Tessarolo F, Caola I, Wennström J et al (2013) Morphogenesis of peri-implant mucosa revisited: an experimental study in humans. Clin Oral Implants Res. doi:10.1111/clr.12223
Rozario T, De Simone DW (2010) The extracellular matrix in development and morphogenesis: a dynamic view. Dev Biol 341:126–140
Chavrier C, Hartmann DJ, Couble ML, Herbage D (1988) Distribution and organization of the elastic system fibres in healthy human gingiva. Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical study. Histochemistry 89:47–52
Hynes RO, Yamada KM (1982) Fibronectins: multifunctional modular glycoproteins. J Cell Biol 95:369–377
Jones FS, Jones PL (2000) The Tenascin family of ECM glycoproteins: structure, function, and regulation during embryonic development and tissue remodeling. Dev Dyn 218:235–259
Schroeder HE, Listgarten MA (1997) The gingival tissues: the architecture of periodontal protection. Periodontol 2000(13):91–120
Fleetwood AJ, Cook AD, Hamilton JA (2005) Functions of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Crit Rev Immunol 25:405–428
Hamilton JA, Anderson GP (2004) GM-CSF biology. Growth Factors 22:225–231
Postiglione L, Montagnani S, Riccio A, Montuori N et al (2002) Enhanced expression of the receptor for granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating factor on dermal fibroblasts from scleroderma patients. J Rheumatol 29:94–101
Postiglione L, Di Domenico G, Montagnani S, Di Spigna G et al (2003) Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating (GM-CSF) induces the osteoblastic differentiation of the human osteosarcoma cell line SaOS-2. Calcif Tissue Int 72:85–97
Di Domenico G, Del Vecchio L, Ramaglia L, Postiglione L (2003) Immunophenotipic analysis of human gingival fibroblasts and its regulation by granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF). Minerva Stomatol 52:81–91
Davies JE (1998) Mechanisms of endosseous integration. Int J Prosthodont 11:391–401
Szmukler-Moncler S, Testori T, Bernard JP (2004) Etched implants: a comparative surface analysis of four implant systems. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 69:46–57
Brunette DM (1988) The effects of implant surface topography on the behaviour of cells. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 3:231–246
Anselme K, Bigerelle M, Noel B, Dufresne E et al (2000) Qualitative and quantitative study of human osteoblast adhesion on materials with various surface roughnesses. J Biomed Mater Res 49:155–166
Ramaglia L, Postiglione L, Di Spigna G, Capece G et al (2011) Sandblasted-acid-etched titanium surface influences in vitro the biological behavior of SaOS-2 human osteoblast-like cells. Dent Mater J 30:183–192
Palaiologou A, Stoute D, Fan Y, Lallier TE (2012) Altered cell motility and attachment with titanium surface modifications. J Periodontol 83:90–100
Lowenberg BF, Pilliar RM, Aubin JE, Fernie GR et al (1987) Migration, attachment, and orientation of human gingival fibroblasts to root slices, naked and porous-surfaced titanium alloy discs and zircalloy-2 discs in vitro. J Dent Res 66:1000–1005
Guy SC, McQuade MJ, Scheidt MJ, McPherson JC III et al (1993) In vitro attachment of human gingival fibroblasts to endosseous implant materials. J Periodontol 64:542–546
Abrahamsson I, Zitzmann NU, Berglundh T, Wennerberg A et al (2001) Bone and soft tissue integration to titanium implants with different surface topography: an experimental study in the dog. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 16:323–332
Abrahamsson I, Zitzmann NU, Berglundh T, Linder E et al (2002) The mucosal attachment to titanium implants with different surface characteristics: an experimental study in dogs. J Clin Periodontol 29:448–455
Berglundh T, Lindhe J, Ericsson I, Marinello CP et al (1991) The soft tissue barrier at implants and teeth. Clin Oral Implants Res 2:81–90
Listgarten MA, Lang NP, Schroeder HE, Scheroeder A (1991) Periodontal tissues and their counterparts around endosseous implants. Clin Oral Implants Res 2:1–19
Berglundh T, Lindhe J (1996) Dimension of the peri-implant mucosa. Biological width revisited. J Clin Periodontol 23:971–973
Lindhe J, Berglundh T (1998) The interface between the mucosa and the implant. J Periodontol 17:47–54
Schupbach P, Glauser R (2007) The defense architecture of the human peri-implant mucosa: a histological study. J Prosthet Dent 97:S15–S25
Kononen M, Hormia M, Kivilahti J, Hautaniemi J et al (1992) Effect of surface processing on the attachment, orientation, and proliferation of human gingival fibroblasts on titanium. J Biomed Mater Res 26:1325–1341
Kunzler TP, Drobek T, Schuler M, Spencer ND (2007) Systematic study of osteoblast and fibroblast response to roughness by means of surface-morphology gradients. Biomaterials 28:2175–2182
Oates TW, Maller SC, West J, Steffensen B (2005) Human gingival fibroblast integrin subunit expression on titanium implant surfaces. J Periodontol 76:1743–1750
Grossner-Schreiber B, Herzog M, Hedderich J, Duck A et al (2006) Focal adhesion contact formation by fibroblasts cultured on surface modified dental implants: an in vitro study. Clin Oral Implants Res 17:736–745
Albrektsson T, Wennerberg A (2004) Oral implant surfaces: part 1-review focusing on topographic and chemical properties of different surfaces and in vivo responses to them. Int J Prosthodont 17:536–543
Wennerberg A, Albrektsson T (2010) On implant surfaces: a review of current knowledge and opinions. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 25:63–74
Postiglione L, Di Domenico G, Ramaglia L, Montagnani S et al (2003) Behavior of SaOS-2 cells cultured on different titanium surfaces. J Dent Res 82:692–696
Postiglione L, Di Domenico G, Ramaglia L, Di Lauro AE et al (2004) Different titanium surfaces modulate the bone phenotype of SaOS-2 osteoblast-like cells. Eur J Histochem 48:213–222
Wirth C, Comte V, Lagneau C (2005) Nitinol surface roughness modulates in vitro cell response: a comparison between fibroblasts and osteoblasts. Mater Sci Eng C 25:51–60
Asano Y, Ihn H, Yamane K, Kubo M et al (2004) Impaired Smad7-Smurf-mediated negative regulation of TGF-β signaling in scleroderma fibroblasts. J Clin Invest 113:253–264
Holmes A, Abraham DJ, Sa S, Shiwen X et al (2001) CTGF and SMADs, maintenance of scleroderma phenotype is independent of SMAD signaling. J Biol Chem 14:10594–10601
Mori Y, Chen SJ, Varga J (2003) Expression and regulation of intracellular SMAD signaling in scleroderma skin fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum 48:1964–1978
Zetterqvist L, Feldman S, Rotter B, Vincenzi G et al (2010) A prospective, multicenter, randomized-controlled 5-year study of hybrid and fully etched implants for the incidence of peri-implantitis. J Periodontol 81:493–501
Rodriguez y Baena R, Arciola CR, Selan L, Battaglia R et al (2012) Evaluation of bacterial adhesion on machined titanium, Osseotite® and Nanotite® discs. Int J Artif Organs 35:754–761
Ramaglia L, Sbordone L, Ciaglia R, Barone A et al (1999) A clinical comparison of the efficacy and efficiency of two professional prophylaxis procedures in orthodontic patients. Eur J Orthod 21:423–428
Ramaglia L, di Lauro AE, Morgese F, Squillace A (2006) Profilometric and standard error of the mean analysis of rough implant surfaces treated with different instrumentations. Implant Dent 15:77–82
Yeo IS, Kim HY, Lim KS, Han JS (2012) Implant surface factors and bacterial adhesion: a review of the literature. Int J Artif Organs 35:762–772
Stach RM, Kohles SS (2003) A meta-analysis examining the clinical survivability of machined-surface Osseotite implants in poor-quality bone. Implant Dent 12:87–96
Toti P, Sbordone C, Martuscelli R, Califano L et al (2013) Gene clustering analysis in human osteoporosis disease and modifications of the jawbone. Arch Oral Biol 58:912–929
Ramaglia L, Morgese F, Filippella M, Colao A (2007) Oral and maxillofacial manifestations of Gardner’s syndrome associated with growth hormone deficiency: case report and literature review. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 103:e30–34
Sullivan D, Sherwood R, Porter S (2001) Long-term performance of Osseotite implants: a 6-year clinical follow-up. Compend Contin Educ Dent 22:326–334
Acknowledgments
The investigation was supported in part by a grant from “Regione Campania”, Department of Scientific and Technological Research, Italy, L.R. n. 5/02 to Prof. Luca Ramaglia and in part by a grant from Biomax SpA, Vicenza, Italy, to Prof. Luca Ramaglia. The authors thank Dr. Maria Pia Bruno (Department of Neurosciences, Reproductive and Odontostomatological Sciences; University of Naples “Federico II”, Naples, Italy) for her assistance in manuscript preparation.
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that no financial relationships, current or within the past 5 years, exist regarding any of the products involved in this study. The manuscript does not contain clinical studies or patient data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramaglia, L., Di Spigna, G., Capece, G. et al. Differentiation, apoptosis, and GM-CSF receptor expression of human gingival fibroblasts on a titanium surface treated by a dual acid-etched procedure. Clin Oral Invest 19, 2245–2253 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-015-1469-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-015-1469-5