Abstract
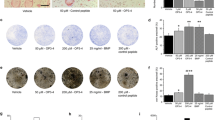
Etanercept (ETN), which is a recombinant human soluble tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor that inhibits TNF activity, is effective in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. We investigated the effect of ETN on recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2)-induced ectopic bone formation in vivo. A block copolymer composed of poly-d,l-lactic acid with random insertion of p-dioxanone and polyethylene glycol (PLA–DX–PEG polymer) was used as the delivery system. Polymer discs (6 mm, 30 mg) containing 5 μg rhBMP-2 were implanted into the left dorsal muscle pouch of mice (n = 50). In the systemic administration groups (n = 5 per group), ETN was subcutaneously injected (25 mg/human = 12.5 μg/mouse) twice per week in a dose-dependent manner (placebo, 12.5 × 10−3, 12.5 × 10−1, 12.5, 125 μg), whereas a single dose of ETN (placebo, 12.5 × 10−3, 12.5 × 10−1, 12.5, 125 μg) was embedded in each rhBMP-2 polymer disc in the local administration groups (n = 5 per group). Three weeks after implantation, the mice were killed and the implants were analyzed. Implants in the optimally dosed groups had increased radiodensity, which was consistent with a significant increase in bone mineral content of the ossicles. Bone histomorphology revealed a significant increase in bone volume/total volume, number of osteoblasts, osteoblast surface/bone surface, and a significant decrease in the number of osteoclasts, osteoclast surface/bone surface in the optimal dosed systemic and locally administered groups. These data suggest that the optimal dose of ETN, administered either systemically or locally, enhanced the bone-inducing capacity of BMP with no apparent adverse systemic effects.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li P, Schwarz EM, O’Keefe RJ, Ma L, Boyce BF, Xing L (2004) RANK signaling is not required for TNF-alpha-mediated increase in CD11(hi) osteoclast precursors but is essential for mature osteoclast formation in TNFalpha-mediated inflammatory arthritis. J Bone Miner Res 19:207–213
Takayanagi H, Ogasawara K, Hida S, Chiba T, Murata S, Sato K, Takaoka A, Yokochi T, Oda H, Tanaka K, Nakamura K, Taniguchi T (2000) T-cell-mediated regulation of osteoclastogenesis by signalling cross-talk between RANKL and IFN-gamma. Nature (Lond) 408:600–605
Theill LE, Boyle WJ, Penninger JM (2002) RANK-L and RANK: T cells, bone loss, and mammalian evolution. Annu Rev Immunol 20:795–823
Chopin F, Garnero P, le Henanff A, Debiais F, Daragon A, Roux C, Sany J, Wendling D, Zarnitsky C, Ravaud P, Thomas T (2008) Long-term effects of infliximab on bone and cartilage turnover markers in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 67:353–357
Kageyama Y, Takahashi M, Nagafusa T, Torikai E, Nagano A (2008) Etanercept reduces the oxidative stress marker levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 28:245–251
Nakase T, Takaoka K, Masuhara K, Shimizu K, Yoshikawa H, Ochi T (1997) Interleukin-1 beta enhances and tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits bone morphogenetic protein-2-induced alkaline phosphatase activity in MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells. Bone (NY) 21:17–21
Yamashita M, Otsuka F, Mukai T, Otani H, Inagaki K, Miyoshi T, Goto J, Yamamura M, Makino H (2008) Simvastatin antagonizes tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibition of bone morphogenetic proteins-2-induced osteoblast differentiation by regulating Smad signaling and Ras/Rho-mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Endocrinol 196:601–613
Kaneki H, Guo R, Chen D, Yao Z, Schwarz EM, Zhang YE, Boyce BF, Xing L (2006) Tumor necrosis factor promotes Runx2 degradation through up-regulation of Smurf1 and Smurf2 in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem 281:4326–4333
Kaymakcalan Z, Sakorafas P, Bose S, Scesney S, Xiong L, Hanzatian DK, Salfeld J, Sasso EH (2009) Comparisons of affinities, avidities, and complement activation of adalimumab, infliximab, and etanercept in binding to soluble and membrane tumor necrosis factor. Clin Immunol 131:308–316
Scallon B, Cai A, Solowski N, Rosenberg A, Song XY, Shealy D, Wagner C (2002) Binding and functional comparisons of two types of tumor necrosis factor antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 301:418–426
Saito N, Okada T, Horiuchi H, Murakami N, Takahashi J, Nawata M, Ota H, Nozaki K, Takaoka K (2001) A biodegradable polymer as a cytokine delivery system for inducing bone formation. Nat Biotechnol 19:332–335
Kato M, Toyoda H, Namikawa T, Hoshino M, Terai H, Miyamoto S, Takaoka K (2006) Optimized use of a biodegradable polymer as a carrier material for the local delivery of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 (rhBMP-2). Biomaterials 27:2035–2041
Suzuki A, Terai H, Toyoda H, Namikawa T, Yokota Y, Tsunoda T, Takaoka K (2006) A biodegradable delivery system for antibiotics and recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2: a potential treatment for infected bone defects. J Orthop Res 24:327–332
Toyoda H, Terai H, Sasaoka R, Oda K, Takaoka K (2005) Augmentation of bone morphogenetic protein-induced bone mass by local delivery of a prostaglandin E EP4 receptor agonist. Bone (NY) 37:555–562
Yano K, Hoshino M, Ohta Y, Manaka T, Naka Y, Imai Y, Sebald W, Takaoka K (2009) Osteoinductive capacity and heat stability of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 produced by Escherichia coli and dimerized by biochemical processing. J Bone Miner Metab 27:355–363
Zhao B, Katagiri T, Toyoda H, Takada T, Yanai T, Fukuda T, Chung UI, Koike T, Takaoka K, Kamijo R (2006) Heparin potentiates the in vivo ectopic bone formation induced by bone morphogenetic protein-2. J Biol Chem 281:23246–23253
Nakamura T, Imai Y, Matsumoto T, Sato S, Takeuchi K, Igarashi K, Harada Y, Azuma Y, Krust A, Yamamoto Y, Nishina H, Takeda S, Takayanagi H, Metzger D, Kanno J, Takaoka K, Martin TJ, Chambon P, Kato S (2007) Estrogen prevents bone loss via estrogen receptor alpha and induction of Fas ligand in osteoclasts. Cell 130:811–823
Parfitt AM, Drezner MK, Glorieux FH, Kanis JA, Malluche H, Meunier PJ, Ott SM, Recker RR (1987) Bone histomorphometry: standardization of nomenclature, symbols, and units. Report of the ASBMR Histomorphometry Nomenclature Committee. J Bone Miner Res 2:595–610
Simonet WS, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Kelley M, Chang MS et al (1997) Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the regulation of bone density. Cell 89:309–319
Kawaguchi A, Nakaya H, Okabe T, Tensho K, Nawata M, Eguchi Y, Imai Y, Takaoka K, Wakitani S (2009) Blocking of tumor necrosis factor activity promotes natural repair of osteochondral defect in rabbit knee. Acta Orthopaedica (in press)
van der Heijde DM (1995) Joint erosions and patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol 34(suppl 2):74–78
Quinn MA, Conaghan PG, Emery P (2001) The therapeutic approach of early intervention for rheumatoid arthritis: what is the evidence? Rheumatology (Oxf) 40:1211–1220
Mohler KM, Torrance DS, Smith CA, Goodwin RG, Stremler KE, Fung VP, Madani H, Widmer MB (1993) Soluble tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptors are effective therapeutic agents in lethal endotoxemia and function simultaneously as both TNF carriers and TNF antagonists. J Immunol 151:1548–1561
Scott DL, Kingsley GH (2006) Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors for rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 355:704–712
Bathon JM, Martin RW, Fleischmann RM, Tesser JR, Schiff MH, Keystone EC, Genovese MC, Wasko MC, Moreland LW, Weaver AL, Markenson J, Finck BK (2000) A comparison of etanercept and methotrexate in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 343:1586–1593
Gerstenfeld LC, Cho TJ, Kon T, Aizawa T, Tsay A, Fitch J, Barnes GL, Graves DT, Einhorn TA (2003) Impaired fracture healing in the absence of TNF-alpha signaling: the role of TNF-alpha in endochondral cartilage resorption. J Bone Miner Res 18:1584–1592
Hashimoto J, Yoshikawa H, Takaoka K, Shimizu N, Masuhara K, Tsuda T, Miyamoto S, Ono K (1989) Inhibitory effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha on fracture healing in rats. Bone (NY) 10:453–457
Hong JH, Lee GT, Lee JH, Kwon SJ, Park SH, Kim SJ, Kim IY (2009) Effect of bone morphogenetic protein-6 on macrophages. Immunology 128:442–450
Urist MR (1965) Bone: formation by autoinduction. Science 150:893–899
Wozney JM, Rosen V, Celeste AJ, Mitsock LM, Whitters MJ, Kriz RW, Hewick RM, Wang EA (1988) Novel regulators of bone formation: molecular clones and activities. Science 242:1528–1534
Hirata K, Mizuno A, Yamaguchi A (2007) Transplantation of skin fibroblasts expressing BMP-2 contributes to the healing of critical-sized bone defects. J Bone Miner Metab 25:6–11
Nakase T, Yoshikawa H (2006) Potential roles of bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) in skeletal repair and regeneration. J Bone Miner Metab 24:425–433
Bhandari M, Guyatt GH, Swiontkowski MF, Schemitsch EH (2001) Treatment of open fractures of the shaft of the tibia. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 83:62–68
Valentin-Opran A, Wozney J, Csimma C, Lilly L, Riedel GE (2002) Clinical evaluation of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2. Clin Orthop Relat Res 395:110–120
Yoneda M, Terai H, Imai Y, Okada T, Nozaki K, Inoue H, Miyamoto S, Takaoka K (2005) Repair of an intercalated long bone defect with a synthetic biodegradable bone-inducing implant. Biomaterials 26:5145–5152
Namikawa T, Terai H, Hoshino M, Kato M, Toyoda H, Yano K, Nakamura H, Takaoka K (2007) Enhancing effects of a prostaglandin EP4 receptor agonist on recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 mediated spine fusion in a rabbit model. Spine 32:2294–2299
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan (Project Grants 16109009 and 1679085 to KT, and 19791018 to YI). We extend our appreciation to Ms K. Kamei, A. Inagaki, K. Hata, and Y. Hanamoto for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Eguchi, Y., Wakitani, S., Imai, Y. et al. Antitumor necrotic factor agent promotes BMP-2-induced ectopic bone formation. J Bone Miner Metab 28, 157–164 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-009-0127-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-009-0127-x