Abstract
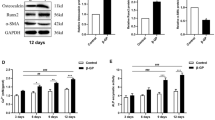
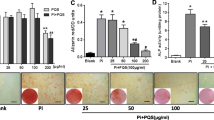
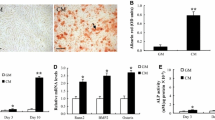
Accumulating evidence has indicated that vascular smooth muscular cells (VSMCs) play an important role in the development of vascular calcification (VC). Cortistatin (CST), a novel bio-active peptide, has been shown to exert multiple protective effects on the cardiovascular system. However, the role and possible mechanism of CST in VC remain unclear. Therefore, we used β-glycerophosphoric acid (β-GP) to induce calcification in rat and human VSMCs to determine the effects of CST on osteoblastic differentiation and VSMC mineralization in vitro. Compared with the control, β-GP significantly increased alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity and calcium content in cultured rat and human VSMCs, as well as multicellular node formation and calcium deposition, as confirmed by von Kossa and Alizarin Red S staining assays. After incubating rat and human VSMCs with β-GP in the presence of different doses of CST (10−8 or 10−7 mol/L), CST clearly reversed the β-GP-induced increases in ALP activity and calcium content and formation of pathological calcified nodes of VSMCs in a dose-independent manner. Moreover, 10−8 and 10−7 mol/L CST inhibited the phenotypic transformation of VSMCs into osteoblastic cells by decreasing the osteocalcin protein levels, increasing the SM-α-actin protein levels, and reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress by decreasing the protein expression of glucose-regulated protein 94 and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein. In conclusion, CST directly inhibited β-GP-induced calcification of VSMCs in vitro, probably by suppressing ERS and phenotypic transformation of VSMCs into osteoblastic cells. These results indicate that CST represents a potential target for the prevention and treatment of VC.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander MY, Wilkinson FL, Kirton JP, Rock CF, Collett GD, Jeziorska M, Smyth JV, Heagerty AM, Canfield AE (2005) Identification and characterization of vascular calcification-associated factor, a novel gene upregulated during vascular calcification in vitro and in vivo. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:1851–1857
Aoki S, Watanabe Y, Tanabe D, Arai M, Suna H, Miyamoto K, Tsujibo H, Tsujikawa K, Yamamoto H, Kobayashi M (2007) Structure-activity relationship and biological property of cortistatins, anti-angiogenic spongean steroidal alkaloids. Bioorg Med Chem 15:6758–6762
Braun H, Schulz S, Becker A, Schroder H, Hollt V (1998) Protective effects of cortistatin (CST-14) against kainate-induced neurotoxicity in rat brain. Brain Res 803:54–60
Broglio F, Grottoli S, Arvat E, Ghigo E (2008) Endocrine actions of cortistatin: in vivo studies. Mol Cell Endocrinol 286:123–127
Chang JR, Duan XH, Zhang BH, Teng X, Zhou YB, Liu Y, Yu YR, Zhu Y, Tang CS, Qi YF (2013) Intermedin1-53 attenuates vascular smooth muscle cell calcification by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress via cyclic adenosine monophosphate/protein kinase A pathway. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 238:1136–1146
Cirelli C, Faraguna U, Tononi G (2006) Changes in brain gene expression after long-term sleep deprivation. J Neurochem 98:1632–1645
Dalm VA, Van Hagen PM, de Krijger RR, Kros JM, Van Koetsveld PM, Van Der Lely AJ, Lamberts SW, Hofland LJ (2004) Distribution pattern of somatostatin and cortistatin mRNA in human central and peripheral tissues. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 60:625–629
de Lecea L, Criado JR, Prospero-Garcia O, Gautvik KM, Schweitzer P, Danielson PE, Dunlop CL, Siggins GR, Henriksen SJ, Sutcliffe JG (1996) A cortical neuropeptide with neuronal depressant and sleep-modulating properties. Nature 381:242–245
Demer LL, Tintut Y (2008) Vascular calcification: pathobiology of a multifaceted disease. Circulation 117:2938–2948
Duan X, Zhou Y, Teng X, Tang C, Qi Y (2009) Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis is activated in vascular calcification. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 387:694–699
Duan XH, Chang JR, Zhang J, Zhang BH, Li YL, Teng X, Zhu Y, Du J, Tang CS, Qi YF (2013) Activating transcription factor 4 is involved in endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis contributing to vascular calcification. Apoptosis 18:1132–1144
Duran-Prado M, Morell M, Delgado-Maroto V, Castano JP, Aneiros-Fernandez J, de Lecea L, Culler MD, Hernandez-Cortes P, O’Valle F, Delgado M (2013) Cortistatin inhibits migration and proliferation of human vascular smooth muscle cells and decreases neointimal formation on carotid artery ligation. Circ Res 112:1444–1455
Fu Y, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Zhu Y, Chi J, Hu J, Zhang X, Yin X (2012) Adenovirus-mediated tissue factor pathway inhibitor gene transfer induces apoptosis by blocking the phosphorylation of JAK-2/STAT-3 pathway in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell Signal 24:1909–1917
Gonzalez-Rey E, Chorny A, Robledo G, Delgado M (2006) Cortistatin, a new antiinflammatory peptide with therapeutic effect on lethal endotoxemia. J Exp Med 203:563–571
Gonzalez-Rey E, Chorny A, Del Moral RG, Varela N, Delgado M (2007) Therapeutic effect of cortistatin on experimental arthritis by downregulating inflammatory and Th1 responses. Ann Rheum Dis 66:582–588
Hruska KA (2009) Vascular smooth muscle cells in the pathogenesis of vascular calcification. Circ Res 104:710–711
Lee KM, Kang HA, Park M, Lee HY, Choi HR, Yun CH, Oh JW, Kang HS (2012) Interleukin-24 attenuates beta-glycerophosphate-induced calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells by inhibiting apoptosis, the expression of calcification and osteoblastic markers, and the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 428:50–55
Liang QH, Jiang Y, Zhu X, Cui RR, Liu GY, Liu Y, Wu SS, Liao XB, Xie H, Zhou HD, Wu XP, Yuan LQ, Liao EY (2012) Ghrelin attenuates the osteoblastic differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells through the ERK pathway. PLoS One 7:e33126
Liberman M, Johnson RC, Handy DE, Loscalzo J, Leopold JA (2011) Bone morphogenetic protein-2 activates NADPH oxidase to increase endoplasmic reticulum stress and human coronary artery smooth muscle cell calcification. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 413:436–441
Liu Y, Shanahan CM (2010) Signalling pathways and vascular calcification. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 16:1302–1314
Liu Y, Yin XH, Qi YF (2009) Progress in biological effects of cortistatin. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan 40:219–224
Liu Y, Zhou YB, Zhang GG, Cai Y, Duan XH, Teng X, Song JQ, Shi Y, Tang CS, Yin XH, Qi YF (2010) Cortistatin attenuates vascular calcification in rats. Regul Pept 159:35–43
Markovics A, Szoke E, Sandor K, Borzsei R, Bagoly T, Kemeny A, Elekes K, Pinter E, Szolcsanyi J, Helyes Z (2012) Comparison of the anti-inflammatory and anti-nociceptive effects of cortistatin-14 and somatostatin-14 in distinct in vitro and in vivo model systems. J Mol Neurosci 46:40–50
Masuda M, Ting TC, Levi M, Saunders SJ, Miyazaki-Anzai S, Miyazaki M (2012) Activating transcription factor 4 regulates stearate-induced vascular calcification. J Lipid Res 53:1543–1552
Masuda M, Miyazaki-Anzai S, Levi M, Ting TC, Miyazaki M (2013) PERK-eIF2alpha-ATF4-CHOP signaling contributes to TNFalpha-induced vascular calcification. J Am Heart Assoc 2:e000238
Miyazaki-Anzai S, Masuda M, Demos-Davies KM, Keenan AL, Saunders SJ, Masuda R, Jablonski K, Cavasin MA, Kendrick J, Chonchol M, McKinsey TA, Levi M, Miyazaki M (2014) Endoplasmic reticulum stress effector CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein (CHOP) regulates chronic kidney disease-induced vascular calcification. J Am Heart Assoc 3:e000949
Muccioli G, Papotti M, Locatelli V, Ghigo E, Deghenghi R (2001) Binding of 125I-labeled ghrelin to membranes from human hypothalamus and pituitary gland. J Endocrinol Invest 24:RC-7–RC-9
Qiao W, Chen L, Zhang M (2014) MicroRNA-205 regulates the calcification and osteoblastic differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 33:1945–1953
Reynolds JL, Joannides AJ, Skepper JN, McNair R, Schurgers LJ, Proudfoot D, Jahnen-Dechent W, Weissberg PL, Shanahan CM (2004) Human vascular smooth muscle cells undergo vesicle-mediated calcification in response to changes in extracellular calcium and phosphate concentrations: a potential mechanism for accelerated vascular calcification in ESRD. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:2857–2867
Robas N, Mead E, Fidock M (2003) MrgX2 is a high potency cortistatin receptor expressed in dorsal root ganglion. J Biol Chem 278:44400–44404
Rogers M, Goettsch C, Aikawa E (2013) Medial and intimal calcification in chronic kidney disease: stressing the contributions. J Am Heart Assoc 2:e000481
Sage AP, Tintut Y, Demer LL (2010) Regulatory mechanisms in vascular calcification. Nat Rev Cardiol 7:528–536
Shioi A, Nishizawa Y, Jono S, Koyama H, Hosoi M, Morii H (1995) Beta-glycerophosphate accelerates calcification in cultured bovine vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 15:2003–2009
Spier AD, de Lecea L (2000) Cortistatin: a member of the somatostatin neuropeptide family with distinct physiological functions. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 33:228–241
Tallent MK, Fabre V, Qiu C, Calbet M, Lamp T, Baratta MV, Suzuki C, Levy CL, Siggins GR, Henriksen SJ, Criado JR, Roberts A, de Lecea L (2005) Cortistatin overexpression in transgenic mice produces deficits in synaptic plasticity and learning. Mol Cell Neurosci 30:465–475
Vliegenthart R, Oudkerk M, Hofman A, Oei HH, van Dijck W, van Rooij FJ, Witteman JC (2005) Coronary calcification improves cardiovascular risk prediction in the elderly. Circulation 112:572–577
Wallin R, Wajih N, Greenwood GT, Sane DC (2001) Arterial calcification: a review of mechanisms, animal models, and the prospects for therapy. Med Res Rev 21:274–301
Yan S, Li M, Chai H, Yang H, Lin PH, Yao Q, Chen C (2005) TNF-alpha decreases expression of somatostatin, somatostatin receptors, and cortistatin in human coronary endothelial cells. J Surg Res 123:294–301
Zavaczki E, Jeney V, Agarwal A, Zarjou A, Oros M, Katko M, Varga Z, Balla G, Balla J (2011) Hydrogen sulfide inhibits the calcification and osteoblastic differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Kidney Int 80:731–739
Zhang B, Liu Y, Zhang JS, Zhang XH, Chen WJ, Yin XH, Qi YF (2015) Cortistatin protects myocardium from endoplasmic reticulum stress induced apoptosis during sepsis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 406:40–48
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81200235 and 81200143), Research Foundation of Education Bureau of Heilongjiang Province, China (Grant No. 12541338) and Foundation of the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China (Grant No. 2015B005). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Handling Editor: T. Langer.
Y. Liu and F. Lin contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Lin, F., Fu, Y. et al. Cortistatin inhibits calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells by depressing osteoblastic differentiation and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Amino Acids 48, 2671–2681 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2303-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2303-3