Abstract
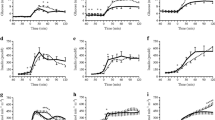
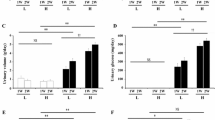
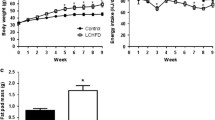
The purpose of this investigation was to test an amino acid mixture on glucose tolerance in obese Zucker rats [experiment (Exp)-1] and determine whether differences in blood glucose were associated with alterations in muscle glucose uptake [experiment (Exp)-2]. Exp-1 rats were gavaged with either carbohydrate (OB-CHO), carbohydrate plus amino acid mixture (OB-AA-1), carbohydrate plus amino acid mixture with increased leucine concentration (OB-AA-2) or water (OB-PLA). The glucose response in OB-AA-1 and OB-AA-2 were similar, and both were lower compared to OB-CHO. This effect of the amino acid mixtures did not appear to be solely attributable to an increase in plasma insulin. Rats in Exp-2 were gavaged with carbohydrate (OB-CHO), carbohydrate plus amino acid mixture (OB-AA-1) or water (OB-PLA). Lean Zuckers were gavaged with carbohydrate (LN-CHO). Fifteen minutes after gavage, a radiolabeled glucose analog was infused through a catheter previously implanted in the right jugular vein. Blood glucose was significantly lower in OB-AA-1 compared to OB-CHO while the insulin responses were similar. Glucose uptake was greater in OB-AA-1 compared with OB-CHO, and similar to that in LN-CHO in red gastrocnemius muscle (5.15 ± 0.29, 3.8 ± 0.27, 5.18 ± 0.34 µmol/100 g/min, respectively). Western blot analysis showed that Akt substrate of 160 kDa (AS160) phosphorylation was enhanced for OB-AA-1 and LN-CHO compared to OB-CHO. These findings suggest that an amino acid mixture improves glucose tolerance in an insulin resistant model and that these improvements are associated with an increase in skeletal muscle glucose uptake possibly due to improved intracellular signaling.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atherton PJ, Smith K, Etheridge T, Rankin D, Rennie MJ (2010) Distinct anabolic signaling responses to amino acids in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. Amino Acids 38:1533–1539
Axelson JF, Bruot BC (1982) An improved jugular vein cannulation procedure and cannula storage apparatus. Physiol Behav 29:949–951
Banks EA, Brozinick JT, Yaspelkis BB 3rd, Kang HY, Ivy JL (1992) Muscle glucose transport, GLTU-4 content, and degree of exercise training in obese Zucker rats. Am J Physiol 263:E1010–E1015
Benton CR, Holloway GP, Han XX, Yoshida Y, Snook LA, Lally J, Giatz JF, Luikenn JJ, Chadowski A, Bonen A (2010) Increased levels of peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor gamma, coactivator 1 alpha (PGC-1α) improve lipid utilization, insulin signaling and glucose transport in skeletal muscle of lean and insulin-resistance obese Zucker rats. Diabetologia 53:2008–2019
Bernard JR, Liao YH, Hara D, Ding Z, Chen CY, Nelson JL, Ivy JL (2011) An amino acid mixture improves glucose tolerance and insulin signaling in Sprague Dawley rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 300:E752–E760
Bernard JR, Liao YH, Doerner PG 3rd, Ding Z, Hsieh M, Wang W, Nelson JL, Ivy JL (2012) An amino acid mixture is essential to optimize insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and GLUT4 translocation in perfused rodent hindlimb muscle. J Appl Physiol 113:97–104
Brozinick JT, Etgen GJ Jr, Yaspelkis BB 3rd, Kang HY, Ivy JL (1993) Effects of exercise training on muscle GLUT-4 protein content and translocation in obese Zucker rats. Am J Physiol 265:E419–E427
Christ CY, Hunt D, Hancock J, Garcia-Macedo R, Mandarino LJ, Ivy JL (2002) Exercise training improves muscle insulin resistance but not insulin receptor signaling in obese Zucker rats. J Appl Physiol 92:736–744
Crettaz M, Prentki M, Zaninetti D, Jeanrenaud B (1980) Insulin resistance in soleus muscle from Zucker obese rats. Involvement of several defective sites. Biochem J 186:525–534
DeFronzo RA, Jacot E, Jequier E, Maeder E, Wahren J, Felber JP (1981) The effect of insulin on the disposal of intravenous glucose. Results from indirect calorimetry and hepatic and femoral venous catheterization. Diabetes 30:1000–1007
Doi M, Yamaoka I, Fukunaga T, Nakayama M (2003) Isoleucine, a potent plasma glucose-lowering amino acid, stimulates glucose uptake in C2C12 myotubes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 312:1111–1117
Doi M, Yamaoka I, Nakayama M, Sugahara K, Yoshizawa F (2007) Hypoglycemic effect of isoleucine involves muscle glucose uptake and whole body glucose oxidation and decreased hepatic gluconeogenesis. Am J Endocrinol Metab 292:E1683–E1693
Felig P, Marliss E, Cahill GF Jr (1969) Plasma amino acid levels and insulin secretion in obesity. N Engl J Med 281:811–816
Felig P, Wahren J, Hendler R, Brundin T (1974) Splanachic glucose and amino acid metabolism in obesity. J Clin Invest 53:582–590
Fingar DC, Blenis J (2004) Target of rapamycin (TOR): an integration of nutrient and growth factor signals and coordinator of cell growth and cell cycle progression. Oncogene 23:3151–3171
Floyd JC Jr, Fajans SS, Conn JW, Knopf RF, Rull J (1966) Stimulation of insulin secretion by amino acids. J Clin Invest 45:1487–1502
Friedman JE, Sherman WM, Reed MJ, Elton CW, Dohm GL (1990) Exercise training increases glucose transporter protein GLUT-4 in skeletal muscle of obese Zucker (fa/fa) rats. FEBS Lett 288:13–16
Kalogeropoulou D, Lafave L, Schweim K, Gannon MC, Nuttall FQ (2008) Leucine, when ingested with glucose, synergistically stimulates insulin secretion and lowers blood glucose. Metabolism 57:1747–1752
Katta A, Kakarla S, Wu M, Paturi S, Gadde MK, Arvapalli R, Kolli M, Rice KM, Blough ER (2009) Altered regulation of contraction-induced Akt/mTOR/p70S6k pathway signaling in skeletal muscle in obese Zucker rat. Exp Diabetes Res. Article ID 384683
Katz LD, Glickman MG, Rapoport S, Ferrannini E, DeFronzo RA (1983) Splanchnic and peripheral disposal of oral glucose in man. Diabetes 32:675–679
Kern M, Wells JA, Stephens JM, Elton CW, Friedman JE, Tapscott EB, Pekala PH, Dohm GL (1990) Insulin responsiveness in skeletal muscle is determined by glucose transporter (Glut4) protein level. Biochem J 270:397–400
Kleinert M, Liao YH, Nelson JL, Bernard JR, Wang W, Ivy JL (2011) An amino acid mixture enhances insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in isolated rat epitrochlearis muscle. J Appl Physiol 111:163–169
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Linn T, Geyer R, Prassek S, Laube H (1996) Effect of dietary protein intake on insulin secretion and glucose metabolism in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:3938–3943
Linn T, Santosa B, Gronemeyer D, Aygen S, Scholz N, Busch M, Bretzel RG (2000) Effect of long-term dietary protein intake on glucose metabolism in humans. Diabetologia 43:1257–1265
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Newgard CB, An J, Bain JR, Muehlbauer MJ et al (2009) A branched-chain amino acid-related metabolic signature that differentiates obese and lean humans and contributes to insulin resistance. Cell Metab 9:311–326
Nishitani S, Matsumura T, Fujitani S, Sonaka I, Miura Y, Yagasaki K (2002) Leucine promotes glucose uptake in skeletal muscle of rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 299:693–696
Nuttall FQ, Mooradian AD, Gannon MC, Billington C, Krezowski P (1984) Effect of protein ingestion on the glucose and insulin response to a standard oral glucose load. Diabetes Care 7:465–470
Nuttall FQ, Schweim K, Gannon MC (2008) Effect of orally administered isoleucine with and without glucose on insulin, glucagons and glucose concentrations in non-diabetic subjects. Eur J Clin Nutr Metab 3:e152–e158
Romanul FCA (1965) Capillary supply and metabolism of muscle fibers. Arch Neurol 12:497–509
Sano H, Kane S, Sano E, Miinea CP, Asara JM, Lane WS, Garner CW, Lienhard GE (2003) Insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of a rab GTPase-activating protein regulates GLUT4 translocation. J Biol Chem 278:14599–14602
Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM, Sabatini DM (2005) Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science 307:1098–1101
Sherman WM, Katz AL, Cutler CL, Withers RT, Ivy JL (1988) Glucose transport: locus of muscle insulin resistance in obese Zucker rats. Am J Physiol 255:E374–E382
Skurat AV, Dietrich AD, Roach PJ (2000) Glycogen synthase sensitivity to insulin and glucose-6-phosphate is mediated by both NH2- and COOH-terminal phosphorylation sites. Diabetes 49:1096–1100
Tremblay F, Marette A (2001) Amino acid and insulin signaling via the mTOR/p70 S6 kinase pathway. A negative feedback mechanism leading to insulin resistance in skeletal muscle cells. J Biol Chem 276:38052–38060
Tremblay F, Brule S, Hee Um S, Li Y, Masuda K, Roden M, Sun XJ, Krebs M, Polakiewicz RD, Thomas G, Marette A (2007) Identification of IRS-1 Ser-1101 as a target of S6K1 in nutrient- and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:14056–14061
van Loon LJ, Saris WH, Verhagen H, Wagenmakers AJ (2000) Plasma insulin responses after ingestion of different amino acids or protein mixtures with carbohydrates. Am J Clin Nutr 72:96–105
van Loon LJ, Kruijshoop M, Menheere PP, Wagenmakers AJ, Saris WH, Keizer HA (2003) Amino acid ingestion strongly enhances insulin secretion in patients with long-term type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 26:625–630
Watson RT, Pessin JE (2006) Bridging the GAP between insulin signaling and GLUT4 translocation. Trends in Biochem Sci 31:215–222
Zawadzki KM, Yaspelkis BB 3rd, Ivy JL (1992) Carbohydrate-protein complex increases the rate of muscle glycogen storage after exercise. J Appl Physiol 72:1854–1859
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Martin Job and Dr. Simon Schenk for their assistance in preparing our lab for the jugular vein catheterization procedure. We would also like to thank Lynne Kammer and Mina Rathbun for their excellent technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
This research was support by a grant from Abbott Nutrition, Abbott Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio. Dr. Jeffrey Nelson is an employee of Abbott Nutrition. His role in the current study was assisting with the experimental design, helping with the interpretation of the results and the writing of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bernard, J.R., Liao, YH., Ding, Z. et al. An amino acid mixture improves glucose tolerance and lowers insulin resistance in the obese Zucker rat. Amino Acids 45, 191–203 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-013-1488-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-013-1488-y