Abstract
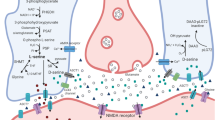
The discovery of large amounts of d-serine in the brain challenged the dogma that only l-amino acids are relevant for eukaryotes. The levels of d-serine in the brain are higher than many l-amino acids and account for as much as one-third of l-serine levels. Several studies in the last decades have demonstrated a role of d-serine as an endogenous agonist of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors (NMDARs). d-Serine is required for NMDAR activity during normal neurotransmission as well as NMDAR overactivation that takes place in neurodegenerative conditions. Still, there are many unanswered questions about d-serine neurobiology, including regulation of its synthesis, release and metabolism. Here, we review the mechanisms of d-serine synthesis by serine racemase and discuss the lessons we can learn from serine racemase knockout mice, focusing on the roles attributed to d-serine and its cellular origin.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agulhon C, Petravicz J, McMullen AB, Sweger EJ, Minton SK, Taves SR, Casper KB, Fiacco TA, McCarthy KD (2008) What is the role of astrocyte calcium in neurophysiology? Neuron 59(6):932–946. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2008.09.004
Agulhon C, Fiacco TA, McCarthy KD (2010) Hippocampal short- and long-term plasticity are not modulated by astrocyte Ca2+ signaling. Science 327(5970):1250–1254. doi:10.1126/science.1184821
Balan L, Foltyn VN, Zehl M, Dumin E, Dikopoltsev E, Knoh D, Ohno Y, Kihara A, Jensen ON, Radzishevsky IS, Wolosker H (2009) Feedback inactivation of d-serine synthesis by NMDA receptor-elicited translocation of serine racemase to the membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(18):7589–7594
Balu DT, Coyle JT (2011) Glutamate receptor composition of the post-synaptic density is altered in genetic mouse models of NMDA receptor hypo- and hyperfunction. Brain Res 1392:1–7. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2011.03.051
Balu DT, Basu AC, Corradi JP, Cacace AM, Coyle JT (2012) The NMDA receptor co-agonists, d-serine and glycine, regulate neuronal dendritic architecture in the somatosensory cortex. Neurobiol Dis 45(2):671–682. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2011.10.006
Basu AC, Tsai GE, Ma CL, Ehmsen JT, Mustafa AK, Han L, Jiang ZI, Benneyworth MA, Froimowitz MP, Lange N, Snyder SH, Bergeron R, Coyle JT (2009) Targeted disruption of serine racemase affects glutamatergic neurotransmission and behavior. Molecular psychiatry 14(7):719–727. doi:10.1038/mp.2008.130
Baumgart F, Mancheno JM, Rodriguez-Crespo I (2007) Insights into the activation of brain serine racemase by the multi-PDZ domain glutamate receptor interacting protein, divalent cations and ATP. FEBS J 274(17):4561–4571
Benneyworth MA, Basu AC, Coyle JT (2011) Discordant behavioral effects of psychotomimetic drugs in mice with altered NMDA receptor function. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 213(1):143–153. doi:10.1007/s00213-010-2023-4
Benneyworth MA, Li Y, Basu AC, Bolshakov VY, Coyle JT (2012) Cell selective conditional null mutations of serine racemase demonstrate a predominate localization in cortical glutamatergic neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol 32(4):613–624. doi:10.1007/s10571-012-9808-4
Bergersen LH, Morland C, Ormel L, Rinholm JE, Larsson M, Wold JF, Roe AT, Stranna A, Santello M, Bouvier D, Ottersen OP, Volterra A, Gundersen V (2011) Immunogold detection of l-glutamate and d-serine in small synaptic-like microvesicles in adult hippocampal astrocytes. Cereb Cortex. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhr254
Cadenhead KS, Swerdlow NR, Shafer KM, Diaz M, Braff DL (2000) Modulation of the startle response and startle laterality in relatives of schizophrenic patients and in subjects with schizotypal personality disorder: evidence of inhibitory deficits. Am J Psychiatry 157(10):1660–1668
Cook SP, Galve-Roperh I, Martinez Del Pozo A, Rodriguez-Crespo I (2002) Direct calcium binding results in activation of brain serine racemase. J Biol Chem 277(31):27782–27792
De Miranda J, Santoro A, Engelender S, Wolosker H (2000) Human serine racemase: molecular cloning, genomic organization and functional analysis. Gene 256(1–2):183–188
De Miranda J, Panizzutti R, Foltyn VN, Wolosker H (2002) Cofactors of serine racemase that physiologically stimulate the synthesis of the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor coagonist d-serine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(22):14542–14547
DeVito LM, Balu DT, Kanter BR, Lykken C, Basu AC, Coyle JT, Eichenbaum H (2011) Serine racemase deletion disrupts memory for order and alters cortical dendritic morphology. Genes Brain Behav 10(2):210–222. doi:10.1111/j.1601-183X.2010.00656.x
Dumin E, Bendikov I, Foltyn VN, Misumi Y, Ikehara Y, Kartvelishvily E, Wolosker H (2006) Modulation of d-serine levels via ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation of serine racemase. J Biol Chem 281(29):20291–20302
Dun Y, Duplantier J, Roon P, Martin PM, Ganapathy V, Smith SB (2008) Serine racemase expression and d-serine content are developmentally regulated in neuronal ganglion cells of the retina. J Neurochem 104(4):970–978. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05015.x
Dunlop DS, Neidle A (1997) The origin and turnover of d-serine in brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 235(1):26–30
Dunlop DS, Neidle A (2005) Regulation of serine racemase activity by amino acids. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 133(2):208–214
Foltyn VN, Bendikov I, De Miranda J, Panizzutti R, Dumin E, Shleper M, Li P, Toney MD, Kartvelishvily E, Wolosker H (2005) Serine racemase modulates intracellular d-serine levels through an alpha, beta-elimination activity. J Biol Chem 280(3):1754–1763
Foltyn VN, Zehl M, Dikopoltsev E, Jensen ON, Wolosker H (2010) Phosphorylation of mouse serine racemase regulates d-serine synthesis. FEBS Lett 584(13):2937–2941
Fujii K, Maeda K, Hikida T, Mustafa AK, Balkissoon R, Xia J, Yamada T, Ozeki Y, Kawahara R, Okawa M, Huganir RL, Ujike H, Snyder SH, Sawa A (2006) Serine racemase binds to PICK1: potential relevance to schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 11(2):150–157
Goto M, Yamauchi T, Kamiya N, Miyahara I, Yoshimura T, Mihara H, Kurihara T, Hirotsu K, Esaki N (2009) Crystal structure of a homolog of mammalian serine racemase from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Biol Chem 284(38):25944–25952
Hashimoto A, Nishikawa T, Oka T, Takahashi K, Hayashi T (1992) Determination of free amino acid enantiomers in rat brain and serum by high-performance liquid chromatography after derivatization with N-tert.-butyloxycarbonyl-l-cysteine and o-phthaldialdehyde. J Chromatogr 582(1–2):41–48
Hashimoto A, Nishikawa T, Konno R, Niwa A, Yasumura Y, Oka T, Takahashi K (1993) Free d-serine, d-aspartate and d-alanine in central nervous system and serum in mutant mice lacking d-amino acid oxidase. Neurosci Lett 152(1–2):33–36
Henneberger C, Papouin T, Oliet SH, Rusakov DA (2010) Long-term potentiation depends on release of d-serine from astrocytes. Nature 463(7278):232–236
Hikida T, Mustafa AK, Maeda K, Fujii K, Barrow RK, Saleh M, Huganir RL, Snyder SH, Hashimoto K, Sawa A (2008) Modulation of d-serine levels in brains of mice lacking PICK1. Biol Psychiatry 63(10):997–1000
Horio M, Kohno M, Fujita Y, Ishima T, Inoue R, Mori H, Hashimoto K (2011) Levels of d-serine in the brain and peripheral organs of serine racemase (Srr) knock-out mice. Neurochem Int 59(6):853–859. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2011.08.017
Horio M, Kohno M, Fujita Y, Ishima T, Inoue R, Mori H, Hashimoto K (2012) Role of serine racemase in behavioral sensitization in mice after repeated administration of methamphetamine. PLoS One 7(4):e35494. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035494
Huttlin EL, Jedrychowski MP, Elias JE, Goswami T, Rad R, Beausoleil SA, Villen J, Haas W, Sowa ME, Gygi SP (2010) A tissue-specific atlas of mouse protein phosphorylation and expression. Cell 143(7):1174–1189. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.12.001
Inoue R, Hashimoto K, Harai T, Mori H (2008) NMDA- and beta-amyloid1-42-induced neurotoxicity is attenuated in serine racemase knock-out mice. J Neurosci 28(53):14486–14491. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5034-08.2008
Iwama H, Takahashi K, Kure S, Hayashi F, Narisawa K, Tada K, Mizoguchi M, Takashima S, Tomita U, Nishikawa T (1997) Depletion of cerebral d-serine in non-ketotic hyperglycinemia: possible involvement of glycine cleavage system in control of endogenous d-serine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 231(3):793–796. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.6184
Kartvelishvily E, Shleper M, Balan L, Dumin E, Wolosker H (2006) Neuron-derived d-serine release provides a novel means to activate N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors. J Biol Chem 281(20):14151–14162
Katsuki H, Nonaka M, Shirakawa H, Kume T, Akaike A (2004) Endogenous d-serine is involved in induction of neuronal death by N-methyl-d-aspartate and simulated ischemia in rat cerebrocortical slices. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 311(2):836–844
Kim PM, Aizawa H, Kim PS, Huang AS, Wickramasinghe SR, Kashani AH, Barrow RK, Huganir RL, Ghosh A, Snyder SH (2005) Serine racemase: activation by glutamate neurotransmission via glutamate receptor interacting protein and mediation of neuronal migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(6):2105–2110
Konno R (2003) Rat cerebral serine racemase: amino acid deletion and truncation at carboxy terminus. Neurosci Lett 349(2):111–114
Labrie V, Fukumura R, Rastogi A, Fick LJ, Wang W, Boutros PC, Kennedy JL, Semeralul MO, Lee FH, Baker GB, Belsham DD, Barger SW, Gondo Y, Wong AH, Roder JC (2009) Serine racemase is associated with schizophrenia susceptibility in humans and in a mouse model. Hum Mol Genet 18(17):3227–3243
Martineau M, Galli T, Baux G, Mothet JP (2008) Confocal imaging and tracking of the exocytotic routes for d-serine-mediated gliotransmission. Glia 56:1271–1284. doi:10.1002/glia.20696
Miya K, Inoue R, Takata Y, Abe M, Natsume R, Sakimura K, Hongou K, Miyawaki T, Mori H (2008) Serine racemase is predominantly localized in neurons in mouse brain. J Comp Neurol 510(6):641–654. doi:10.1002/cne.21822
Mori H, Inoue R (2010) Serine racemase knockout mice. Chem Biodivers 7(6):1573–1578. doi:10.1002/cbdv.200900293
Morris RG, Anderson E, Lynch GS, Baudry M (1986) Selective impairment of learning and blockade of long-term potentiation by an N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist, AP5. Nature 319(6056):774–776. doi:10.1038/319774a0
Mothet JP, Parent AT, Wolosker H, Brady RO Jr, Linden DJ, Ferris CD, Rogawski MA, Snyder SH (2000) d-serine is an endogenous ligand for the glycine site of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(9):4926–4931
Mothet JP, Pollegioni L, Ouanounou G, Martineau M, Fossier P, Baux G (2005) Glutamate receptor activation triggers a calcium-dependent and SNARE protein-dependent release of the gliotransmitter d-serine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(15):5606–5611
Mustafa AK, Kumar M, Selvakumar B, Ho GP, Ehmsen JT, Barrow RK, Amzel LM, Snyder SH (2007) Nitric oxide S-nitrosylates serine racemase, mediating feedback inhibition of d-serine formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(8):2950–2955
Mustafa AK, van Rossum DB, Patterson RL, Maag D, Ehmsen JT, Gazi SK, Chakraborty A, Barrow RK, Amzel LM, Snyder SH (2009) Glutamatergic regulation of serine racemase via reversal of PIP2 inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(8):2921–2926
Mustafa AK, Ahmad AS, Zeynalov E, Gazi SK, Sikka G, Ehmsen JT, Barrow RK, Coyle JT, Snyder SH, Dore S (2010) Serine racemase deletion protects against cerebral ischemia and excitotoxicity. J Neurosci 30(4):1413–1416
Nagata Y, Homma H, Matsumoto M, Imai K (1999) Stimulation of steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) gene expression by d-aspartate in rat Leydig cells. FEBS Lett 454(3):317–320
Neidle A, Dunlop DS (2002) Allosteric regulation of mouse brain serine racemase. Neurochem Res 27(12):1719–1724
Nishikawa T (2005) Metabolism and functional roles of endogenous d-serine in mammalian brains. Biol Pharm Bull 28(9):1561–1565
O’Brien KB, Bowser MT (2006) Measuring d-serine efflux from mouse cortical brain slices using online microdialysis-capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 27(10):1949–1956
Panatier A, Theodosis DT, Mothet JP, Touquet B, Pollegioni L, Poulain DA, Oliet SH (2006) Glia-derived d-serine controls NMDA receptor activity and synaptic memory. Cell 125(4):775–784
Panizzutti R, De Miranda J, Ribeiro CS, Engelender S, Wolosker H (2001) A new strategy to decrease N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor coactivation: inhibition of d-serine synthesis by converting serine racemase into an eliminase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(9):5294–5299
Ribeiro CS, Reis M, Panizzutti R, de Miranda J, Wolosker H (2002) Glial transport of the neuromodulator d-serine. Brain Res 929(2):202–209
Rosenberg D, Kartvelishvily E, Shleper M, Klinker CM, Bowser MT, Wolosker H (2010) Neuronal release of d-serine: a physiological pathway controlling extracellular d-serine concentration. FASEB J 24(8):2951–2961
Schell MJ, Molliver ME, Snyder SH (1995) d-serine, an endogenous synaptic modulator: localization to astrocytes and glutamate-stimulated release. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(9):3948–3952
Schell MJ, Brady RO Jr, Molliver ME, Snyder SH (1997) d-serine as a neuromodulator: regional and developmental localizations in rat brain glia resemble NMDA receptors. J Neurosci 17(5):1604–1615
Shleper M, Kartvelishvily E, Wolosker H (2005) d-serine is the dominant endogenous coagonist for NMDA receptor neurotoxicity in organotypic hippocampal slices. J Neurosci 25(41):9413–9417
Smith MA, Mack V, Ebneth A, Moraes I, Felicetti B, Wood M, Schonfeld D, Mather O, Cesura A, Barker J (2010) The structure of mammalian serine racemase: evidence for conformational changes upon inhibitor binding. J Biol Chem 285(17):12873–12881
Strisovsky K, Jiraskova J, Mikulova A, Rulisek L, Konvalinka J (2005) Dual substrate and reaction specificity in mouse serine racemase: identification of high-affinity dicarboxylate substrate and inhibitors and analysis of the beta-eliminase activity. Biochemistry 44(39):13091–13100
Suh YH, Checler F (2002) Amyloid precursor protein, presenilins, and alpha-synuclein: molecular pathogenesis and pharmacological applications in Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol Rev 54(3):469–525
Sullivan SJ, Esguerra M, Wickham RJ, Romero GE, Coyle JT, Miller RF (2011) Serine racemase deletion abolishes light-evoked NMDA receptor currents in retinal ganglion cells. J Physiol 589(Pt 24):5997–6006. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2011.217059
Takahashi K, Hayashi F, Nishikawa T (1997) In vivo evidence for the link between l- and d-serine metabolism in rat cerebral cortex. J Neurochem 69(3):1286–1290
Uo T, Yoshimura T, Shimizu S, Esaki N (1998) Occurrence of pyridoxal 5′-phosphate-dependent serine racemase in silkworm Bombyx mori. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 246(1):31–34
Williams SM, Diaz CM, Macnab LT, Sullivan RK, Pow DV (2006) Immunocytochemical analysis of d-serine distribution in the mammalian brain reveals novel anatomical compartmentalizations in glia and neurons. Glia 53(4):401–411
Wisniewski JR, Nagaraj N, Zougman A, Gnad F, Mann M (2010) Brain phosphoproteome obtained by a FASP-based method reveals plasma membrane protein topology. J Proteome Res 9(6):3280–3289. doi:10.1021/pr1002214
Wolosker H (1814) (2011) Serine racemase and the serine shuttle between neurons and astrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1814(11):1558–1566
Wolosker H, Blackshaw S, Snyder SH (1999a) Serine racemase: a glial enzyme synthesizing d-serine to regulate glutamate-N-methyl-d-aspartate neurotransmission. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 96(23):13409–13414
Wolosker H, Sheth KN, Takahashi M, Mothet JP, Brady RO Jr, Ferris CD, Snyder SH (1999b) Purification of serine racemase: biosynthesis of the neuromodulator d-serine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(2):721–725
Wood PL, Hawkinson JE, Goodnough DB (1996) Formation of d-serine from l-phosphoserine in brain synaptosomes. J Neurochem 67(4):1485–1490
Yang Y, Ge W, Chen Y, Zhang Z, Shen W, Wu C, Poo M, Duan S (2003) Contribution of astrocytes to hippocampal long-term potentiation through release of d-serine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(25):15194–15199
Yang S, Qiao H, Wen L, Zhou W, Zhang Y (2005) d-Serine enhances impaired long-term potentiation in CA1 subfield of hippocampal slices from aged senescence-accelerated mouse prone/8. Neurosci Lett 379(1):7–12
Yoshikawa M, Takayasu N, Hashimoto A, Sato Y, Tamaki R, Tsukamoto H, Kobayashi H, Noda S (2007) The serine racemase mRNA is predominantly expressed in rat brain neurons. Arch Histol Cytol 70(2):127–134
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Ran Inoue and Jeffrey Ehmsen for critical reading of the manuscript. Work in H.W. laboratory was supported by grants from IMHRO, Israel Science Foundation, ISF-Legacy Heritage Fund, Jessie Kaplan Research Fund, Dears Foundation, L. Aronberg Research Fund in Neurology and Albert Goodstein Research Fund. H.M. was supported by a grant from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan (Grant No. 221S0003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wolosker, H., Mori, H. Serine racemase: an unconventional enzyme for an unconventional transmitter. Amino Acids 43, 1895–1904 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1370-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-012-1370-3