Abstract
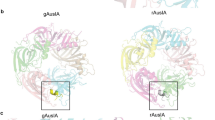
α-Pharmacological conotoxins are among the most selective ligands of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors with typical cysteine frameworks. They are characterized by the intercysteine loop and classified into various subfamilies, such as α3/5 and α4/7 conotoxins. A novel α-conotoxin, Pu14a (DCPPHPVPGMHKCVCLKTC), with a distinct loop spacing pattern between cysteines was reported recently. Pu14a belongs to the Cys framework 14 (–C–C–C–C) family containing four proline residues in the loop 1 region. Similar to another framework 14 conotoxin Lt14a (MCPPLCKPSCTNC-NH2), Pu14a has C1–C3/C2–C4 disulfide linkage, and can inhibit some subtypes of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. In this study, the solution structure of Pu14a was investigated using 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to understand the structure-activity relationship of this conotoxin. 20 converged structures of this conopeptide, with RMSD value of 0.77 Å, were obtained based on distance constraints, dihedral angles and disulfide bond constraints. The three-dimensional structure of Pu14a showed remarkable difference from typical α-conotoxins because of a large intercysteine loop between C2 and C13, as well as a 310-helix near the C-terminal. Furthermore, four proline residues in Pu14a adopted the trans conformation that may correlate with the large loop configuration and the biological activity of this conopeptide. The distinct structural characteristics of Pu14a will be very useful for studying the structure-activity relationship of α-conotoxins.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armishaw CJ, Daly NL, Nevin ST, Adams DJ, Craik DJ, Alewood PF (2006) α-Selenoconotoxins, a new class of potent α7 neuronal nicotinic receptor antagonists. J Biol Chem 281:14136–14143
Craik DJ, Adams DJ (2007) Chemical modification of conotoxins to improve stability and activity. ACS Chem Biol 2:457–468
Exarchos KP, Exarchos TP, Papaloukas C, Troganis AN, Fotiadis DI (2009) Detection of discriminative sequence patterns in the neighborhood of proline cis peptide bonds and their functional annotation. BMC Bioinformatics 10:113
Gehrmann J, Daly NL, Alewood PF, Craik DJ (1999) Solution structure of α-Conotoxin ImI by 1H nuclearmagnetic resonance. J Med Chem 42:2364–2372
Gray WR, Luque A, Olivera BM, Barrett J, Cruz LJ (1981) Peptide toxins from Conus geographus venom. J Biol Chem 256:4734–4740
Hu SH, Gehrman J, Guddat LW, Alewood PF, Craik DJ, Martin JL (1996) The 1.1 Å crystal structure of the neuronal acetylcholine receptor antagonist, α-conotoxin PnIA from Conus pennaceus. Structure 4:417–423
Imperial JS, Bansal PS, Alewood PF, Daly NL, Craik DJ, Sporning A, Terlau H, López-Vera E, Bandyopadhyay PK, Olivera BM (2006) A novel conotoxin inhibitor of Kv1.6 channel and nAChR subtypes defines a new superfamily of conotoxins. Biochemistry 45:331–8340
Janes RW (2005) α-Conotoxins as selective probes for nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subclasses. Curr Opin Pharmacol 5:280–292
Jensen AA, Frølund B, Liljefors T, Krogsgaard-Larsen P (2005) Neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: structural revelations, target identifications, and therapeutic inspirations. J Med Chem 48:4705–4745
Kaas Q, Westermann JC, Craik DJ (2010) Conopeptide characterization and classifications: an analysis using ConoServer. Toxicon 55:1491–1509
Kaas Q, Westermann JC, Halai R, Wang CK, Craik DJ (2008) Conoserver, a database for conopeptide sequences and structures. Bioinformatics 24:445–446
Kang TS, Vivekanandan S, Jois SDS, Kini RM (2005) Effect of C-terminal amidation on folding and disulfide-pairing of α-conotoxin ImI. Angew Chem Int Ed 117:6491–6495
Koradi R, Billeter M, Wüthrich K (1996) MOLMOL: a program for display and analysis of macromolecular structures. J Mol Graph 14(51–55):29–32
Lopez-Vera1 E, Aguilar MB, Schiavon E, Marinzi C, Ortiz E, Cassulini RR, Batista CVF, Possani LD, de la Cotera EPH, Peri F, Becerril B, Wanke E (2007) Novel α-conotoxins from conus spurius and theα-conotoxin EI share high-affinity potentiation and low-affinity inhibition of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. FEBS J 274:3972–3985
Luo SL, Akondi KB, Zhangsun D, Wu Y, Zhu XP, Hu YY, Christensen S, Dowell C, Daly NL, Craik DJ, Wang CA, Lewis RJ, Alewood PF, McIntosh JM (2010) A typical α-conotoxin ltIA from conus litteratus targets a novel microsite of the α3β2 nicotinic receptor. J Biol Chem 285:12355–12366
Luo SL, Nguyen TA, Cartier GE, Olivera BM, Yoshikami D, McIntosh JM (1999) Single-residue alteration in alpha-conotoxin PnIA switches its nAChR subtype selectivity. Biochemistry 38:14542–14548
Loughnan ML, Nicke A, Jones A, Adams DJ, Alewood PF, Lewis RJ (2004) Chemical and functional identification and characterization of novel sulfated α-conotoxins from the cone snail Conus anemone. J Med Chem 47:1234–1241
McIntosh JM, Corpuz GO, Layer RT, Garrett JE, Wagstaff JD, Bulaj G, Vyazovkina A, Yoshikami D, Cruz LJ, Olivera BM (2000) Isolation and characterization of a novel Conus peptide with apparent antinociceptive activity. J Biol Chem 275:32391–32397
McIntosh JM, Cruz LJ, Hunkapiller MW, Gray WR, Olivera BM (1982) Isolation and structure of a peptide toxin from the marine snail Conusmagus. Arch Biochem Biophys 5:280–292
McIntosh JM, Yoshikami D, Mahe E, Nielsen DB, Rivier JE, Gray WR, Olivera BM (1994) A nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ligand of unique specificity, alpha- conotoxin ImI. J Biol Chem 269:16733–16739
Millard EL, Daly NL, Craik DJ (2004) Structure-activity relationships and α-conotoxins targeting neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Eur J Biochem 271:2320–2326
Möller C, Rahmankhah S, Lauer-Fields J, Bubis J, Fields GB, Marí F (2005) A novel conotoxin framework with a helix loop helix (Cs α/α) fold. Biochemistry 44:15986–15996
Nicke A, Loughnan ML, Millard EL, Alewood PF, Adams DJ, Daly NL, Craik DJ, Lewis RJ (2003) Isolation, structure, and activity of GID, a novel α4/7-conotoxin with an extended N-terminal sequence. J Biol Chem 278:3137–3144
Olivera BM, Cruz LJ (2001) Conotoxins, inretrospect. Toxicon 39:7–14
Olivera BM, Gray WR, Zeikus R, McIntosh JM, Varga J, Rivier J, de Santos V, Cruz LJ (1985) Peptide neurotoxins from fish-hunting cone snails. Science 230:1338–1343
Oliveral BM, Quik M, Vincler M, Mclntosh JM (2008) Subtype-selective conopeptides targeted to nicotinic receptors: concerted discovery and biomedical applications. Channels 2:143–152
Pahlke D, Freund C, Leitner D, Labudde D (2005) Statistically significant dependence of the Xaa-Pro peptide bond conformation on secondary structure and amino acid sequence. BMC Struct Biol 5:8
Park KH, Suk JE, Jacobsen R, Gray WR, McIntosh JM, Han KH (2001) Solution conformation of α-conotoxin EI, a neuromuscular toxin specific for the α1/δ subunit interface of Torpedo nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem 276:49028–49033
Peng C, Tang SJ, Pi CH, Liu JL, Wang F, Wang L, Zhou WL, Xu AL (2006) Discovery of a novel class of conotoxin from Conus litteratus, Lt14a, with a unique cysteine pattern. Peptides 27:2174–2181
Peng C, Ye MY, Wang YF, Shao XX, Yuan DD, Liu J, Hawrot E, Wang CG, Chi CW (2010) A new subfamily of conotoxins belonging to the A-superfamily. Peptides 31:2009–2016
Pi CH, Liu JL, Peng C, Liu Y, Jiang XH, Zhao Y, Tang SJ, Wang L, Dong ML, Chen SW, Xu AL (2006) Diversity and evolution of conotoxins based on gene expression profiling of Conus litteratus. Genomics 88:809–819
Sun DD, Ren ZH, Zeng XY, You YW, Pan WG, Zhou MJ, Wang L, Xu AL (2010) Structure–function relationship of conotoxin Lt14a, a potential analgesic with low cytotoxicity. Peptides 32:300–305
Terlau H, Olivera BM (2004) Conus venoms: a rich source of novel ion channel targeted peptides. Physiol Rev 84:41–68
Weiss MS, Jabs A, Hilgenfeld R (1998) Peptide bonds revisited. Nat Struct Biol 5:676
Wuthrich K (1986) NMR of proteins and nucleic acids. Wiley, New York
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Chunguang Wang and Prof. Chengwu Chi from Tongji University for supplying the sample of Pu14a friendly. This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program (No. 2011CB808503), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and the Research Funds of Renmin University of China (No. 10XNJ011).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Huang, F. & Du, W. Solution structure of a novel α-conotoxin with a distinctive loop spacing pattern. Amino Acids 43, 389–396 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1093-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-1093-x