Summary.
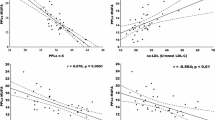
The purpose of the study was to correlate degree of hypocholesterolemia to changes in plasma levels of amino acids and other metabolic variables in severely injured septic patients. Measurements included plasma cholesterol, full amino-acidograms, acute phase proteins, complementary variables and blood cell counts. The Fischer plasma molar amino acid ratio (leucine+isoleucine+valine)/(phenylalanine+tyrosine) was calculated. Plasma cholesterol for all measurements (n=145) was 3.1±1.1 mmol/L and, upon entry in the study, it was correlated inversely with sepsis severity score (p<0.05). Along the clinical course, changes in cholesterol were clearly paralleled by opposite changes in C-reactive protein, which was the best correlate of cholesterol (r2=0.70, p<0.0001). Furthermore cholesterol was inversely related to phenylalanine, fibrinogen, lactate and white blood cell count, and directly to the Fischer molar amino acid ratio, cystathionine, methionine, glycine and transferrin (r2 between 0.36 and 0.15, p<0.0001 for all). Within this pattern of correlations, cholesterol was also directly related to alkaline phosphatase, which accounted for the effect of cholestasis, when present. For any given value of the other variables, cholesterol increased significantly with increase in alkaline phosphatase (p<0.0001). C-reactive protein (CRP, mg/dl) and alkaline phosphatase (ALKPH, U/L) together in the same regression explained 79% of the variability of cholesterol (CHOL, mmol/L): CHOL=5.90–0.74[LogeCRP]+0.004[ALKPH]; multiple r2=0.79, p<0.0001. Inclusion in this regression of other variables did not increase the r2. By using only amino acid variables, the best fit was provided by a regression including the Fischer ratio and cystathionine, which explained 55% of the variability of cholesterol (multiple r2=0.55 p<0.0001), and this result was not improved by the inclusion of other amino acids. These data show that severity of hypocholesterolemia in sepsis is quantifiably related to changes in plasma amino acids, and to severity of acute phase response and metabolic decompensation. More study is needed to understand whether hypocholesterolemia in sepsis has only diagnostic or prognostic implications, or that it may also contribute actively to worsening of the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiarla, C., Giovannini, I. & Siegel, J. The relationship between plasma cholesterol, amino acids and acute phase proteins in sepsis. Amino Acids 27, 97–100 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-004-0064-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-004-0064-x