Summary.
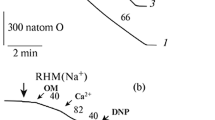
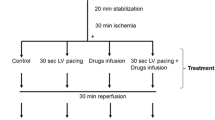
Occlusion of the left main coronary artery led to a time-dependent release of taurine from the heart. Upon reperfusion, there was a second phase of taurine release, which exceeded the amount of taurine that exited the heart during the 45 min ischemic insult. To obtain information on the mechanism underlying the release of taurine, three variables were examined, acidosis, hypoxia and calcium overload. It was found that large amounts of taurine also leave the cell during the calcium paradox, a condition induced by perfusing the heart with calcium containing buffer following a period of calcium free perfusion. However, little taurine effluxes the hearts exposed to buffer whose pH was lowered to 6.6. Isolated neonatal cardiomyocytes subjected to chemical hypoxia also lost large amounts of taurine. However, the amount of taurine leaving the cells appeared to be correlated with the intracellular sodium concentration, [Na+]i. The data suggest that taurine efflux is regulated by [Na+]i and cellular osmolality, but not by cellular pH.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received November 15, 2001 Accepted January 15, 2002 Published online October 3, 2002
Acknowledgements This study was supported with a grant from the Taisho Pharmaceutical Company.
Authors' address: Dr. Stephen W. Schaffer, Department of Pharmacology, University of South Alabama, School of Medicine, Mobile, Alabama, U.S.A., E-mail: sschaffe@jaguarl.usouthal.edu
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schaffer, S., Pastukh, V., Solodushko, V. et al. Effect of ischemia, calcium depletion and repletion, acidosis and hypoxia on cellular taurine content. Amino Acids 23, 395–400 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-002-0201-3
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-002-0201-3