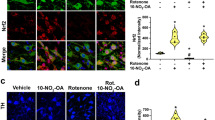
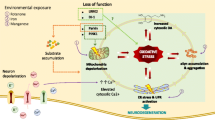
Summary.
Despite its being the most efficacious drug for symptom reversal in Parkinson's disease (PD), there is concern that chronic levodopa (L-DOPA) treatment may be detrimental. In this paper we review the potential for L-DOPA to 1) autoxidize from a catechol to a quinone, and 2) generate other reactive oxygen species (ROS). Overt toxicity and neuroprotective effects of L-DOPA, both in vivo and in vitro, are described in the context of whether L-DOPA may accelerate or delay progression of human Parkinson's disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received June 29, 2001 Accepted August 6, 2001 Published online June 3, 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kostrzewa, R., Kostrzewa, J. & Brus, R. Neuroprotective and neurotoxic roles of levodopa (L-DOPA) in neurodegenerative disorders relating to Parkinson's disease. Amino Acids 23, 57–63 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-001-0110-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-001-0110-x