Abstract
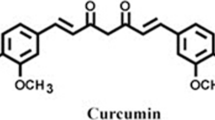
Oxidative stress and inflammatory damage play an important role in cerebral ischemic pathogenesis and may represent a target for treatment. The development of new strategies for enhancing drug delivery to the brain is of great importance in diagnostics and therapeutics of central nervous diseases. The present study examined the hypothesis that intranasal delivery of nanoformulation of curcuminoids would reduce oxidative stress-associated brain injury after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). The rats were subjected to 2 h of MCAO followed by 22 h reperfusion, after which the grip strength, locomotor activity was performed. The effects of treatment in the rats were assessed by grip strength, locomotor activity and biochemical studies (glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase, lipid peroxidation, superoxide dismutase, and catalase) in the brain. Pretreatment with polymeric N-isopropyl acryl amide (PNIPAM) nanoparticles formulation of all three curcuminoids (curcumin (Cur), demethoxycurcumin (DMC), and bisdemethoxycurcumin (BDMC)) at doses (100 μg/kg body weight) given intranasally was effective in bringing significant changes on all the parameters. While nanoformulation of curcumin at a dose of 100 μg/kg body weight was most active in the treatment of cerebral ischemia as compared to others nanoformulation of curcuminoids. The potency of antioxidant activity significantly decreased in the order of PNIPAM nanoformulation of Cur > DMC >> BDMC, thus suggesting the critical role of methoxy groups on the phenyl ring.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhtar M, Pillai K, Vohora D (2008) Effect of thioperamide on oxidative stress markers in middle cerebral artery occlusion model of focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 27:761–767
Ali A, Ahmad FJ, Pillai KK, Vohora D (2004) Evidence of the antiepileptic potential of amiloride with neuropharmacological benefits in rodent models of epilepsy and behavior. Epilepsy Behav 5:322–328
Allen CL, Bayraktutan U (2009) Oxidative stress and its role in the pathogenesis of ischaemic stroke. Int J Stroke 4:461–470
Alsarra IA, Hamed AY, Alanazi FK, Neau SH (2011) Rheological and mucoadhesive characterization of poly(vinylpyrrolidone) hydrogels designed for nasal mucosal drug delivery. Arch Pharm Res 34(4):573–582. doi:10.1007/s12272-011-0407-6
Anand P, Nair HB, Sung B, Kunnumakkara AB, Yadav VR, Tekmal RR, Aggarwal BB (2010) Design of curcumin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles formulation with enhanced cellular uptake, and increased bioactivity in vitro and superior bioavailability in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol 79:330–338
Ashafaq M, Khan MM, Raza SS, Ahmad A, Khuwaja G, Javed H, Khan A, Islam F, Siddiqui MS, Safhi MM (2012) S-allyl cysteine mitigates oxidative damage and improves neurologic deficit in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Nutr Res 32:133–143
Avci G, Kadioglu H, Sehirli AO, Bozkurt S, Guclu O, Arslan E, Muratli SK (2012) Curcumin protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat skeletal muscle. J Surg Res 172:39–46
Badary OA, Taha RA, Gamal el-Din AM, Abdel-Wahab MH (2003) Thymoquinone is a potent superoxide anion scavenger. Drug Chem Toxicol 26:87–98
Berner MD, Sura ME, Alves BN Jr, Hunter KW (2005) IFN-gamma primes macrophages for enhanced TNF-alpha expression in response to stimulatory and non-stimulatory amounts of microparticulate beta-glucan. Immunol Lett 98:115–122
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Dehmlow C, Erhard J, de Groot H (1996) Inhibition of Kupffer cell functions as an explanation for the hepatoprotective properties of silibinin. Hepatology 23:749–754
Fukui K, Omoi NO, Hayasaka T, Shinnkai T, Suzuki S, Abe K, Urano S (2002) Cognitive impairment of rats caused by oxidative stress and aging, and its prevention by vitamin E. Ann N Y Acad Sci 959:275–284
Gang L, Pandya DP, Seong SS (2009) Thermoresponsive core polystyrene–shell NIPAm microgels. Int J Polymer Anal Charact 14:351–363. doi:10.1080/10236660902875208
Hanson LR, Frey WH (2008) Intranasal delivery bypasses the blood–brain barrier to target therapeutic agents to the central nervous system and treat neurodegenerative disease. BMC Neurosci 9:S5
Hunter AJ, Mackay KB, Rogers DC (1998) To what extent have functional studies of ischaemia in animals been useful in the assessment of potential neuroprotective agents? Trends Pharmacol Sci 19:59–66
Iida M, Miyazaki I, Tanaka K, Kabuto H, Iwata-Ichikawa E, Ogawa N (1999) Dopamine D2 receptor-mediated antioxidant and neuroprotective effects of ropinirole, a dopamine agonist. Brain Res 838:51–59
Jayaprakasha GK, Jaganmohan Rao L, Sakariah KK (2006) Antioxidant activities of curcumin, demethoxycurcumin and bisdemethoxycurcumin. Food Chem 98:720–724
Kale M, Rathore N, John S, Bhatnagar D (1999) Lipid peroxidative damage on pyrethroid exposure and alterations in antioxidant status in rat erythrocytes: a possible involvement of reactive oxygen species. Toxicol Lett 105:197–205
Khan MM, Ahmad A, Ishrat T, Khuwaja G, Srivastawa P, Khan MB, Raza SS, Javed H, Vaibhav K, Khan A, Islam F (2009) Rutin protects the neural damage induced by transient focal ischemia in rats. Brain Res 1292:123–135
Khuwaja G, Khan MM, Ishrat T, Ahmad A, Raza SS, Ashafaq M, Javed H, Khan MB, Khan A, Vaibhav K, Safhi MM, Islam F (2011) Neuroprotective effects of curcumin on 6-hydroxydopamine-induced Parkinsonism in rats: behavioral, neurochemical and immunohistochemical studies. Brain Res 1368:254–263
Kim Y, So HS, Kim JK, Park C, Lee JH, Woo WH, Cho KH, Moon BS, Park R (2007) Anti-inflammatory effect of oyaksungisan in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from cerebral infarction patients. Biol Pharm Bull 30:1037–1041
Lannert H, Hoyer S (1998) Intracerebroventricular administration of streptozotocin causes long-term diminutions in learning and memory abilities and in cerebral energy metabolism in adult rats. Behav Neurosci 112:1199–1208
Locher R, Suter PM, Weyhenmeyer R, Vetter W (1998) Inhibitory action of silibinin on low density lipoprotein oxidation. Arzneimittelforschung 48:236–239
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91
Loo-Teck N, Hiroshi N, Isao K, Kumao U (2005) Photocuring of stimulus responsive membranes for controlled-release of drugs having different molecular weights Radiat. Phys Chem 73–117
Mistry A, Stolnik S, Illum L (2009) Nanoparticles for direct nose-to-brain delivery of drugs. Int J Pharm 379:146–157
Mohandas J, Marshall JJ, Duggin GG, Horvath JS, Tille DJ (1984) Differential distribution of glutathione and glutathione-related enzymes in rabbit kidney. Possible implications in analgesic nephropathy. Biochem Pharmacol 33:1801–1807
Naha PC, Casey A, Tenuta T, Lynch I, Dawson KA, Byrne HJ, Davoren M (2009) Preparation, characterization of NIPAM and NIPAM/BAM copolymer nanoparticles and their acute toxicity testing using an aquatic test battery. Aquat Toxicol 92:146–154
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Ramírez-Fuentes YS, Bucio E, Burillo G (2008) Thermo and pH sensitive copolymer based on acrylic acid and N-isopropylacrylamide grafted onto polypropylene. Polym Bull 60:79–87. doi:10.1007/s00289-007-0827-0
Raza SS, Khan MM, Ahmad A, Ashafaq M, Khuwaja G, Tabassum R, Javed H, Siddiqui MS, Safhi MM, Islam F (2011) Hesperidin ameliorates functional and histological outcome and reduces neuroinflammation in experimental stroke. Brain Res 1420:93–105
Robinson BR, Sullivan FM, Borzelleca JF (1990) In: Schwartz SL (ed) A critical review of kinetics and toxicology of PVP (povidone). Lewis, Chelsea
Sandur SK, Pandey MK, Sung B, Ahn KS, Murakami A, Sethi G, Limtrakul P, Badmaev V, Aggarwal BB (2007) Curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin, tetrahydrocurcumin and turmerones differentially regulate anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative responses through a ROS-independent mechanism. Carcinogenesis 28:1765–1773
Somparn P, Phisalaphong C, Nakornchai S, Unchern S, Morales NP (2007) Comparative antioxidant activities of curcumin and its demethoxy and hydrogenated derivatives. Biol Pharm Bull 30:74–78
Sun M, Zhao Y, Gu Y, Xu C (2009) Inhibition of nNOS reduces ischemic cell death through down-regulating calpain and caspase-3 after experimental stroke. Neurochem Int 54:339–346
Thiyagarajan M, Sharma SS (2004) Neuroprotective effect of curcumin in middle cerebral artery occlusion induced focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Life Sci 74:969–985
Thiyagarajan M, Kaul CL, Sharma SS (2004) Neuroprotective efficacy and therapeutic time window of peroxynitrite decomposition catalysts in focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Br J Pharmacol 142:899–911
Umar S, Zargan J, Umar K, Ahmad S, Katiyar CK, Khan HA (2012) Modulation of the oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokine response by thymoquinone in the collagen induced arthritis in Wistar rats. Chem Biol Interact 197:40–46
Xu FJ, Kang ET, Neoh KG (2006) pH- and temperature-responsive hydrogels from crosslinked triblock copolymers prepared via consecutive atom transfer radical polymerizations. Biomaterials 27:2787–2797
Yang KY, Lin LC, Tseng TY, Wang SC, Tsai TH (2007) Oral bioavailability of curcumin in rat and the herbal analysis from Curcuma longa by LC-MS/MS. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 853:183–189
Zafar KS, Siddiqui A, Sayeed I, Ahmad M, Salim S, Islam F (2003) Dose-dependent protective effect of selenium in rat model of Parkinson’s disease: neurobehavioral and neurochemical evidences. J Neurochem 84:438–446
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research, Pusa Road, New Delhi, for the granting CSIR-SRF which supported this study.
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest in this paper. The author (Niyaz Ahmad) is grateful to the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research, Pusa Road, New Delhi, for financial grant of this research.
Animal study
Experiments were conducted in accordance with Hamdard Institutional Ethics Committee (JH/FP/0847/2012). Approval for the animal study was given by Institutional Animal Ethical Committee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Damjana Drobne
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, N., Umar, S., Ashafaq, M. et al. A comparative study of PNIPAM nanoparticles of curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxycurcumin and their effects on oxidative stress markers in experimental stroke. Protoplasma 250, 1327–1338 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-013-0516-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-013-0516-9