Abstract
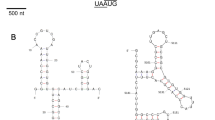
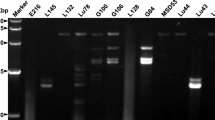
A new bisegmented dsRNA virus has been detected in shoots of blue spruce with bud blight disease symptoms and infection by Cucurbitaria piceae (Bortw.) fungus. The virus genome consists of two segments that are 2071 and 2257 nt long, encoding the putative RNA polymerase and capsid protein, respectively. Rosellinia necatrix partitivirus 1 is a closely related virus with 45 % amino acid sequence identity in the polymerase, and crimson clover cryptic virus 2 has 36 % amino acid sequence identity in the capsid protein. Based on taxonomic criteria, the virus should be classified as a member of the genus Betapartitivirus (family Partitiviridae). The name Cucurbitaria piceae partitivirus 1 and acronym CpPV1 are proposed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borthwick AW (1909) A new disease of Picea. Notes Roy Bot Gard Edinburgh 4:259–261
Shoemaker RA (1967) Cucurbitaria piceae and associated sphaeropsidales parasitic on spruce buds. Can J Bot 45:1243–1248
Soukup F, Pešková V (2009) Picea pungens wilting in the Ore Mountains (in Czech). Chřadnutí smrku pichlavého v Krušných horách. Lesnická práce 88:724–725
Zi-Qing Y, Xue-Wei W (1995) A taxonomic study on fungi associated with spruce bud blight in China. Mycotaxon 53:371–376
Pešková V, Soukup F (2013) Present status of Picea pungens forests in the Ore Mountains (in Czech) Současná situace v porostech smrku pichlavého v Krušných horách. Lesnická práce 92:46–47
De Paulo JJ, Powel CA (1995) Extraction of double-stranded RNA from plant tissue without the use of organic solvents. Plant Dis 79:246–248
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols, a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 315–322
Bruenn JA (1993) A closely related group of RNA-dependent RNA polymerases from double-stranded RNA viruses. Nucleic Acids Res 21:5667–5669
Acknowledgments
This work was performed with the support of grant LH13136 from the Kontakt II project of the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sport of the Czech Republic for TS, and IK, project No.: P501/12/1747 of the Czech Science Agency, and with institutional support RVO: 60077344 of the Biology Centre. The authors thank Olga Kubešová for her excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petrzik, K., Koloniuk, I., Sarkisova, T. et al. Detection and genome sequence of a new betapartitivirus associated with Cucurbitaria piceae Borthw. fungus causing bud blight of spruce in the Czech Republic. Arch Virol 161, 1405–1409 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-015-2692-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-015-2692-8