Abstract
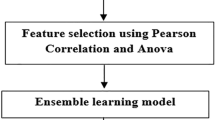
The mountainous areas are vulnerable to climate change and may have many socio-economic and environmental implications. The changing pattern of meteorological variables has deleterious effects on natural resources and livelihood. This paper makes an attempt to analyse trend and forecast metrological variables in Nainital district of India. Monthly, seasonal, and annual trends in rainfall and temperature were examined by Modified Mann–Kendall during 1989–2019. The magnitude of trend in temperature and rainfall was determined using Sen's slope estimator. Ensemble machine learning model was utilized for forecasting the variables for the next 16 years (2020–2035). The effectiveness of the model was examined through statistical performance assessors. The results revealed a significant increasing trend in the rainfall (at the rate of 9.42 mm/year) during 1989–2019. Increasing trend in the mean, minimum, and maximum temperatures on an annual basis was observed in the district. A remarkable increase in the rainfall and temperature was forecasted during various seasons. The findings of the study may help the stakeholders in devising suitable adaptation measures to climate variability. The bagging approach has shown its effectiveness in forecasting meteorological variables. The other geographical regions may find the methodology effective for analyzing climate variability and lessening its impact.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Achite M, Bazrafshan O, Azhdari Z et al (2022) Forecasting of SPI and SRI using multiplicative ARIMA under climate variability in a Mediterranean Region: Wadi Ouahrane Basin, Algeria. Climate 10:36. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli10030036
Ahokpossi Y (2018) Analysis of the rainfall variability and change in the Republic of Benin (West Africa). Hydrol Sci J 63:2097–2123. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2018.1554286
Akoglu H (2018) User’s guide to correlation coefficients. Turkish J Emerg Med 18:91–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tjem.2018.08.001
Anochi JA, de Almeida VA, de Campos Velho HF (2021) Machine learning for climate precipitation prediction modeling over South America. Remote Sens 13:2468. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13132468
Archer DR, Fowler HJ (2004) Spatial and temporal variations in precipitation in the Upper Indus Basin, global teleconnections and hydrological implications. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 8:47–61. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-8-47-2004
Ayinu YT, Ayal DY, Zeleke TT, Beketie KT (2022) Impact of climate variability on household food security in Godere District, Gambella Region, Ethiopia. Clim Serv 27:100307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cliser.2022.100307
Breiman L (1996) Bagging predictors. Mach Learn 24:123–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00058655
Belaid S, Mellit A (2016) Prediction of daily and mean monthly global solar radiation using support vector machine in an arid climate. Energy Convers Manag 118:105–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2016.03.082
Bhutiyani MR, Kale VS, Pawar NJ (2007) Long-term trends in maximum, minimum and mean annual air temperatures across the Northwestern Himalaya during the twentieth century. Clim Chang 85:159–177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-006-9196-1
Bhutiyani MR, Kale VS, Pawar NJ (2010) Climate change and the precipitation variations in the northwestern Himalaya: 1866–2006. Int J Climatol 30:535–548. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1920
Cai W, Wei R, Xu L, Ding X (2022) A method for modelling greenhouse temperature using gradient boost decision tree. Inf Process Agric 9:343–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inpa.2021.08.004
Census of India (2011) Census of India - Tehsils
CGWB (2019) Ground water year book- India 2019–20. http://cgwb.gov.in/Annual-Reports/ANNUAL/REPORT/CGWB/2018-19_final.pdf. Accessed 21 Jan 2022
Chauhan D, Thiyaharajan M, Pandey A et al (2022) Climate change water vulnerability and adaptation mechanism in a Himalayan City, Nainital, India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:85904–85921. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-15713-5
Chen H, Guo J, Zhang Z, Xu C-Y (2013) Prediction of temperature and precipitation in Sudan and South Sudan by using LARS-WG in future. Theor Appl Climatol 113:363–375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-012-0793-9
Cramer S, Kampouridis M, Freitas AA, Alexandridis AK (2017) An extensive evaluation of seven machine learning methods for rainfall prediction in weather derivatives. Expert Syst Appl 85:169–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2017.05.029
Dad JM, Muslim M, Rashid I et al (2021) Time series analysis of climate variability and trends in Kashmir Himalaya. Ecol Indic 126:107690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107690
Dalakoti H, Mishra S, Chaudhary M, Singal SK (2018) Appraisal of water quality in the Lakes of Nainital District through numerical indices and multivariate statistics, India. Int J River Basin Manag 16:219–229. https://doi.org/10.1080/15715124.2017.1394316
Dang V-H, Dieu TB, Tran X-L, Hoang N-D (2019) Enhancing the accuracy of rainfall-induced landslide prediction along mountain roads with a GIS-based random forest classifier. Bull Eng Geol Environ 78:2835–2849. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-018-1273-y
Dankwa P, Cudjoe E, Amuah EEY et al (2021) Analyzing and forecasting rainfall patterns in the Manga-Bawku area, northeastern Ghana: possible implication of climate change. Environ Challenges 5:100354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2021.100354
Dash RR, Mehrotra I, Kumar P, Grischek T (2008) Lake bank filtration at Nainital, India: water-quality evaluation. Hydrogeol J 16:1089–1099. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-008-0295-0
Dikshit A, Pradhan B, Alamri AM (2021) Pathways and challenges of the application of artificial intelligence to geohazards modelling. Gondwana Res 100:290–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2020.08.007
El Alani O, Hajjaj C, Ghennioui H et al (2022) Performance assessment of SARIMA, MLP and LSTM models for short-term solar irradiance prediction under different climates in Morocco. Int J Ambient Energy:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2022.2127889
Estrada F, Gay C, Conde C (2012) A methodology for the risk assessment of climate variability and change under uncertainty. A case study: coffee production in Veracruz, Mexico. Clim Chang 113:455–479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-011-0353-9
Fahad S, Su F, Khan SU et al (2023) Implementing a novel deep learning technique for rainfall forecasting via climatic variables: an approach via hierarchical clustering analysis. Sci Total Environ 854:158760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158760
Fan J, Wang X, Wu L et al (2018) Comparison of Support Vector Machine and Extreme Gradient Boosting for predicting daily global solar radiation using temperature and precipitation in humid subtropical climates: a case study in China. Energy Convers Manag 164:102–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.02.087
Fan D, Sun H, Yao J et al (2021) Well production forecasting based on ARIMA-LSTM model considering manual operations. Energy 220:119708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.119708
Farooq I, Shah AR, Salik KM, Ismail M (2021) Annual, seasonal and monthly trend analysis of temperature in Kazakhstan during 1970–2017 using non-parametric statistical methods and GIS technologies. Earth Syst Environ 5:575–595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41748-021-00244-3
Feng P, Wang B, Liu DL et al (2020) Machine learning-based integration of large-scale climate drivers can improve the forecast of seasonal rainfall probability in Australia. Environ Res Lett 15:084051. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ab9e98
Ghil M, Lucarini V (2020) The physics of climate variability and climate change. Rev Mod Phys 92:035002. https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.92.035002
Guo F, Rasmussen B (2023) Predictive maintenance for residential air conditioning systems with smart thermostat data using modified Mann-Kendall tests. Appl Therm Eng 222:119955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2022.119955
Hamed KH, Ramachandra Rao A (1998) A modified Mann-Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data. J Hydrol 204:182–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(97)00125-X
Hashimoto H, Wang W, Melton FS et al (2019) High-resolution mapping of daily climate variables by aggregating multiple spatial data sets with the random forest algorithm over the conterminous United States. Int J Climatol 39:2964–2983. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5995
He M, Tang L, Li C et al (2022) Dynamics of soil organic carbon and nitrogen and their relations to hydrothermal variability in dryland. J Environ Manage 319:115751. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.115751
Hill AJ, Schumacher RS (2021) Forecasting excessive rainfall with random forests and a deterministic convection-allowing model. Weather Forecast. https://doi.org/10.1175/WAF-D-21-0026.1
Hong H, Liu J, Zhu A-X (2020) Modeling landslide susceptibility using LogitBoost alternating decision trees and forest by penalizing attributes with the bagging ensemble. Sci Total Environ 718:137231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137231
IPCC (2014) AR5 synthesis report: climate change 2014
Jaswal AK, Kumar N, Khare P (2014) Climate variability in Dharamsala - a hill station in Western Himalayas. J Indian Geophys Union 18:336–355
Jeelani G (2008) Aquifer response to regional climate variability in a part of Kashmir Himalaya in India. Hydrogeol J 16:1625–1633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-008-0335-9
Jhajharia D, Singh VP (2011) Trends in temperature, diurnal temperature range and sunshine duration in Northeast India. Int J Climatol 31:1353–1367. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.2164
Kathayat G, Cheng H, Sinha A et al (2017) The Indian monsoon variability and civilization changes in the Indian subcontinent. Sci Adv 3. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1701296
Khan MI, Maity R (2020) Hybrid deep learning approach for multi-step-ahead daily rainfall prediction using GCM simulations. IEEE Access 8:52774–52784. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2980977
Khatiwada K, Panthi J, Shrestha M, Nepal S (2016) Hydro-climatic variability in the Karnali River Basin of Nepal Himalaya. Climate 4:17. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli4020017
King MA, Lyu K, Zhang X (2023) Climate variability a key driver of recent Antarctic ice-mass change. Nat Geosci 16:1128–1135. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-023-01317-w
Kocsis T, Kovács-Székely I, Anda A (2020) Homogeneity tests and non-parametric analyses of tendencies in precipitation time series in Keszthely, Western Hungary. Theor Appl Climatol 139:849–859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-019-03014-4
Kubiak-Wójcicka K, Pilarska A, Kamiński D (2021) The analysis of long-term trends in the meteorological and hydrological drought occurrences using non-parametric methods—case study of the catchment of the upper Noteć River (Central Poland). Atmosphere (basel) 12:1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12091098
Kumar ED, Sannasiraj SA, Sundar V, Polnikov VG (2013) Wind-wave characteristics and climate variability in the Indian Ocean Region using altimeter data. Mar Geod 36:303–318. https://doi.org/10.1080/01490419.2013.771718
Kumar P, Sharma MC, Saini R, Singh GK (2020) Climatic variability at Gangtok and Tadong weather observatories in Sikkim, India, during 1961–2017. Sci Rep 10:15177. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-71163-y
Kumar S, Suryavanshi S (2020) Assessment of long-term climatic variability of Uttarakhand. Nat Resour Conserv Res 3. https://doi.org/10.24294/nrcr.v3i1.744
Kumari G, Sajjad H, Rahaman MH et al (2022) Climate variability induced livelihood vulnerability: a systematic review and future prospects. Area. https://doi.org/10.1111/area.12822
Liu Z, Peng C, Xiang W et al (2010) Application of artificial neural networks in global climate change and ecological research: an overview. Chinese Sci Bull 55:3853–3863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-010-4183-3
Macchi M, Gurung AM, Hoermann B (2015) Community perceptions and responses to climate variability and change in the Himalayas. Clim Dev 7:414–425. https://doi.org/10.1080/17565529.2014.966046
Mahesh C, Prakash S, Gairola RM et al (2014) Meteorological sub-divisional scale rainfall monitoring using Kalpana-1 VHRR measurements. Geogr Res 52:328–336. https://doi.org/10.1111/1745-5871.12068
Mainali J, All J, Jha PK, Bhuju DR (2015) Responses of montane forest to climate variability in the central Himalayas of Nepal. Mt Res Dev 35:66–77. https://doi.org/10.1659/MRD-JOURNAL-D-13-00101.1
Malik A, Kumar A (2020) Spatio-temporal trend analysis of rainfall using parametric and non-parametric tests: case study in Uttarakhand, India. Theor Appl Climatol 140:183–207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-019-03080-8
Maqsood I, Khan M, Abraham A (2004) An ensemble of neural networks for weather forecasting. Neural Comput Appl 13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-004-0413-4
McGovern A, Elmore KL, Gagne DJ et al (2017) Using artificial intelligence to improve real-time decision-making for high-impact weather. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 98:2073–2090. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-16-0123.1
Mishra B, Babel MS, Tripathi NK (2014) Analysis of climatic variability and snow cover in the Kaligandaki River Basin, Himalaya, Nepal. Theor Appl Climatol 116:681–694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-013-0966-1
Mishra S, Mishra D, Santra GH (2020) Adaptive boosting of weak regressors for forecasting of crop production considering climatic variability: an empirical assessment. J King Saud Univ - Comput Inf Sci 32:949–964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2017.12.004
Monego VS, Anochi JA, de Campos Velho HF (2022) South America seasonal precipitation prediction by gradient-boosting machine-learning approach. Atmosphere (Basel) 13:243. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos13020243
Mosavi A, Sajedi Hosseini F, Choubin B et al (2021) Ensemble boosting and bagging based machine learning models for groundwater potential prediction. Water Resour Manag 35:23–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-020-02704-3
Narasimha Murthy KV, Saravana R, Rajendra P (2019) Unobserved component modeling for seasonal rainfall patterns in Rayalaseema region, India 1951–2015. Meteorol Atmos Phys 131:1387–1399. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-018-0645-y
Nashwan MS, Shahid S (2019) Symmetrical uncertainty and random forest for the evaluation of gridded precipitation and temperature data. Atmos Res 230:104632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.104632
Nijhawan R, Raman B, Das J (2018) Meta-classifier approach with ANN, SVM, rotation forest, and random forest for snow cover mapping. In: Chaudhuri B, Kankanhalli M, Raman B (eds) Proceedings of 2nd international conference on computer vision & image processing. Adv Intell Sys Comput, vol 704. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-7898-9_23
Nkuna TR, Odiyo J (2016) The relationship between temperature and rainfall variability in the Levubu sub-catchment, South Africa. Int J Educ Learn Syst 1:66–75
NyeinNaing WY, Htike ZZ (2015) State of the art machine learning techniques for time series forecasting: a survey. Adv Sci Lett 21:3574–3576. https://doi.org/10.1166/asl.2015.6586
Nzabarinda V, Bao A, Xu W et al (2021) Assessment and evaluation of the response of vegetation dynamics to climate variability in Africa. Sustainability 13:1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031234
Obahoundje S, Diedhiou A, Dubus L et al (2022) Modeling climate change impact on inflow and hydropower generation of Nangbeto dam in West Africa using multi-model CORDEX ensemble and ensemble machine learning. Appl Energy 325:119795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2022.119795
Oguntunde PG, Lischeid G, Dietrich O (2018) Relationship between rice yield and climate variables in southwest Nigeria using multiple linear regression and support vector machine analysis. Int J Biometeorol 62:459–469. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-017-1454-6
Pande RK, Pande N (2008) Nainital: a landslide town of Uttarakhand (India). Disaster Prev Manag an Int J 17:478–487. https://doi.org/10.1108/09653560810901728
Qasem SN, Samadianfard S, Kheshtgar S et al (2019) Modeling monthly pan evaporation using wavelet support vector regression and wavelet artificial neural networks in arid and humid climates. Eng Appl Comput Fluid Mech 13:177–187. https://doi.org/10.1080/19942060.2018.1564702
Rahaman MH, Saha TK, Masroor M et al (2023) Trend analysis and forecasting of meteorological variables in the lower Thoubal river watershed, India using non-parametrical approach and machine learning models. Model Earth Syst Environ. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-023-01799-y
Ravuri S, Lenc K, Willson M et al (2021) Skilful precipitation nowcasting using deep generative models of radar. Nature 597:672–677. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03854-z
Rawat KS, Sahu SR, Singh SK, Mishra AK (2022) Cloudburst analysis in the Nainital district, Himalayan Region, 2021. Discov Water 2:12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43832-022-00020-y
Ribeiro MHDM, dos Santos CL (2020) Ensemble approach based on bagging, boosting and stacking for short-term prediction in agribusiness time series. Appl Soft Comput 86:105837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105837
Romshoo SA, Dar RA, Rashid I et al (2015) Implications of shrinking cryosphere under changing climate on the streamflows in the lidder catchment in the upper Indus Basin, India. Arctic Antarct Alp Res 47:627–644. https://doi.org/10.1657/AAAR0014-088
Roshani SH, Kumar P et al (2022a) Forest vulnerability to climate change: a review for future research framework. Forests 13:917. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13060917
Roshani SH, Saha TK et al (2022b) Analyzing trend and forecast of rainfall and temperature in Valmiki Tiger Reserve, India, using non-parametric test and random forest machine learning algorithm. Acta Geophys. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11600-022-00978-2
Roxy MK, Ritika K, Terray P et al (2015) Drying of Indian subcontinent by rapid Indian Ocean warming and a weakening land-sea thermal gradient. Nat Commun 6:7423. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms8423
Saha S, Sarkar R, Roy J, Saha TK, Bhardwaj D, Acharya S (2022) Predicting the Landslide susceptibility using ensembles of bagging with RF and REPTree in Logchina, Bhutan. In: Sarkar R, Shaw R, Pradhan B (eds) Impact of climate change, land use and land cover, and socio-economic dynamics on landslides. Disaster Risk Reduct. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-7314-6_12
Sahu R, Gupta RD (2020) Snow cover area analysis and its relation with climate variability in Chandra basin, Western Himalaya, during 2001–2017 using MODIS and ERA5 data. Environ Monit Assess 192:489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-020-08442-8
Sam MG, Nwaogazie IL, Ikebude C (2022) Climate change and trend analysis of 24-hourly annual maximum series using mann-kendall and sen slope methods for rainfall IDF modeling. Int J Environ Clim Chang:44–60. https://doi.org/10.9734/ijecc/2022/v12i230628
Samal N, Ashwin R, Singhal A et al (2023) Using a Bayesian joint probability approach to improve the skill of medium-range forecasts of the Indian summer monsoon rainfall. J Hydrol Reg Stud 45:101284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2022.101284
Sanwal J, Kotlia BS, Rajendran C et al (2013) Climatic variability in Central Indian Himalaya during the last ∼1800 years: evidence from a high resolution speleothem record. Quat Int 304:183–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2013.03.029
Saravi S, Kalawsky R, Joannou D et al (2019) Use of artificial intelligence to improve resilience and preparedness against adverse flood events. Water 11:973. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11050973
Sarkar J, Chicholikar JR, Rathore LS (2015) Predicting future changes in temperature and precipitation in arid climate of Kutch, Gujarat: analyses based on LARS-wG model. Curr Sci 109:2084. https://doi.org/10.18520/v109/i11/2084-2093
Schober P, Boer C, Schwarte LA (2018) Correlation coefficients. Anesth Analg 126:1763–1768. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000002864
Shafiq MU, Rasool R, Ahmed P, Dimri AP (2019) Temperature and Precipitation trends in Kashmir valley, North Western Himalayas. Theor Appl Climatol 135:293–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2377-9
Sharma Y, Ahmed R, Sajjad H (2022) Assessing vegetation condition across topography in Nainital district, India using temperature vegetation dryness index model. Model Earth Syst Environ 8:2167–2181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-021-01208-2
Shen Z, Yong B (2021) Downscaling the GPM-based satellite precipitation retrievals using gradient boosting decision tree approach over Mainland China. J Hydrol 602:126803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126803
Shrestha UB, Gautam S, Bawa KS (2012) Widespread climate change in the Himalayas and associated changes in local ecosystems. PLoS ONE 7:e36741. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036741
Shukla A, Garg S, Mehta M et al (2020) Temporal inventory of glaciers in the Suru sub-basin, western Himalaya: impacts of regional climate variability. Earth Syst Sci Data 12:1245–1265. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-12-1245-2020
Singh V, Pandey A (2020) Urban water resilience in Hindu Kush Himalaya: issues, challenges and way forward. Water Policy 22:33–45. https://doi.org/10.2166/wp.2019.329
Singh D, Rai SP, Kumar B et al (2016) Study of hydro-chemical characteristics of Lake Nainital in response of human interventions, and impact of twentieth century climate change. Environ Earth Sci 75:1380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6177-1
Stepanov N, Alekseeva D, Ometov A, Lohan ES (2020) Applying machine learning to LTE traffic prediction: comparison of bagging, random forest, and SVM. 2020 12th international congress on ultra modern telecommunications and control systems and workshops (ICUMT), Brno, Czech Republic, 2020:119–123. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICUMT51630.2020.9222418
Tabari H (2020) Climate change impact on flood and extreme precipitation increases with water availability. Sci Rep 10:13768. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70816-2
Tian C, Ma J, Zhang C, Zhan P (2018) A deep neural network model for short-term load forecast based on long short-term memory network and convolutional neural network. Energies 11:3493. https://doi.org/10.3390/en11123493
Tiwari PC, Joshi B (2020) Challenges of urban growth in Himalaya with reference to climate change and disaster risk mitigation: a case of Nainital Town in Kumaon Middle Himalaya, India. Himalayan weather and climate and their impact on the environment. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 473–491
Tiwari DK, Tiwari HL, Nateriya R (2022) Runoff modeling in Kolar river basin using hybrid approach of wavelet with artificial neural network. J Water Clim Chang 13:963–974. https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2021.246
Tripathi S, Srinivas VV, Nanjundiah RS (2006) Downscaling of precipitation for climate change scenarios: a support vector machine approach. J Hydrol 330:621–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.04.030
Vijay A, Varija K (2022) Machine learning–based assessment of long-term climate variability of Kerala. Environ Monit Assess 194:498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-022-10011-0
Wahla SS, Kazmi JH, Sharifi A et al (2022) Assessing spatio-temporal mapping and monitoring of climatic variability using SPEI and RF machine learning models. Geocarto Int:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2022.2093411
Wu Y, Ke Y, Chen Z et al (2020) Application of alternating decision tree with AdaBoost and bagging ensembles for landslide susceptibility mapping. CATENA 187:104396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2019.104396
Xia J, Ghamisi P, Yokoya N, Iwasaki A (2018) Random forest ensembles and extended multiextinction profiles for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56:202–216. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2017.2744662
Yadav RR, Park W-K, Singh J, Dubey B (2004) Do the western Himalayas defy global warming? Geophys Res Lett 31:n/a-n/a. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004GL020201
Yoo C, Han D, Im J, Bechtel B (2019) Comparison between convolutional neural networks and random forest for local climate zone classification in mega urban areas using Landsat images. ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens 157:155–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.09.009
Yu P-S, Yang T-C, Chen S-Y et al (2017) Comparison of random forests and support vector machine for real-time radar-derived rainfall forecasting. J Hydrol 552:92–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.06.020
Yue S, Wang C (2004) The Mann-Kendall test modified by effective sample size to detect trend in serially correlated hydrological series. Water Resour Manag 18:201–218. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WARM.0000043140.61082.60
Zermane H, Drardja A (2022) Development of an efficient cement production monitoring system based on the improved random forest algorithm. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 120:1853–1866. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-022-08884-z
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions which has increased the overall quality of the Manuscript.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Writing-original draft preparation, Methodological framework,conceptualization, framework, reviewing and Software: YS; Methodological framework and software: TKS; Data curation: AS; Visualization and validation: NB and RA; Methodological framework, Reviewing, Editing and Supervision: HS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, Y., Sajjad, H., Saha, T.K. et al. Analyzing and forecasting climate variability in Nainital district, India using non-parametric methods and ensemble machine learning algorithms. Theor Appl Climatol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-024-04920-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-024-04920-y