Abstract
Object
This study was undertaken to analyze outcomes and to assess the prognostic impact of age, location, surgery, radiotherapy (RT), and histopathology in a series of adult infratentorial ependymomas.
Methods
This was a retrospective study of a population of 106 adult patients with infratentorial ependymomas diagnosed between 1990 and 2004. A central pathological review of all cases was performed. Grading was according to the WHO and Marseille’s neograding classifications.
Results
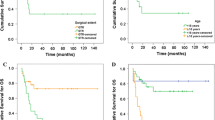
The series consisted of 58 males (54.7%) and 48 females (45.3%) in the age range of 18-82 years. Using the WHO classification, 88 patients (83.0%) had grade II and 18 patients (17.0%) grade III ependymomas. Using the Marseille’s neograding system, 91 patients were low-grade and 15 high-grade. Gross total resection was achieved in 66 patients (62.3%). Thirty-seven patients (35.0%) received adjuvant RT. The 5- and 10-year overall survival rates for the entire cohort were 86.1% and 80.5%, respectively. On multivariate analysis, a preoperative Karnofski performance status score > 80, no recessus lateral extension and a low histological grade (Marseille’s grading) were associated with a longer overall survival. The 5- and 10-year progression-free survival rates for the entire cohort were 70.8% and 57.7%, respectively. On multivariate analysis, no recessus lateral extension, gross total resection and a low histological grade (Marseille’s grading) were associated with a longer progression-free survival. Adjuvant RT was significantly associated with a better overall and progression-free survival in incompletely resected WHO grade II ependymomas.
Conclusions
This study highlights the key role of histology in the clinical outcome and the fact that gross total resection is a main prognostic factor and the treatment of choice for posterior fossa ependymomas. The use of adjuvant RT in patients with incompletely resected WHO grade II ependymomas appears beneficial, but its effect on high-grade tumors remains to be determined.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- GTR (+):
-
Gross total resection
- GTR (-):
-
Incomplete resection
- KPS:
-
Karnofski performance status
- Max:
-
Maximum
- Min:
-
Minimum
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PFS:
-
Progression free-survival
- RT:
-
Radiotherapy
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
Donahue B, Steinfeld A (1998) Intracranial ependymoma in the adult patient: successful treatment with surgery and radiotherapy. J Neurooncol 37:131–133. doi:10.1023/A:1005965328104
Ernestus RI, Schroder R, Stutzer H, Klug N (1997) The clinical and prognostic relevance of grading in intracranial ependymomas. Br J Neurosurg 11(5):421–428. doi:10.1080/02688699745925
Guyotat J, Signorelli F, Desme S, Frappaz D, Madarassy G, Fèvre-Montange M, Bret P (2002) Intracranial ependymomas in adult patient: analyses of prognostic factors. J Neurooncol 60:255–268. doi:10.1023/A:1021136029072
Korshunov A, Golanov A, Sycheva R, Timirgaz V (2004) The histologic grade is a main prognostic factor for patients with intracranial ependymomas treated in the microneurosurgical era: an analysis of 258 patients. Cancer 100(6):1230–1237. doi:10.1002/cncr.20075
Rawlings CE 3rd, Giangaspero F, Burger PC, Bullard DE (1988) Ependymomas: a clinicopathologic study. Surg Neurol 29(4):271–281. doi:10.1016/0090-3019(88)90158-9
Reni M, Brandes AA, Vavassori V, Cavallo G, Casagrande F, Vastalo F, Magli A, Franzin A, Basso U, Villa E (2004) A multicenter study of the prognosis and treatment of adult brain ependymal tumors. Cancer 100(6):1221–1229. doi:10.1002/cncr.20074
Ferrante L, Mastronardi L, Schettini G, Lunardi P, Fortuna A (1994) Fourth ventricle ependymomas. A study of 20 cases with survival analysis. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 131(1-2):67–74. doi:10.1007/BF01401455
Figarella-Branger D, Civatte M, Bouvier-Labit C, Gouvernet J, Gamberelli D, Gentet JC, Lena G, Choux M, Pelissier JF (2000) Prognostic factors in intracranial ependymomas in children. J Neurosurg 93(4):605–613
Healey EA, Barnes PD, Kupsky WJ, Scott TM, Sallan SE, Black PM, Tarbell NJ (1991) The prognostic significance of post-operative residual tumor in ependymoma. Neurosurgery 28:666–672. doi:10.1097/00006123-199105000-00005
Ikezaki K, Matsushima T, Inoue T, Yokoyama N, Kaneko Y, Fukui M (1993) Correlation of microanatomical localization with postoperative survival in posterior fossa ependymomas. Neurosurgery 32:38–44. doi:10.1097/00006123-199301000-00006
Lyons MK, Kelly PJ (1991) Posterior fossa ependymomas: report of 30 cases and review of the literature. Neurosurgery 28:659–664. doi:10.1097/00006123-199105000-00004 discussion 664-665
Rogers L, Pueschel J, Spetzler R, Shapiro W, Coons S, Thomas T, Speiser B (2005) Is gross-total resection sufficient treatment for posterior fossa ependymomas? J Neurosurg 102(4):629–636
Spagnoli D, Tomei G, Ceccarelli G, Grimoldi N, Lanterna A, Bello L, Sinisi MM, De Santis A, Villani RM (2000) Combined treatment of fourth ventricle ependymomas: report of 26 cases. Surg Neurol 54:19–26. doi:10.1016/S0090-3019(00)00272-X
Davis C, Symon L (1986) Posterior fossa ependymomas in adults. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 82:115–117. doi:10.1007/BF01456370
Metellus P, Barrie M, Figarella-Branger D, Chinot O, Giorgi R, Gouvernet J, Jouvet A, Guyotat J (2007) Multicentric French study on adult intracranial ependymomas: prognostic factors analysis and therapeutic considerations from a cohort of 152 patients. Brain 130:1338–1349. doi:10.1093/brain/awm046
Kleihues P, Cavence WK (2000) Pathology and genetics of tumours of the nervous system. IARC Press, Lyon, France
Vanuytsel LJ, Bessell EM, Ashley SE, Bloom HJ, Brada M (1992) Intracranial ependymoma: long-term results of a policy or surgery and radiotherapy. In J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 23:313–319
Verstegen MJ, Leenstra DT, Ijlst-Keizers H, Bosch DA (2002) Proliferation- and apoptosis-related proteins in intracranial ependymomas: an immuno-histochemical analysis. J Neurooncol 56:21–28. doi:10.1023/A:1014471714058
Oya N, Shibamoto Y, Nagata Y, Negoro Y, Hiraoka M (2002) Postoperative radiotherapy for intracranial ependymoma: analysis of prognostic factors and patterns of failure. J Neurooncol 56(1):87–94. doi:10.1023/A:1014442106111
Wolfsberg S, Fischer I, Hoftberger R, Birner P, Slavc I, Dieckmann K, Czech T, Budka H, Hainfellner J (2004) Ki-67 immunolabeling index is an accurate predictor of outcome in patients with intracranial ependymoma. Am J Surg Pathol 28:914–920. doi:10.1097/00000478-200407000-00011
Stuben G, Stuschke M, Kroll M, Havers W, Sack H (1997) Post-operative radiotherapy of spinal and intracranial ependymomas: analysis of prognostic factors. Radiother Oncol 45:3–10. doi:10.1016/S0167-8140(97)00138-2
Metellus P, Figarella-Branger D, Guyotat J, Barrie M, Giorgi R, Jouvet A, Chinot O (2008) Supratentorial ependymomas: prognostic factors and outcome analysis in a retrospective series of 46 adult patients. Cancer 113:175–185. doi:10.1002/cncr.23530
McLaughlin MP, Marcus RB Jr, Buatti JM, McCollough WM, Mickle JP, Kedar A, Maria BL, Million RR (1998) Ependymoma: results, prognostic factors and treatment recommendations. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 40:845–850. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(97)00893-6
Korshunov A, Neben K, Wrobel G, Tews B, Benner A, Hahn M, Golanov A, Lichter P (2003) Gene expression patterns in ependymomas correlate with tumor location, grade, and patient age. Am J Pathol 163(5):1721–1727
Kawabata Y, Takahasi JA, Arakawa Y, Hashimoto N (2005) Long-term outcome in patients harbouring intracranial ependymoma. J Neurosurg 103:31–37
Paulino AC, Wen BC, Buatti JM (2002) Intracranial ependymomas: an analysis of prognostic factors and patterns of failure. Am J Clin Oncol 25(2):117–122. doi:10.1097/00000421-200204000-00003
Robertson PL, Zeltzer PM, Boyett JM, Rorke LB, Allen JC, Russel Geyer J, Stanley P, Li H, Leland Albright A, Mc Guire-Gullen P, Finlay JL, Stevens KR, Milstein JM, Packer RJ, Wisoff J, and the Children’s Cancer Group (1998) Survival and prognostic factors following radiation therapy and chemotherapy for ependymomas in children: a report of the Children’s Cancer Group. J Neurosurg 88(4):695–703
Shiffer D, Chio A, Cravioto H, Giordana MT, Migheli A, Sofietti R, Vigliani C (1991) Ependymoma: internal correlations among pathological signs: the anaplastic variant. Neurosurgery 29(2):206–210. doi:10.1097/00006123-199108000-00006
Schild SE, Nisi K, Scheithauer BW, Wong WW, Lyons MK, Schomberg PJ, Shaw EG (1998) The results of radiotherapy for ependymomas: the Mayo Clinic experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 42(5):953–958. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(98)00350-2
Gerszten PC, Pollack IF, Martinez AJ, Lo KH, Jonosky J, Albright A (1996) Intracranial ependymomas of childhood. Lack of correlation of histopathology and clinical outcome. Pathol Res Pract 192:515–522
Foreman NK, Love S, Gille SS, Coakhman HB (1997) Second-look surgery for incompletely resected fourth ventricle ependymomas. Technical case report. Neurosurgery 40(4):856–860. doi:10.1097/00006123-199704000-00042
Kurt E, Zheng PP, Hop WC, van der Weiden M, Bol M, van den Bent MJ, Avezaat CJJ, Kros JM (2006) Identification of relevant prognostic histopathologic features in 69 intracranial ependymomas, excluding myxopapillary ependymomas and subependymomas. Cancer 106:388–395. doi:10.1002/cncr.21608
Prayson RA (1998) Cyclin D1 and MIB-1 immunohistochemistry in ependymomas: a study of 41 cases. Am J Clin Pathol 110(5):629–634
Suzuki S, Oka H, Kawano N, Tanaka S, Utsuki S, Fujii K (2001) Prognostic value of Ki-67 (MIB-1) and p53 in ependymomas. Brain Tumor Pathol 18:151–154. doi:10.1007/BF02479429
Rezai AR, Woo HH, Lee M, Cohen H, Zagzag D, Epstein FJ (1996) Disseminated ependymomas of the central nervous system. J Neurosurg 85(4):618–624
Salazar OM, Castro-Vita H, VanHoutte P, Rubin P, Aygun C (1983) Improved survival in cases of intracranial ependymoma after radiation therapy. Late report and recommendations. J Neurosurg 59:652–659
Read G (1984) The treatment of ependymoma of the brain or spinal canal by radiotherapy: a report of 79 cases. Clin Radiol 35:163–166. doi:10.1016/S0009-9260(84)80027-6
Mansur DB, Perry A, Rajaram V, Michalski JM, Park TS, Leonard JR, Luchtman-Jones L, Rich KM, Grisby P, Lockett MA, Wahab SH, Simpson JR (2005) Postoperative radiation therapy for grade II and III intracranial ependymoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 61:387–391. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp. 2004.06.002
Paulino AC, Wen BC (2000) The significance of radiotherapy treatment duration in intracranial ependymoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 47(3):585–589. doi:10.1016/S0360-3016(99)00535-0
Shaw EG, Evans RG, Scheithauer BW, Ilstrup DM, Earle JD (1987) Postoperative radiotherapy of intracranial ependymoma in pediatric and adult patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 13:1457–1462
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the French Neurosurgical Society of (SFNC) and the ANOCEF group (Association of French-speaking Neurologists and Neuro-oncologists) who supported this study with two grants awarded to P. Metellus and M. Barrie to collect data from the 24 French neurosurgical centers. We also thank Jacques Champier for reviewing the manuscript and all the neurosurgeons and pathologists who participated in this multi-institutional study. We also thank Dr Tom Barkas for linguistic help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Club de Neuro-Oncologie de la Société Française de Neurochirurgie (SFNC) and the Association des Neuro-Oncologues d’Expression Française (ANOCEF)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guyotat, J., Metellus, P., Giorgi, R. et al. Infratentorial ependymomas: prognostic factors and outcome analysis in a multi-center retrospective series of 106 adult patients. Acta Neurochir 151, 947–960 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-009-0417-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-009-0417-z