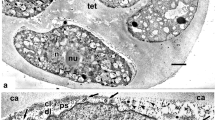
Abstract
Most biological construction systems operate within the colloidal dimension. In view of this, it seems reasonable to reassess what is known of the early stages of exine development in the light of a brief excursion into colloid and micelle behaviour. The results of this analysis show remarkable similarity of structures and suggest that almost all of the features seen during early pollen wall development can be easily interpreted using simple, established colloidal principles. This study of exine framework and endexine development offers the possibility that growth of the early exine progresses by successive transitory mesophases of a constrained micellar system. The self-assembling micelle mesophases will all be clearly recognized as constituents of the developing exine. They include spherical, cylindrical, continuous layers of hexagonally-packed cylindrical units and lamellar mesophases which most probably correspond to future granules, columellae, complex columellar (and alveolar) microarchitecture and ``white-line-centred'' lamellae. Furthermore, the various types of micelle involved have the potential to perform the functions previously loosely assigned to the exine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Angel H. Hoffman M. Lobl K. Reizlein H. Thurn I. Wunderlich (1984) ArticleTitleFrom rodlike micelles to lyotropic liquid crystals Progr. Colloid Polymer Sci. 69 12–28 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXhtVWju7o%3D
P. Ball (1994) Designing the molecular world Princeton University Press Princeton 216–255
O. Bayer H. Hoffman W. Ulbricht H. Thurn (1986) ArticleTitleThe influence of solubilized additives on surfactant solutions with rodlike micelles Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 26 177–203 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0001-8686(86)80021-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXitlGqsw%3D%3D
Berezin I. V. (1985) Enzyme action in reverse micelles. 39th Bach's Readings, Nauka, Moscow, pp. 1–40.
S. Blackmore (1990) ArticleTitleSporoderm homologies and morphogenesis in land plants, with a discussion on Echinops sphaerocephala (Compositae) Pl. Syst. Evol. 5 1–12
S. Blackmore D. Claugher (1987) ArticleTitleObservations an the substructural organization of the exine in Fagus sylvatica L. (Fagaceae) and Scorzonera hispanica L. (Compositae: Lactuceae) Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 53 175–184 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0034-6667(87)90013-3
D. Bray (1973) ArticleTitleModel for membrane movements in the neural growth cone Nature 244 93–96 Occurrence Handle4583488 Occurrence Handle10.1038/244093a0 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaE2c%2FhtlCrsA%3D%3D
A. O. Dahl J. R. Rowley (1991) ArticleTitleMicrospore development in Calluna (Ericaceae). Exine formation Ann. Sci. Nat., Bot., Paris 13e sér., vol. 11 155–176
H. G. Dickinson J. M. Sheldon (1986) The generation of patterning at the plasma membrane of the young microspore of Lilium S. Blackmore I. K. Ferguson (Eds) Pollen and Spores: form and function. . Linn. Soc. Symp. Ser., No. 12 Acad. Press London 1–18
A. Dunbar J. R. Rowley (1984) ArticleTitle Betula pollen development before and after dormancy: exine and intine Pollen Spores 26 299–338
A. T. Florence (1977) Biological meaning of micellization K. L. Mittal (Eds) Micellization, solubilization, and microemulsions, vol. 1, 2 Plenum Press New York London 42–62
Fridrichsberg D. A. (1995) Colloidal chemistry. ``Chemistry'', St. Petersburg.
Gabarayeva N. I. (1986) The development of the exine in Michelia fuscata (Magnoliaceae) in connection with the changes in cytoplasmic organelles of microspores and tapetum. Bot. Zhurn. (Leningrad) 71: 311–322 (In Russian, with English summary).
Gabarayeva N. I. (1987) Ultrastructure and sporoderm development in Manglietia tenuipes (Magnoliaceae) in the tetrad period: the establishment of primexine in connection with functioning of cytoplasmic organelles. Bot. Zhurn. (Leningrad) 72: 281–290 (In Russian, with English summary).
Gabarayeva N. I. (1990) Hypothetical ways of exine structure determination. Bot. Zhurn. (Leningrad) 75: 1353–1362 (In Russian, with English summary).
Gabarayeva N. I. (1991) The ultrastructure and development of exine and orbicules of Magnolia delavayi (Magnoliaceae) in the tetrad and the beginning of posttetrad periods. Bot. Zhurn. (Leningrad) 76: 10–19 (In Russian, with English summary).
Gabarayeva N. I. (1993a) Hypothetical ways of exine pattern determination. Grana 33 (Suppl. 2): 54–59.
Gabarayeva N. I. (1993b) Sporoderm development in Asimina triloba (Annonaceaee). II. The developmental events after callose dissolution. Grana 32: 210–220.
N. I. Gabarayeva (1995) ArticleTitlePollen wall and tapetum development in Anaxagorea brevipes (Annonaceae): sporoderm substructure, cytoskeleton, sporopollenin precursor particles, and the endexine problem Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 85 123–152 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0034-6667(94)00125-4
N. I. Gabarayeva (1996) ArticleTitleSporoderm development in Liriodendron chinense (Magnoliaceae): a probable role of the endoplasmic reticulum Nordic J. Bot. 16 1–17 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1756-1051.1996.tb00239.x
N. I. Gabarayeva (2000) Principles and recurrent themes in sporoderm development M. Harley C. M. Morton S. Blackmore (Eds) Pollen and spores: morphology and biology Royal Botanic Gardens Kew 1–17
Gabarayeva N. I. (2001) Theoretical prerequisites of the origin of development deviations in pollen wall structure. In: Belonin M. D., Kirichkova A. I. (eds.) ``Pollen as indicator of environmental state and paleoecological reconstructions''. Proceedings of Ist International Seminar VNIGRI, St. Petersburg, pp. 49–61.
N. I. Gabarayeva S. Blackmore J. R. Rowley (2003) ArticleTitleObservations on the experimental destruction and on substructural organization of the pollen wall of some selected Gymnosperms and Angiosperms Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 124 203–226 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0034-6667(02)00245-2
N. I. Gabarayeva G. El-Ghazaly (1997) ArticleTitleSporoderm development in Nymphaea mexicana (Nymphaeaceae) Pl. Syst. Evol. 204 1–19 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00982528
N. I. Gabarayeva V. V. Grigorjeva (2002) ArticleTitleExine development in Stangeria eriopus (Stangeriaceae): ultrastructure and substructure, sporopollenin accumulation, the equivocal character of the aperture, and stereology of microspore organelles Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 122 185–218 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0034-6667(02)00183-5
N. I. Gabarayeva V. V. Grigorjeva (2004) ArticleTitleExine development in Encephalartos altensteinii (Cycadaceae): ultrastructure, substructure and the modes of sporopollenin accumulation Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 132 175–193 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.revpalbo.2004.05.005
N. I. Gabarayeva V. V. Grigorjeva J. R. Rowley (2003) ArticleTitleSporoderm ontogeny in Cabomba aquatica (Cabombaceae) Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 127 147–173 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0034-6667(03)00081-2
N. I. Gabarayeva A. R. Hemsley (2006) ArticleTitleMerging Concepts: the role of self-assembly in the development of pollen wall structure Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 138 121–139 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.revpalbo.2005.12.001
N. I. Gabarayeva J. R. Rowley (1994) ArticleTitleExine development in Nymphaea colorata (Nymphaeaceae) Nord. J. Bot. 14 671–691
Gabarayeva N. I., Rowley J. R., Skvarla J. J. (1998) Exine development in Borago (Boraginaceae). 1. Microspore tetrad period. Taiwania 43, 203–214.
D. Gingell (1973) ArticleTitleMembrane permeability change by aggregation of mobile glycoprotein units J. Theoret. Biol. 38 677–679 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-5193(73)90266-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3sXktVWnsrw%3D
G. W. Gray J. W. Goodby (1984) Smectic liquid crystals – textures and structures Leonard Hill Glasgow London
P. C. Griffiths A. R. Hemsley (2002) ArticleTitleRaspberries and muffins – mimiking biological pattern formation Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 25 163–170 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0927-7765(01)00316-2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XhvVWkt7Y%3D
Halbritter H., Weber M., Zetter R., Frosch-Radivo A., Buchner R., Hesse M. (2005) PalDat – Illustrated Handbook on Pollen Terminology. Vienna. 61 pp. http://www.paldat.org/Paldat_Terminology_large.pdf.
I. Hamley (2000) Introduction to soft matter. Polymers, colloids, amphiphiles and liquid crystals John Wiley Chichester
G. S. Hartley (1936) Aqueous solutions of paraffin chain salts Hermann Press Paris
A. R. Hemsley M. E. Collinson A. P. R. Brain (1992) ArticleTitleColloidal crystal-like structure of sporopollenin in the megaspore walls of recent Selaginella and similar fossil spores Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 108 307–320
A. R. Hemsley M. E. Collinson B. Vicent P. C. Griffiths P. D. Jenkins (2000) Self-assembly of colloidal units in exine development M. M. Harley C. M. Morton S. Blackmore (Eds) Pollen and spores: morphology and biology Royal Botanic Gardens Kew 31–44
A. R. Hemsley J. Lewis P. C. Griffiths (2004) ArticleTitleSoft and sticky development: some underlying reasons for microarchitectural pattern convergence Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 130 105–119 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.revpalbo.2003.12.004
J. Heslop-Harrison (1972) ArticleTitlePattern in plant cell wall morphogenesis in miniature Proc. Roy. Inst. Great Britain 45 335–351
M. Hesse (1984) ArticleTitleAn exine architecture model for viscin threads Grana 23 69–75
M. Hesse (1985) ArticleTitleHemispherical surface processes of exine and orbicules in Calluna (Ericaceae) Grana 24 93–98
J. N. Israelachvili (1991) Intermolecular and surface forces EditionNumber2 Academic Press London
H. Kelker R. Hatz (1980) Handbook of liquid crystals Verlag Chemie Weinheim, Deerfield Beach, Florida, Basel
R. Knoth P. Hansmann P. Sitte (1986) ArticleTitleChromoplasts of Palisota bacteri, and the molecular structure of chromoplast tubules Planta 168 167–174 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XkslGqtL0%3D
O. Lehmann (1904) Flüssige Kristalle, sowie Plastizität von Kristallen im Allgemeinen, molekulare Umlagerungen und Aggregatzustandsänderungen Engelmann Leipzig
R. A. Mackay K. Letts G. Jones (1977) Interactions and reactions in microemulsions K. L. Mittal (Eds) Micellization, solubilization, and microemulsions. Vol. 2 Plenum Press New York London 801–816
J. W. McBain (1913) ArticleTitleMobility of highly-charged micelles Trans. Faraday Soc. 9 99–107
K. L. Mittal P. Mukerjee (1977) Wide world of micelles K. L. Mittal (Eds) Micellization, solubilization, and microemulsions. Vol. 1 Plenum Press New York London 1–21
R. Nagarajan (1986) ArticleTitleMicellization, mixed micellization and solubilization: the role of interfacial interactions Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 26 205–264 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0001-8686(86)80022-7 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28Xmtlakurk%3D
J. W. Nowicke J. L. Bittner J. J. Skvarla (1986) Paeonia, exine substructure and plasma ashing S. Blackmore I. K. Ferguson (Eds) Pollen and spores: form and function Academic Press London 81–95
J. M. Pettitt (1979) Ultrastructure and cytochemistry of spore wall morphogenesis A. F. Dyer (Eds) The experimental biology of ferns Academic Press London–New York–San Francisco 211–252
J. M. Pettitt A. C. Jermy (1974) ArticleTitleThe surface coats on spores Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 6 245–257
I. G. Plaschina I. R. Muratalijeva M. G. Semenova E. E. Braudo V. B. Tolstoguzov (1985) Correlation between conformation of flexichain polymers and their capasity to form thermoreversible gels L. S. Gembichki (Eds) Processes of gel-formation in polymer systems Saratov University Saratov 66–69
F. Reinitzer (1888) ArticleTitleBeiträge zur Kenntnis des Cholesterins Monatsschr. Chem. 9 421–445 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01516710
K. Reizlein H. Hoffman (1984) ArticleTitleNew lyotropic nematic liquid crystals Progr. Colloid Polymer Sci. 69 83–93 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXntVOhug%3D%3D
J. R. Rowley (1971) Implications on the nature of sporopollenin based upon pollen development J. Brooks P. R. Grant M. Muir P. Gijzel Particlevan G. Shaw (Eds) Sporopollenin Academic Press London 174–219
J. R. Rowley (1973) ArticleTitleFormation of pollen exine bacules and microchannels on a glycocalyx Grana 13 129–138
Rowley J. R. (1975) Lipopolysaccharide embedded within the exine of pollen grains. In: Bailey G. W. (ed.) 33rd Annual proceedings of the electron microscopy society of America, Las Vegas, Nevada, pp. 572–573.
J. R. Rowley (1981) ArticleTitlePollen wall characters with emphasis on applicability Nordic J. Bot. 1 357–380 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1756-1051.1981.tb00705.x
J. R. Rowley (1987) ArticleTitleExine units are plasmodesmata equivalents La Cellule 74 229–241
Rowley J. R. (1987–1988) Substructure within the endexine, an interpretation. J. Palynology 23–24: 29–42.
Rowley J. R. (1990) The fundamental structure of the pollen exine. Pl. Syst. Evol. (Suppl. 5): 13–29.
J. R. Rowley D. Claugher (1996) ArticleTitleStructure of the exine of Epilobium angustifolium (Onagraceae) Grana 35 79–86 Occurrence Handle10.1080/00173139609429477
J. R. Rowley A. O. Dahl (1977) ArticleTitlePollen development in Artemisia vulgaris with special reference to glycocalyx material Pollen Spores 19 169–284
J. R. Rowley A. O. Dahl (1982) ArticleTitleA similar substructure for tapetal surface and exine “tuft” units Pollen Spores 24 5–8
J. R. Rowley N. I. Gabarayeva (2004) ArticleTitleMicrospore development in Quercus robur (Fagaceae) Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 132 115–132 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.revpalbo.2004.05.003
J. R. Rowley J. J. Skvarla (2006) ArticleTitlePollen development in Epilobium (Onagraceae): late microspore stages (A review) Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 140 91–112 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.revpalbo.2006.03.002
J. R. Rowley J. J. Skvarla G. El-Ghazaly (2003) ArticleTitleTransfer of material through the microspore exine – from the loculus into the cytoplasm Canad. J. Bot. 81 1070–1082 Occurrence Handle10.1139/b03-095
J. M. Sheldon H. G. Dickinson (1983) ArticleTitleDetermination of patterning in the pollen wall of Lilium henryi. J. Cell Sci. 63 191–208 Occurrence Handle6313711 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2c%2Fjt1Ohtg%3D%3D
L. E. Scriven (1977) Equilibrium bicontinuous structures K. L. Mittal (Eds) Micellization, solubilization, and microemulsions. Vol. 1, 2 Plenum Press New York London 548–567
P. Sitte (1981) Role of lipid self-assembly in subcellular morphogenesis O. Kiermayer (Eds) Cytomorphogenesis in plants. Cell Biology Monographs. Vol. 8 Springer Wien New York 401–421
S. G. Starodubchev (1985) Hydrogels of synthetic polymers and their application in medicine L. S. Gembichki (Eds) Processes of gel-formation in polymer systems Saratov University Saratov 40–41
V. G. Syrkin (2000) CVD method. Chemical vapour-phase metallization Nauka Moscow
G. A. Uffelen ParticleVan (1991) The control of spore wall formation S. Blackmore S. H. Barnes (Eds) Pollen and spores: patterns of diversification Clarendon Press Oxford 89–102
D. Vorländer (1924) Chemische Kristallographie der Flüssigkeiten Akad. Verlagsges. Leipzig
H. Wennerström B. Lindman (1979) ArticleTitleMicelles. Physical chemistry of surfactant association Physics Reports (A Review Section of Physics Letters) 52 1–86
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hemsley, A.R., Gabarayeva, N.I. Exine development: the importance of looking through a colloid chemistry ``window''. Plant Syst. Evol. 263, 25–49 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-006-0465-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-006-0465-2